
1-propanol and 2-propanol are………..isomers.
A) Functional
B) Position
C) Chain
D) Stereo
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: The function group present in 1-propanol and 2- propanol is –OH, hydroxyl group.
- The numbers that are given as the prefix prior to the alkyl chain is the position of the functional or C-C multiple bonds etc.
Complete Solution :
- Here in the question two isomers of propanol are given and as there are many classifications of isomers, we have specifically notified, to which classification does these two structures belong to.
- First let’s have a basic idea of isomers and move on to the solution of this question.
- So isomers are those molecules or polyatomic ions having the same molecular formula but they are arranged in different fashion in space. Depending on the difference in the arrangement, the isomers are classified into many.
- So let’s solve this problem with basic ideas that as 1-propanol and 2-propanol are isomers, they both will have the same molecular formulae, which is ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}O$.
- Then we have to trace out the structure of these isomers, to find to which classification it belongs.
The structure of the two isomers given are:
1-Propanol
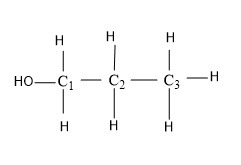
Here the functional group –OH is attached to the ${{C}_{1}}$ Carbon of the propanol chain,
2-propanol
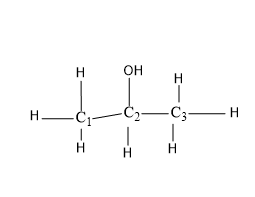
In this structure the functional group –OH is attached to the ${{C}_{2}}$ carbon of the propanol chain,
- So from the structure we can say that in the two isomers the functional groups are the same, but the difference comes in the attachment of the functional group. There is a difference in the position of carbon to which the –OH group is attached too.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Functional isomer is the molecule with same molecular formulae, but difference in the functional group. For example like alcohol and ether.
- Chain isomer-It is an isomer with the same molecular formula but difference in the carbon skeleton or carbon chain of the compound. Example like n-propanol and isopropanol
- Stereoisomer-in stereo isomers difference is there in the spatial arrangement of the atoms.
- So clearly we should know the classifications of the isomers to solve such types of formulae.
- For constitutional isomers i.e. structural isomers it’s always better to draw the structure to avoid confusion.
- The numbers that are given as the prefix prior to the alkyl chain is the position of the functional or C-C multiple bonds etc.
Complete Solution :
- Here in the question two isomers of propanol are given and as there are many classifications of isomers, we have specifically notified, to which classification does these two structures belong to.
- First let’s have a basic idea of isomers and move on to the solution of this question.
- So isomers are those molecules or polyatomic ions having the same molecular formula but they are arranged in different fashion in space. Depending on the difference in the arrangement, the isomers are classified into many.
- So let’s solve this problem with basic ideas that as 1-propanol and 2-propanol are isomers, they both will have the same molecular formulae, which is ${{C}_{3}}{{H}_{8}}O$.
- Then we have to trace out the structure of these isomers, to find to which classification it belongs.
The structure of the two isomers given are:
1-Propanol

Here the functional group –OH is attached to the ${{C}_{1}}$ Carbon of the propanol chain,
2-propanol

In this structure the functional group –OH is attached to the ${{C}_{2}}$ carbon of the propanol chain,
- So from the structure we can say that in the two isomers the functional groups are the same, but the difference comes in the attachment of the functional group. There is a difference in the position of carbon to which the –OH group is attached too.
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Functional isomer is the molecule with same molecular formulae, but difference in the functional group. For example like alcohol and ether.
- Chain isomer-It is an isomer with the same molecular formula but difference in the carbon skeleton or carbon chain of the compound. Example like n-propanol and isopropanol
- Stereoisomer-in stereo isomers difference is there in the spatial arrangement of the atoms.
- So clearly we should know the classifications of the isomers to solve such types of formulae.
- For constitutional isomers i.e. structural isomers it’s always better to draw the structure to avoid confusion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




