
2 kg water at $100^\circ C$ and $2.5kg$ water which is at $50^\circ C$ is kept in two identical containers $A$ and $B$ respectively of water equivalent $0.5kg$ . If the water of the container $A$ is placed poured into the container $B$ the final temperature of mixture is ${T_1}$ and if the water of the container $B$ is poured into the container $A$ the final temperature is ${T_2}$ (heat loss is negligible)
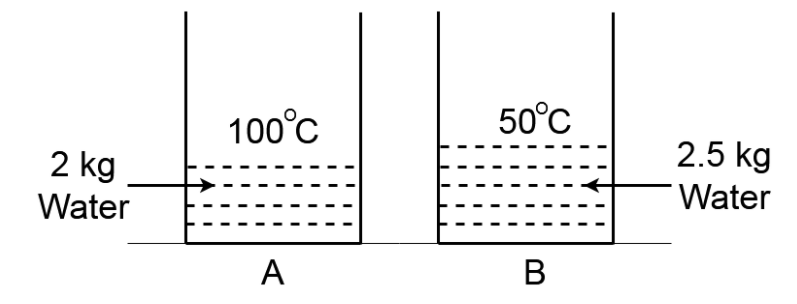
This question has multiple correct options
(A). ${T_1} = {T_2}$
(B). ${T_2} - {T_1} = 5$
(C). ${T_2} = 75^\circ C$
(D). ${T_1} = 75^\circ C$

Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: You can start by defining what water equivalent is and its importance in reaching the solution. Then write the equation for heat, i.e. $Q = mc\Delta T$ . Then mention how heat lost and gained will be the same when the water in the containers is mixed. Used this concept to calculate the value of ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$ . Compare the values of ${T_1}$ and ${T_2}$ to reach the solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before attempting the solution, we should first discuss what water equivalent means.
The water equivalent of a specific body is the amount of water for which the heat evolved or absorbed will be the same as the amount of heat required to raise the body to the same temperature. To better understand it, consider a body, let’s take a ball as reference. So imagine we want to raise the temperature of the ball by $X^\circ $ by supplying it $H$ amount of energy. So the water equivalent of this ball will be the amount of water whose temperature will change by $X^\circ $ on supplying $H$ amount of energy.
It means that when the water will be poured from container $A$ to container $B$ , the container $B$ will have an extra amount of water which will be equal to the water equivalent of the container $B$ as the temperature of $B$ will rise through the same temperature as the water in it. The situation is also similar when water is poured from container $B$ to container $A$ .
We know that
$Q = mc\Delta T$
Here, $Q = $ Heat lost or gained
$m = $ Mass
$c = $ Specific heat of the substance
$\Delta T = $ Difference in temperature
So in case of mixing two solutions, we have
Heat lost $ = $ Heat gained
So, when we pour water from $A$ to $B$
$ \Rightarrow {m_A}c\Delta {t_A} = ({m_B} + 0.5)c\Delta {T_B}$
$ \Rightarrow 2c(100 - {T_1}) = ({m_B} + 0.5)c({T_1} - 50)$
$ \Rightarrow 200 - 2{T_1} = 3{T_1} - 150$
$ \Rightarrow 5{T_1} = 350$
$ \Rightarrow {T_1} = 70^\circ C$
When we pour water from $B$ and $A$
$ \Rightarrow ({m_A} + 0.5)c\Delta {t_A} = {m_B}c\Delta {T_B}$
$ \Rightarrow (2 + 0.5)c(100 - {T_2}) = 2.5c({T_2} - 50)$
$ \Rightarrow 100 - {T_2} = {T_2} - 50$
$ \Rightarrow 2{T_2} = 150$
$ \Rightarrow {T_2} = 75^\circ C$
Hence, ${T_2} - {T_1} = 75 - 70 = 5^\circ C$ .
Hence, options B and C are the correct choices.
Note: The answer that we obtained in the solution may not be the same as what you initially thought. Most of us would think that the total amount of water and the heat energy will be the same, so the final temperature should be the same no matter which container is poured into the other. But this is a misconception as we found out above.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before attempting the solution, we should first discuss what water equivalent means.
The water equivalent of a specific body is the amount of water for which the heat evolved or absorbed will be the same as the amount of heat required to raise the body to the same temperature. To better understand it, consider a body, let’s take a ball as reference. So imagine we want to raise the temperature of the ball by $X^\circ $ by supplying it $H$ amount of energy. So the water equivalent of this ball will be the amount of water whose temperature will change by $X^\circ $ on supplying $H$ amount of energy.
It means that when the water will be poured from container $A$ to container $B$ , the container $B$ will have an extra amount of water which will be equal to the water equivalent of the container $B$ as the temperature of $B$ will rise through the same temperature as the water in it. The situation is also similar when water is poured from container $B$ to container $A$ .
We know that
$Q = mc\Delta T$
Here, $Q = $ Heat lost or gained
$m = $ Mass
$c = $ Specific heat of the substance
$\Delta T = $ Difference in temperature
So in case of mixing two solutions, we have
Heat lost $ = $ Heat gained
So, when we pour water from $A$ to $B$
$ \Rightarrow {m_A}c\Delta {t_A} = ({m_B} + 0.5)c\Delta {T_B}$
$ \Rightarrow 2c(100 - {T_1}) = ({m_B} + 0.5)c({T_1} - 50)$
$ \Rightarrow 200 - 2{T_1} = 3{T_1} - 150$
$ \Rightarrow 5{T_1} = 350$
$ \Rightarrow {T_1} = 70^\circ C$
When we pour water from $B$ and $A$
$ \Rightarrow ({m_A} + 0.5)c\Delta {t_A} = {m_B}c\Delta {T_B}$
$ \Rightarrow (2 + 0.5)c(100 - {T_2}) = 2.5c({T_2} - 50)$
$ \Rightarrow 100 - {T_2} = {T_2} - 50$
$ \Rightarrow 2{T_2} = 150$
$ \Rightarrow {T_2} = 75^\circ C$
Hence, ${T_2} - {T_1} = 75 - 70 = 5^\circ C$ .
Hence, options B and C are the correct choices.
Note: The answer that we obtained in the solution may not be the same as what you initially thought. Most of us would think that the total amount of water and the heat energy will be the same, so the final temperature should be the same no matter which container is poured into the other. But this is a misconception as we found out above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




