
2-Methylpropane on monochlorination under photochemical gives:-
(a)- 2-chloro-2-methylpropane as a major product.
(b)- (1:1) mixture of 1-chloro-2-methylpropane and 2-chloro-2-methylpropane.
(c)- 1-chloro-2-methylpropane as a major product.
(d)- (1:9) mixture of 1-chloro-2-methylpropane and 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
Answer
592.8k+ views
Hint: It is based on the number of primary hydrogens, secondary hydrogen, and tertiary hydrogens present in the reactant compound. Monochlorination reaction proceeds by the formation of a carbocation intermediate.
Complete answer:
Monochlorination is a substitution reaction in which the chlorine atom attaches to one of the places in the reactant.
It is carried out by reacting alkanes with chlorine either in the presence of ultraviolet light or at high temperature.
Chlorination occurs by a free radical mechanism. It consists of three steps:
Chain initiation: When a mixture of alkane and halogen is heated, the halogen absorbs some energy and undergoes homolytic fission
.
Chain propagation: In this step the alkane having carbon atom being more electronegative atom than the hydrogen atom, the carbon atom attracts one electron from the bond with a hydrogen atom and a free radical alkyl group.
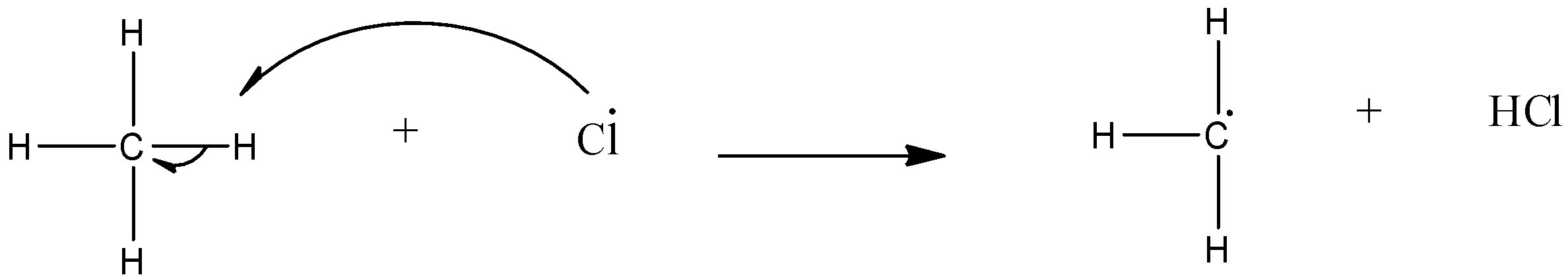
Chain termination: The free radical halogen and free radical alkyl group combine.
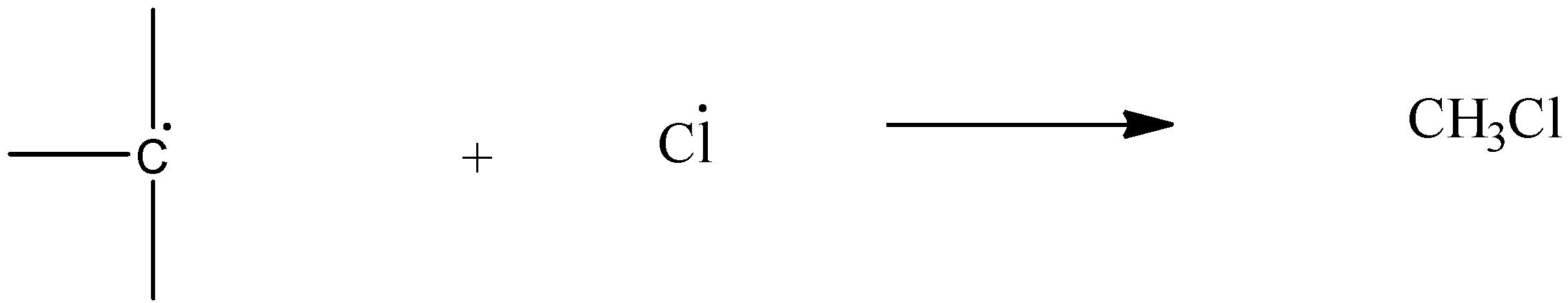
The order of forming or stability of the carbocation is \[{{3}^{\circ }}>{{2}^{\circ }}>{{1}^{\circ }}\] .
In 2-Methylpropane there are 9 primary hydrogens present and tertiary hydrogen is present.
The reaction occurs as:
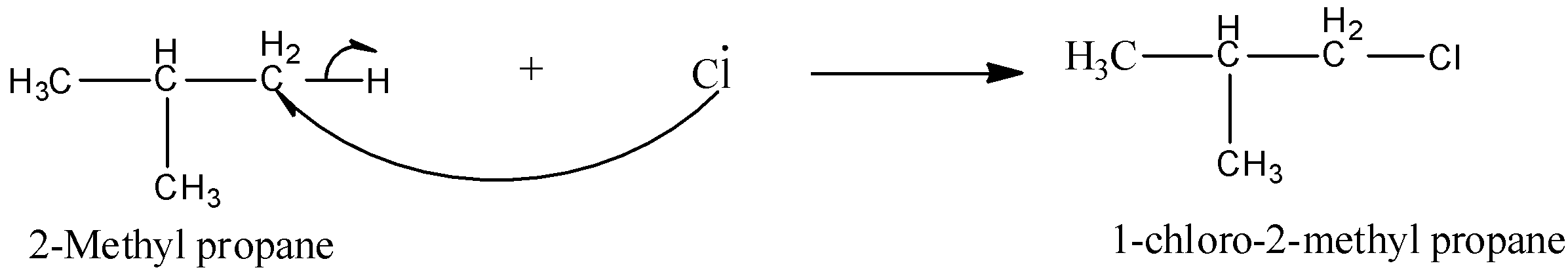
So, instead of forming 2-chloro-2-methylpropane as the major product, it forms 1-chloro-2-methylpropane as a major product because of the presence of 9 primary hydrogens.
Hence, the option (c)- 1-chloro-2-methylpropane as the major product is the correct answer.
Note: You may get confused that 2-chloro-2-methylpropane would be the major product because this would produce through the \[{{3}^{\circ }}\] carbocation, but due to presence of 9 primary hydrogen it forms 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Complete answer:
Monochlorination is a substitution reaction in which the chlorine atom attaches to one of the places in the reactant.
It is carried out by reacting alkanes with chlorine either in the presence of ultraviolet light or at high temperature.
Chlorination occurs by a free radical mechanism. It consists of three steps:
Chain initiation: When a mixture of alkane and halogen is heated, the halogen absorbs some energy and undergoes homolytic fission
.
Chain propagation: In this step the alkane having carbon atom being more electronegative atom than the hydrogen atom, the carbon atom attracts one electron from the bond with a hydrogen atom and a free radical alkyl group.

Chain termination: The free radical halogen and free radical alkyl group combine.
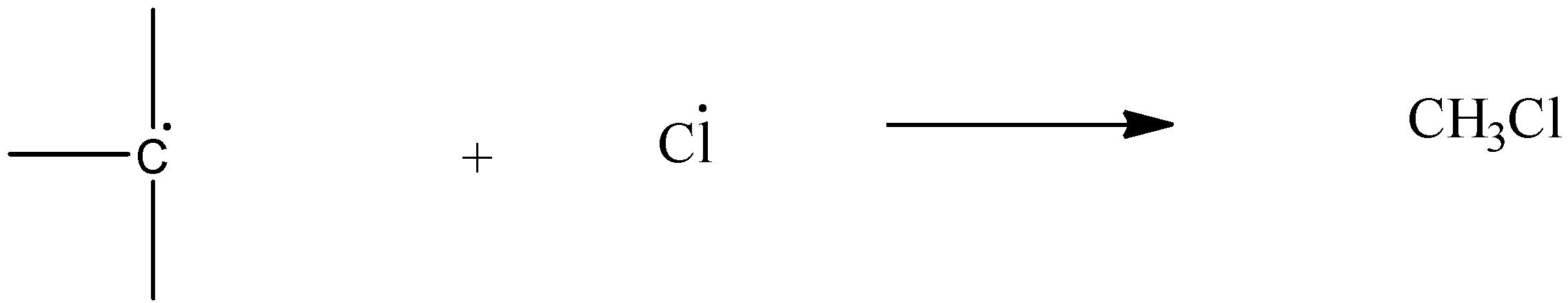
The order of forming or stability of the carbocation is \[{{3}^{\circ }}>{{2}^{\circ }}>{{1}^{\circ }}\] .
In 2-Methylpropane there are 9 primary hydrogens present and tertiary hydrogen is present.
The reaction occurs as:
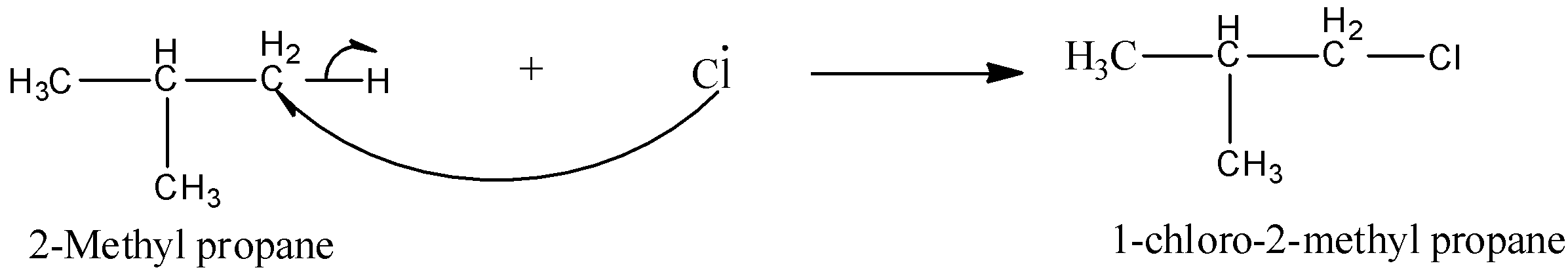
So, instead of forming 2-chloro-2-methylpropane as the major product, it forms 1-chloro-2-methylpropane as a major product because of the presence of 9 primary hydrogens.
Hence, the option (c)- 1-chloro-2-methylpropane as the major product is the correct answer.
Note: You may get confused that 2-chloro-2-methylpropane would be the major product because this would produce through the \[{{3}^{\circ }}\] carbocation, but due to presence of 9 primary hydrogen it forms 1-chloro-2-methylpropane.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




