
3-phenyl-2-propanol could be prepared from which of the following reactions?
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)




Answer
577.8k+ views
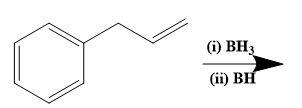
Hint: The reduction of aldehyde or ketone by Grignard reagent gives the corresponding alcohol easily. So, there is a chance of having a right answer in option (A) and (D). Also, formation of alcohol can occur when the halide group is replaced by hydroxyl group. Thus, option (C) can be the answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us now firstly see what would really 3-phenyl-2-propanol look like as this would make it easy to clear the discussion.
3-phenyl-2-propanol:
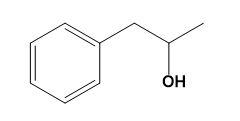
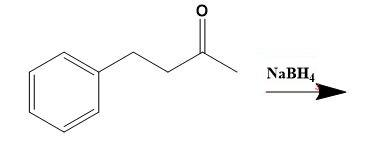
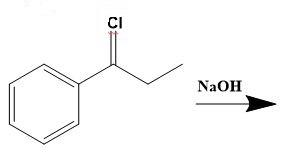
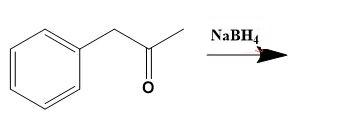
From the above molecular structure, we can see that option (C) cannot give the required molecule. Also, the double bond in Cl cannot justify any reaction. Now, seeing the option (A), we can see that the resulting product of the given reduction cannot be the 3-phenyl-2-propanol. Thus, now we only have option (D) as a better choice. Let us check the same. Option (D) states that,
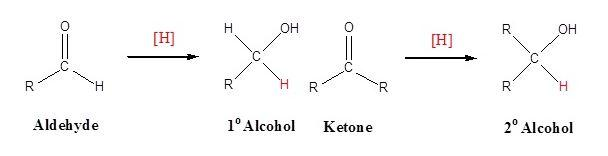
Reduction of phenylacetone by \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\]- Generally, ketone is reduced by \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] to give the alcohol by the following mechanism,
1. Nucleophilic attack by the hydride ion.
2. The alkoxide is protonated and methanol is used as a proton source.
\[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] is the complex metal hydride i.e. sodium borohydride. It is less reactive than that of $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$. On normal basis the reaction can be explained as,
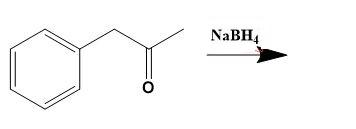
Thus, for solving given illustration we can say that, Phenylacetone reduces using \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] to give 3-phenyl-2-propanol a
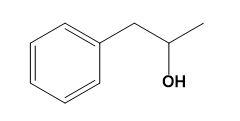
Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note that we can have many choices to get the required answer, so try to check all the options to get the correct answer. Sometimes, it is so easy to get the answer as above and still check the options because the exceptions can also play a major role in solving chemical reactions.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us now firstly see what would really 3-phenyl-2-propanol look like as this would make it easy to clear the discussion.
3-phenyl-2-propanol:

From the above molecular structure, we can see that option (C) cannot give the required molecule. Also, the double bond in Cl cannot justify any reaction. Now, seeing the option (A), we can see that the resulting product of the given reduction cannot be the 3-phenyl-2-propanol. Thus, now we only have option (D) as a better choice. Let us check the same. Option (D) states that,
Reduction of phenylacetone by \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\]- Generally, ketone is reduced by \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] to give the alcohol by the following mechanism,
1. Nucleophilic attack by the hydride ion.
2. The alkoxide is protonated and methanol is used as a proton source.
\[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] is the complex metal hydride i.e. sodium borohydride. It is less reactive than that of $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$. On normal basis the reaction can be explained as,

Thus, for solving given illustration we can say that, Phenylacetone reduces using \[NaB{{H}_{4}}\] to give 3-phenyl-2-propanol a


Therefore, option (D) is correct.
Note: Do note that we can have many choices to get the required answer, so try to check all the options to get the correct answer. Sometimes, it is so easy to get the answer as above and still check the options because the exceptions can also play a major role in solving chemical reactions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




