
4-bromo-2-pentene has a chiral carbon and can show enantiomerism. If a racemic mixture of 4-bromo-trans-2-pentene is treated with $B{{r}_{2}}$ in $CC{{l}_{4}}$ in presence of $FeB{{r}_{3}}$, 2,3,4-tribromopentane is formed. How many stereoisomers would be produced in this reaction?
Answer
572.1k+ views
Hint: For the compound to exhibit stereoisomerism, the compound must have a chiral carbon. Identify the number of chiral carbon present in the product formed. Now determine if there is any symmetry in the compound in each case. Based on that you can determine the number of stereoisomers for the product obtained after the reaction.
Complete answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulas but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their respective orientations of the atoms belonging to the compound in a 3D space.
The types of stereoisomerism are:
- Geometrical
- Optical
It is given to us that when 4-bromo-trans-2-pentene is treated with$B{{r}_{2}}$in $CC{{l}_{4}}$ in presence of $FeB{{r}_{3}}$, 2,3,4-tribromopentane is formed. We will now draw the possible configuration of the product such that they exhibit stereoisomerism.
The structures are given below:
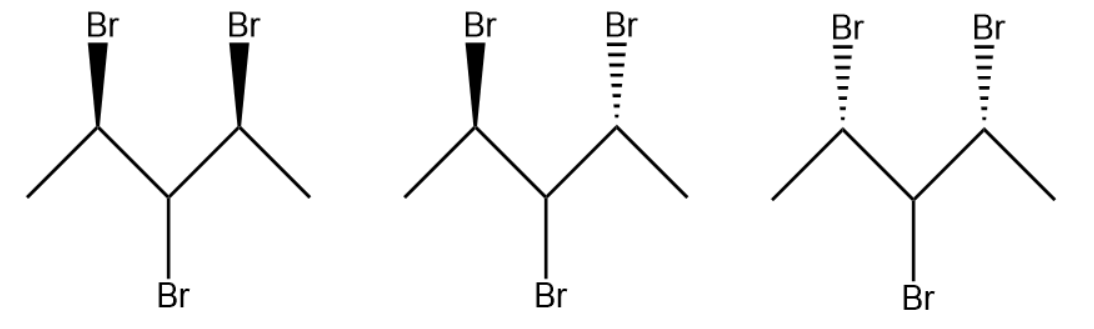
The compound contains 2 chiral centers and the number of stereoisomers is 3.
Additional information: In structural isomerism the functional groups and the atoms in the molecules of these isomers are bonded in different ways. Structural isomers have different IUPAC names although their chemical formulae are the same. The types of structural isomerism are:
- Chain
- Positional
- Functional
- Metamerism
- Tautomerism
- Ring - chain
Note: It is important to know that the reason why 2,3,4-tribromopentane has 3 isomers is symmetry. There is a line of symmetry in the compound and thus one possible structure of the compound is eliminated giving 3 stereoisomers.
Complete answer:
The word “isomer” is derived from the Greek words "isos" and "mers". "Isos" means equal and "mers" means parts, so "isomers" means equal parts.
Isomerism is the phenomenon in which two or more compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in chemical structures. Chemical compounds that have identical chemical formulas but differ in properties and the arrangement of atoms in the molecule are called isomers i.e. they exhibit isomerism.
Isomerism is of two types namely, Structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
In stereoisomerism, the compounds have the same chemical formula but differ in their respective orientations of the atoms belonging to the compound in a 3D space.
The types of stereoisomerism are:
- Geometrical
- Optical
It is given to us that when 4-bromo-trans-2-pentene is treated with$B{{r}_{2}}$in $CC{{l}_{4}}$ in presence of $FeB{{r}_{3}}$, 2,3,4-tribromopentane is formed. We will now draw the possible configuration of the product such that they exhibit stereoisomerism.
The structures are given below:

The compound contains 2 chiral centers and the number of stereoisomers is 3.
Additional information: In structural isomerism the functional groups and the atoms in the molecules of these isomers are bonded in different ways. Structural isomers have different IUPAC names although their chemical formulae are the same. The types of structural isomerism are:
- Chain
- Positional
- Functional
- Metamerism
- Tautomerism
- Ring - chain
Note: It is important to know that the reason why 2,3,4-tribromopentane has 3 isomers is symmetry. There is a line of symmetry in the compound and thus one possible structure of the compound is eliminated giving 3 stereoisomers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




