
A 3p orbital has:
A.two non-spherical nodes
B.two spherical nodes
C.one spherical and non-spherical nodes
D.one spherical and two non-spherical nodes
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Node is a point or space around the nucleus where the probability of finding an electron is zero. This point where the wave function that describes the respective orbital is zero. There are 2 types of nodes, radial nodes also called spherical nodes and angular nodes which can be called non-spherical nodes. Spherical nodes can be found out by equation \[n - 1 - 1\] and there are a number of non-spherical nodes.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to find the number of nodes present in the 3p orbital. For that we want to know the principal quantum number (n) and azimuthal quantum number (l) of 3p orbital. The table given below gives the value of n l and ml value of different orbitals,
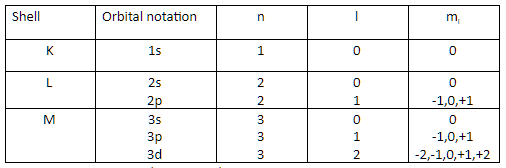
For 3p orbital we have \[n = 3,l = 1\]
Total number of nodes= \[n - 1\] , that is 3-1=2.
Number of spherical nodes= \[n - 1 - 1\] , that is 3-1-1=1
Number of non-spherical node or angular node= \[l = 1\]
There are a total of two nodes, they are one spherical node and one non-spherical node.
Hence, the answer is option (C) i.e One Spherical and non-spherical nodes.
Note: Electrons are arranged in an atom. The energy and the location of every electron in an atom is determined by a set of quantum numbers. The Principal quantum number is the shell number itself which represents the energy level. Azimuthal quantum number l is found by \[n - 1\] and the ml value varies from –l to +l. Azimuthal quantum number gives the orbital angular momentum and describes the shape of the orbital. Magnetics quantum denotes the different orientation possible for the different orbits. Those numbers describe different atomic orbits. Atomic orbital is the region of probability where the electron can be found. a spherical node can be defined as the spherical surface where the probability of finding an electron is zero. Nodes other than spherical nodes are considered as the non-spherical nodes.
Complete step by step solution:
We have to find the number of nodes present in the 3p orbital. For that we want to know the principal quantum number (n) and azimuthal quantum number (l) of 3p orbital. The table given below gives the value of n l and ml value of different orbitals,

For 3p orbital we have \[n = 3,l = 1\]
Total number of nodes= \[n - 1\] , that is 3-1=2.
Number of spherical nodes= \[n - 1 - 1\] , that is 3-1-1=1
Number of non-spherical node or angular node= \[l = 1\]
There are a total of two nodes, they are one spherical node and one non-spherical node.
Hence, the answer is option (C) i.e One Spherical and non-spherical nodes.
Note: Electrons are arranged in an atom. The energy and the location of every electron in an atom is determined by a set of quantum numbers. The Principal quantum number is the shell number itself which represents the energy level. Azimuthal quantum number l is found by \[n - 1\] and the ml value varies from –l to +l. Azimuthal quantum number gives the orbital angular momentum and describes the shape of the orbital. Magnetics quantum denotes the different orientation possible for the different orbits. Those numbers describe different atomic orbits. Atomic orbital is the region of probability where the electron can be found. a spherical node can be defined as the spherical surface where the probability of finding an electron is zero. Nodes other than spherical nodes are considered as the non-spherical nodes.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration Open, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
Understanding Average and RMS Value in Electrical Circuits

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding Atomic Structure for Beginners

Understanding Elastic Collisions in Two Dimensions

For pure water A pH increases while pOH decreases with class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Which of the following is most stable A Sn2+ B Ge2+ class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Other Pages
NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 8 Redox Reactions (2025-26)

An ideal gas is at pressure P and temperature T in class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

In Carius method of estimation of halogens 015g of class 11 chemistry JEE_Main

Understanding Collisions: Types and Examples for Students

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry in Hindi Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry (2025-26)

Happy New Year Wishes 2026 – 100+ Messages, Quotes, Shayari, Images & Status in All Languages




