
A $50\Omega $ is connected to a battery of $5V$. A galvanometer of resistance $100\Omega $ is to be used as an ammeter to measure current through the resistance, for this a resistance ${{r}_{s}}$ is connected to the galvanometer. Which of the following connections should be employed if the measured current is within $1\%$ of the current without the ammeter in the circuit?
A. ${{r}_{s}}=1\Omega $ in parallel with the galvanometer
B. ${{r}_{s}}=0.5\Omega $ in parallel with the galvanometer
C. ${{r}_{s}}=0.5\Omega $ in series with the galvanometer
D. ${{r}_{s}}=1\Omega $ in series with the galvanometer
Answer
603.6k+ views
Hint: A very small shunt resistance is connected in parallel with a galvanometer, which helps in increasing the range of the galvanometer. We can solve this problem by finding the current in the absence of the galvanometer and then in the presence of the galvanometer. We will then equate these two values such that they are within $1\%$ of each other.
Formula used:
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$ where $I$ is the current flowing across a resistor, $V$ is the potential difference applied across it and $R$ is the resistance of the resistor.
When two resistors $R$ and $r$ are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance will be, ${{R}_{equivalent,parallel}}=\dfrac{Rr}{R+r}$
When resistors are parallel, the equivalent resistance is given by,
${{R}_{equivalent,series}}=\sum{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can solve this problem by first finding out the current in the absence of the galvanometer and then the current in the presence of the galvanometer.
Therefore, let us analyze the question.
Let the galvanometer resistance be ${{R}_{G}}=100\Omega $. Shunt resistances are very small resistance values that are connected in parallel with the galvanometer. This increases the range of the galvanometer as a lot of current passes through this small shunt resistance and this increases the total current that can be passed through the galvanometer.
Let the shunt resistance in parallel with the galvanometer be ${{r}_{s}}$. The resistance in the circuit is $R$.
The potential difference in the circuit is provided by the battery. It is $V=5V$.
Now, in the absence of the galvanometer, the circuit will look as follows.
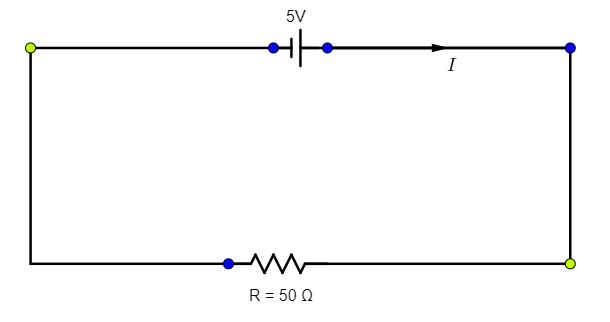
Now,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$ --(1)
where $I$ is the current flowing across a resistor, $V$ is the potential difference applied across it and $R$ is the resistance of the resistor.
Therefore, using (1), the current in the absence of the galvanometer will be $I$, where, $I=\dfrac{5}{50}=\dfrac{1}{10}=0.1A$ --(2)
Now, in the presence of the galvanometer the circuit will be,
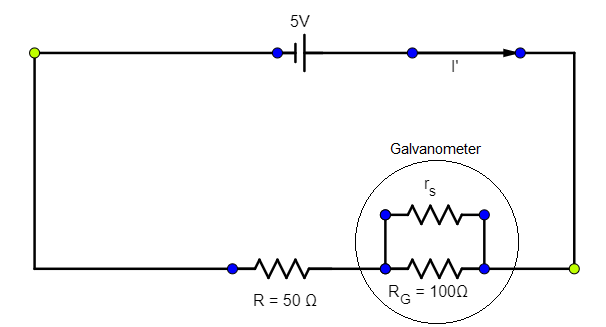
Now, when two resistors $R$ and $r$ are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance will be, ${{R}_{equivalent,parallel}}=\dfrac{Rr}{R+r}$ --(3)
When resistors are parallel, the equivalent resistance is given by,
${{R}_{equivalent,series}}=\sum{R}$ --(4)
Now, using (3) and (4), the equivalent resistance of the circuit will be,
$R+\dfrac{{{R}_{G}}{{r}_{s}}}{{{R}_{G}}+{{r}_{s}}}$ Plugging in the values, we get, $50+\dfrac{100{{r}_{s}}}{100+{{r}_{s}}}$ --(5)
Let the current in the circuit be $I'$. Hence, using (1) and (5), we get,
$I'=\dfrac{5}{\left( 50+\dfrac{100{{r}_{s}}}{100+{{r}_{s}}} \right)}$ --(6)
Now, according to the question, $I'$ is within $1\%$ of $I$.
$\Rightarrow I'=99\%\text{ of }I$ $\Rightarrow I'=\dfrac{99}{100}I$ --(7)
Putting (2) and (6) in (7), we get,
$\dfrac{5}{\left( 50+\dfrac{100{{r}_{s}}}{100+{{r}_{s}}} \right)}=\dfrac{99}{100}\times 0.1$ $\Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{\dfrac{\left( 5000+50{{r}_{s}}+100{{r}_{s}} \right)}{100+{{r}_{s}}}}=\dfrac{9.9}{100}$ $\Rightarrow \dfrac{5\times \left( 100+{{r}_{s}} \right)}{5000+150{{r}_{s}}}=0.099$ $\Rightarrow 500+5{{r}_{s}}=0.099\times \left( 5000+150{{r}_{s}} \right)$ $\Rightarrow 500+5{{r}_{s}}=\left( 0.099\times 5000 \right)+\left( 0.099\times 150{{r}_{s}} \right)$ $\Rightarrow 500+5{{r}_{s}}=495+14.85{{r}_{s}}$ $\Rightarrow 500-495=\left( 14.85-5 \right){{r}_{s}}$ $\Rightarrow 5=9.85{{r}_{s}}$ $\Rightarrow {{r}_{s}}=\dfrac{5}{9.85}=0.508\approx 0.5\Omega $
Hence, a shunt resistance of ${{r}_{s}}=0.5\Omega $ must be connected in parallel with the galvanometer.
Hence, the correct option is B) ${{r}_{s}}=0.5\Omega $ in parallel with the galvanometer.
Note: Students must remember that to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter a very small shunt resistance is connected in parallel with the galvanometer. A lot of the current passes through the shunt resistance which increases the total current that can enter the galvanometer setup and hence increase the range of the formed ammeter.
On the other hand to convert a galvanometer to a voltmeter, a large resistance should be connected in series with the galvanometer. This causes a larger potential drop in the galvanometer setup which would not have been possible by the galvanometer alone. Hence, this increases the potential drop in the galvanometer setup and hence, increases the range of the voltmeter.
Formula used:
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$ where $I$ is the current flowing across a resistor, $V$ is the potential difference applied across it and $R$ is the resistance of the resistor.
When two resistors $R$ and $r$ are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance will be, ${{R}_{equivalent,parallel}}=\dfrac{Rr}{R+r}$
When resistors are parallel, the equivalent resistance is given by,
${{R}_{equivalent,series}}=\sum{R}$
Complete step by step answer:
We can solve this problem by first finding out the current in the absence of the galvanometer and then the current in the presence of the galvanometer.
Therefore, let us analyze the question.
Let the galvanometer resistance be ${{R}_{G}}=100\Omega $. Shunt resistances are very small resistance values that are connected in parallel with the galvanometer. This increases the range of the galvanometer as a lot of current passes through this small shunt resistance and this increases the total current that can be passed through the galvanometer.
Let the shunt resistance in parallel with the galvanometer be ${{r}_{s}}$. The resistance in the circuit is $R$.
The potential difference in the circuit is provided by the battery. It is $V=5V$.
Now, in the absence of the galvanometer, the circuit will look as follows.

Now,
$I=\dfrac{V}{R}$ --(1)
where $I$ is the current flowing across a resistor, $V$ is the potential difference applied across it and $R$ is the resistance of the resistor.
Therefore, using (1), the current in the absence of the galvanometer will be $I$, where, $I=\dfrac{5}{50}=\dfrac{1}{10}=0.1A$ --(2)
Now, in the presence of the galvanometer the circuit will be,

Now, when two resistors $R$ and $r$ are connected in parallel, the equivalent resistance will be, ${{R}_{equivalent,parallel}}=\dfrac{Rr}{R+r}$ --(3)
When resistors are parallel, the equivalent resistance is given by,
${{R}_{equivalent,series}}=\sum{R}$ --(4)
Now, using (3) and (4), the equivalent resistance of the circuit will be,
$R+\dfrac{{{R}_{G}}{{r}_{s}}}{{{R}_{G}}+{{r}_{s}}}$ Plugging in the values, we get, $50+\dfrac{100{{r}_{s}}}{100+{{r}_{s}}}$ --(5)
Let the current in the circuit be $I'$. Hence, using (1) and (5), we get,
$I'=\dfrac{5}{\left( 50+\dfrac{100{{r}_{s}}}{100+{{r}_{s}}} \right)}$ --(6)
Now, according to the question, $I'$ is within $1\%$ of $I$.
$\Rightarrow I'=99\%\text{ of }I$ $\Rightarrow I'=\dfrac{99}{100}I$ --(7)
Putting (2) and (6) in (7), we get,
$\dfrac{5}{\left( 50+\dfrac{100{{r}_{s}}}{100+{{r}_{s}}} \right)}=\dfrac{99}{100}\times 0.1$ $\Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{\dfrac{\left( 5000+50{{r}_{s}}+100{{r}_{s}} \right)}{100+{{r}_{s}}}}=\dfrac{9.9}{100}$ $\Rightarrow \dfrac{5\times \left( 100+{{r}_{s}} \right)}{5000+150{{r}_{s}}}=0.099$ $\Rightarrow 500+5{{r}_{s}}=0.099\times \left( 5000+150{{r}_{s}} \right)$ $\Rightarrow 500+5{{r}_{s}}=\left( 0.099\times 5000 \right)+\left( 0.099\times 150{{r}_{s}} \right)$ $\Rightarrow 500+5{{r}_{s}}=495+14.85{{r}_{s}}$ $\Rightarrow 500-495=\left( 14.85-5 \right){{r}_{s}}$ $\Rightarrow 5=9.85{{r}_{s}}$ $\Rightarrow {{r}_{s}}=\dfrac{5}{9.85}=0.508\approx 0.5\Omega $
Hence, a shunt resistance of ${{r}_{s}}=0.5\Omega $ must be connected in parallel with the galvanometer.
Hence, the correct option is B) ${{r}_{s}}=0.5\Omega $ in parallel with the galvanometer.
Note: Students must remember that to convert a galvanometer into an ammeter a very small shunt resistance is connected in parallel with the galvanometer. A lot of the current passes through the shunt resistance which increases the total current that can enter the galvanometer setup and hence increase the range of the formed ammeter.
On the other hand to convert a galvanometer to a voltmeter, a large resistance should be connected in series with the galvanometer. This causes a larger potential drop in the galvanometer setup which would not have been possible by the galvanometer alone. Hence, this increases the potential drop in the galvanometer setup and hence, increases the range of the voltmeter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




