
A boy stands straight in front of a mirror at a distance 30cm away from it. He sees his erect image whose height is ${{\left( \dfrac{1}{5} \right)}^{th}}$of his real height. The mirror he is using is
a) plane mirror
b) convex mirror
c) concave mirror
d) Plano-concave mirror
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: In the question given to us that the image formed by the mirror is ${{\left( \dfrac{1}{5} \right)}^{th}}$the height of the boy. Therefore we can say that the image formed is diminished. The mirror is 30cm away from the boy and the boy sees his entire image. Hence we can say that if it is a spherical mirror he is standing with in the curvature of the mirror. To approach a correct answer we need to know when the object lies very close to the mirror does the above mirrors form diminished images or not and accordingly we will have a correct answer.
Complete step by step answer:
To begin with let us discuss the magnifications of each of the above mirrors.
Let us say the image distance is at V from the mirror and the object distance is U from the mirror. Than the magnification produced by the mirror is given by,
$m=\dfrac{\text{height of the image}}{\text{height of the object}}=-\dfrac{V}{U}$ .
A plane mirror produces an image at the same distance as that of the object. Hence from the above definition of magnification the ratio is always one. Hence the above mirror cannot be a plane mirror.
In a concave mirror the image is diminished when it is kept beyond the centre of curvature of the lens. Apart from that at all the distances the concave mirror forms magnified images of the object. When the image formed in a concave mirror is diminished its magnification is less than 1, but negative. This suggests that the image formed is inverted. But in the above case the image of the boy is erect, therefore the mirror used cannot be a concave mirror. A similar thing happens in a Plano-concave mirror.
A convex mirror always forms the virtual images. The convex mirror has a wider field of view other than any other mirrors. Hence it forms diminished images. The object distance measured is negative and the image distance measured is always positive. Hence from the above definition of magnification the ratio will be positive indicating the image formed is erect.
Hence the mirror the boy is using is a convex mirror.
Note:
The distances measured in an optical system are always measured from the pole of the mirror. The distance measured along the direction of the incident ray is taken to be positive and the distance measured in the opposite to the direction of the incident ray from the pole of the mirror is taken to be negative. Given below is a figure of convex mirror for an object placed beyond focus.
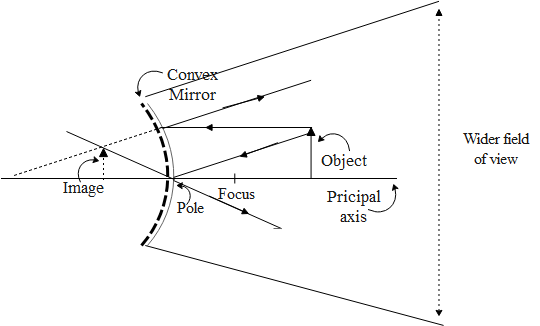
Complete step by step answer:
To begin with let us discuss the magnifications of each of the above mirrors.
Let us say the image distance is at V from the mirror and the object distance is U from the mirror. Than the magnification produced by the mirror is given by,
$m=\dfrac{\text{height of the image}}{\text{height of the object}}=-\dfrac{V}{U}$ .
A plane mirror produces an image at the same distance as that of the object. Hence from the above definition of magnification the ratio is always one. Hence the above mirror cannot be a plane mirror.
In a concave mirror the image is diminished when it is kept beyond the centre of curvature of the lens. Apart from that at all the distances the concave mirror forms magnified images of the object. When the image formed in a concave mirror is diminished its magnification is less than 1, but negative. This suggests that the image formed is inverted. But in the above case the image of the boy is erect, therefore the mirror used cannot be a concave mirror. A similar thing happens in a Plano-concave mirror.
A convex mirror always forms the virtual images. The convex mirror has a wider field of view other than any other mirrors. Hence it forms diminished images. The object distance measured is negative and the image distance measured is always positive. Hence from the above definition of magnification the ratio will be positive indicating the image formed is erect.
Hence the mirror the boy is using is a convex mirror.
Note:
The distances measured in an optical system are always measured from the pole of the mirror. The distance measured along the direction of the incident ray is taken to be positive and the distance measured in the opposite to the direction of the incident ray from the pole of the mirror is taken to be negative. Given below is a figure of convex mirror for an object placed beyond focus.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




