
A breeder crossed a purebred tall pea plant having white flowers to a pure-bred short pea plant with blue flowers. He obtained $202\,{F_1}$ progeny and found that they are tall and have white flowers. Upon selfing these plants, he obtained a progeny of $2160$ plants approximately, how many of these are likely to be short and blue flowers?
(A) $1215$
(B) $405$
(C) $540$
(D) $135$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The dihybrid cross is defined as the cross between the two different genes of the same species. It expresses the dominant and the recessive genes. From the dihybrid test cross ratio, find the number of plants of particular traits asked by using the formula.
Complete answer:
In a dihybrid cross
$n = r \times \left( {\dfrac{T}{R}} \right)$
Where $n$ is the number of plants exhibiting the particular traits, $r$ is the ratio of the particular trait, $T$ is the total number of plants obtained and $R$ is the sum of the ratio of all the traits.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given data in the question,
The number of progenies obtained in the ${F_1}$ generation= $202$
The number of progenies obtained in the ${F_2}$ generation= $2160$
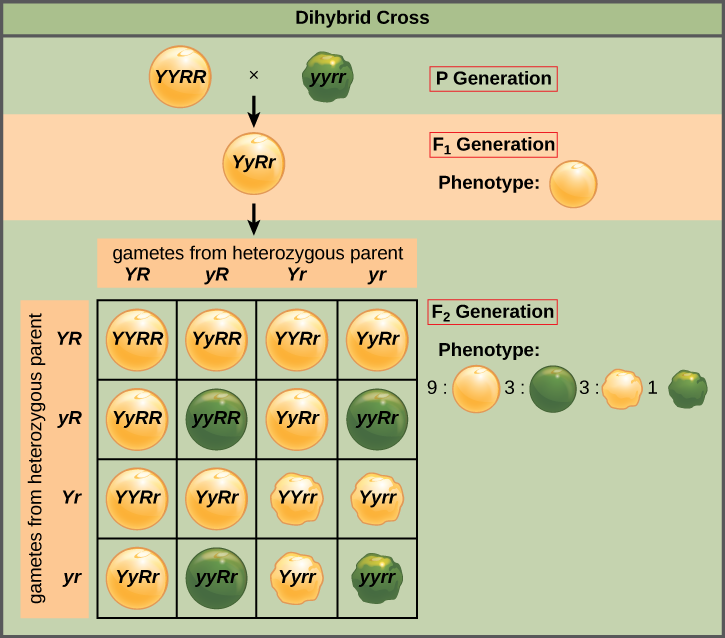
In a dihybrid cross the ${F_2}$ generation obtained is in the ratio of $9:3:3:1$.
This means that the $9x$ species is the number of the expressed dominant gene. That is, it denotes the number of the tall flowers with the white flowers. Then the $3x$denotes the both the dominant and the recessive genes expressed in the ${F_2}$ generation. That is, it may be tall plants with the blue flowers or it may be the short plants with the white plants. Then, $1x$ denotes the expression of the recessive gene in the ${F_2}$ generation. It expresses the short plants with the blue flowers.
Hence the number of the short plants with the blue flower in the ${F_2}$ generation is $1x$.
Applying the dihybrid cross formula.
$n = r \times \left( {\dfrac{T}{R}} \right)$
$n = 1 \times \left( {\dfrac{{2160}}{{9 + 3 + 3 + 1}}} \right)$
$n = \dfrac{{2160}}{{16}}$
$n = 135\,plants$
Hence the correct answer is OPTION(D)
Note: It is to be noted that, in the ${F_1}$ generation plants, the heterogeneous gene is expressed. In the ${F_2}$ generation, the gene with the dominant, recessive and the combination of the both dominant and the recessive characters is expressed.
Complete answer:
In a dihybrid cross
$n = r \times \left( {\dfrac{T}{R}} \right)$
Where $n$ is the number of plants exhibiting the particular traits, $r$ is the ratio of the particular trait, $T$ is the total number of plants obtained and $R$ is the sum of the ratio of all the traits.
Complete step by step solution:
From the given data in the question,
The number of progenies obtained in the ${F_1}$ generation= $202$
The number of progenies obtained in the ${F_2}$ generation= $2160$
In a dihybrid cross the ${F_2}$ generation obtained is in the ratio of $9:3:3:1$.
This means that the $9x$ species is the number of the expressed dominant gene. That is, it denotes the number of the tall flowers with the white flowers. Then the $3x$denotes the both the dominant and the recessive genes expressed in the ${F_2}$ generation. That is, it may be tall plants with the blue flowers or it may be the short plants with the white plants. Then, $1x$ denotes the expression of the recessive gene in the ${F_2}$ generation. It expresses the short plants with the blue flowers.
Hence the number of the short plants with the blue flower in the ${F_2}$ generation is $1x$.
Applying the dihybrid cross formula.
$n = r \times \left( {\dfrac{T}{R}} \right)$
$n = 1 \times \left( {\dfrac{{2160}}{{9 + 3 + 3 + 1}}} \right)$
$n = \dfrac{{2160}}{{16}}$
$n = 135\,plants$

Hence the correct answer is OPTION(D)
Note: It is to be noted that, in the ${F_1}$ generation plants, the heterogeneous gene is expressed. In the ${F_2}$ generation, the gene with the dominant, recessive and the combination of the both dominant and the recessive characters is expressed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




