
When a capacitor of value 200 $\mu F$ charged to $200V$ is discharged separately through resistance of $2\Omega$ and $8 \Omega$, then heat produced in joule will respectively be:
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the question, we will first apply the formula of potential energy in the stored capacitor then we will deduce the heat energy that is dissipated in the process of discharge and hence we will get the total heat energy by adding all energy that in this case will be potential energy
Formula used:
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Here, $U$ is the potential energy
$C$ is the capacitance
$V$ is the voltage
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are given a capacitor which is first charged then it is discharged separately through resistances and the heat is produced and we have to find that heat produced
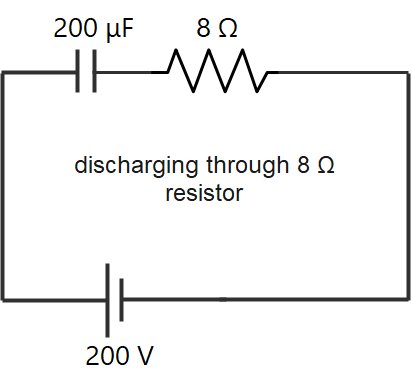
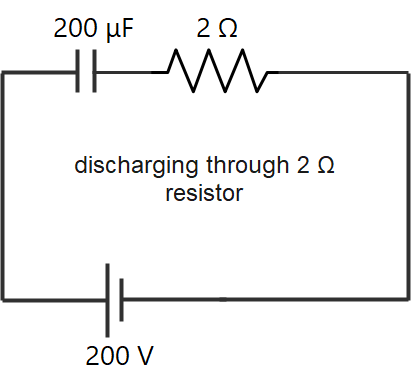
value of capacitor = 200 $\mu F$
potential difference till it is charged to = 200V
resistance = 2 ohms and 8 ohms
First, we will find the potential energy stored in the capacitor for that we will use the formula
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Now we will substitute C = 200$\mu F$, V = 200 V
Changing capacitance from $\mu F$to F
1$\mu F$ = ${10^{ - 6}}F$
200$\mu F$ = 200 $ \times $ ${10^{ - 6}}F$
After changing the $\mu F$ to F we will substitute the values
$U = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (200 \times {10^{ - 6}}F) \times {(200V)^2}$
Solving for potential energy we get
U = 4 Joules
On discharging all the energy that is in this case is potential energy in the capacitor will be dissipated as the heat through the connected resistor
Hence, Heat produced = 4 Joules
Here heat produced is independent of value of resistance connected so, in both the cases heat produced will be 4 Joules.
Note:
There might be a chance of confusing at how will the value of resistance will affect only in the time of discharging and not the heat as a time constant during the discharging the higher the value of resistance is the capacitor will take more time to discharge and hence the heat remains same in both cases
Formula used:
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Here, $U$ is the potential energy
$C$ is the capacitance
$V$ is the voltage
Complete step by step answer:
In the question we are given a capacitor which is first charged then it is discharged separately through resistances and the heat is produced and we have to find that heat produced
value of capacitor = 200 $\mu F$
potential difference till it is charged to = 200V
resistance = 2 ohms and 8 ohms


First, we will find the potential energy stored in the capacitor for that we will use the formula
$U = \dfrac{1}{2}C{V^2}$
Now we will substitute C = 200$\mu F$, V = 200 V
Changing capacitance from $\mu F$to F
1$\mu F$ = ${10^{ - 6}}F$
200$\mu F$ = 200 $ \times $ ${10^{ - 6}}F$
After changing the $\mu F$ to F we will substitute the values
$U = \dfrac{1}{2} \times (200 \times {10^{ - 6}}F) \times {(200V)^2}$
Solving for potential energy we get
U = 4 Joules
On discharging all the energy that is in this case is potential energy in the capacitor will be dissipated as the heat through the connected resistor
Hence, Heat produced = 4 Joules
Here heat produced is independent of value of resistance connected so, in both the cases heat produced will be 4 Joules.
Note:
There might be a chance of confusing at how will the value of resistance will affect only in the time of discharging and not the heat as a time constant during the discharging the higher the value of resistance is the capacitor will take more time to discharge and hence the heat remains same in both cases
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




