
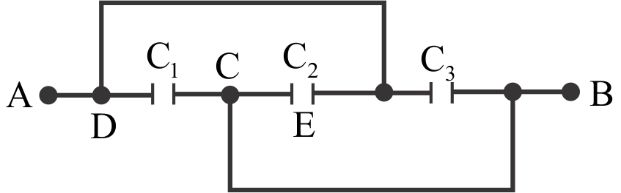
A combination of parallel plate capacitors is maintained at a certain potential difference. When a $3mm$ thick slab is introduced between all the plates, in order to maintain the same potential difference, the distance between the plates is increased by $2.4mm$. Find the dielectric constant of the slab.
A. $4$
B. $5$
C. $3$
D. $6$
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint Find the equivalent capacitance both with and without the slab between the plates and equate them. Use suitable formula to establish the expression for capacitance.
Formulas used:
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$ where $d$ is the distance between the capacitance plates, $A$ is the area of the plates and ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space.
$C' = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{{d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right)}}$ where $K$ is the relative permittivity of the material of the slab and $d'$is the distance between the capacitor plates, $t$ is the thickness of the slab introduced.
Complete step by step answer
A capacitor is a system of conductors and dielectric that can store electric charge. It consists of two conductors containing equal and opposite charges and has a potential difference $V$ between them.
The potential difference between the conductors is proportional to the charge on the capacitor and is given by the relation $Q = CV$where $Q$ is the charge on the positive conductor and $C$ is called the capacitance.
Now, we know that the potential difference between the two plates is given by, $V = E \times d$ where $d$ is the distance between the two plates.
Thus, substituting the value of $V$ in the equation$Q = CV$, we get,
$Q = CEd$
Putting $E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ and $\sigma = \dfrac{Q}{A}$ where $A$ is the area of the capacitor plate, we get
$Q = C \times \dfrac{Q}{{A{\varepsilon _0}}} \times d$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{d}$ where $C$ be the equivalent capacitance between terminals A and B.
Now, introducing a slab of thickness $t$, the resultant capacitance $C'$ becomes
$C' = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{{d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right)}}$ where $K$ is the relative permittivity of the material of the slab and $d'$is the new distance between the capacitor plates.
Now, since the potential difference remains same, the capacitance must also not vary
So, $C = C'$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{d} = \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{{d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right)}}$
$
\Rightarrow d = d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow d = d + 2.4 - 3\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 2.4 - 3 + \dfrac{3}{K} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{K} = 0.6 \\
\Rightarrow K = 5 \\
$
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:To establish the capacitance of an isolated single conductor, we assume the conductor to be a part of a capacitor whose other conductor is at infinity.
Formulas used:
$C = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{d}$ where $d$ is the distance between the capacitance plates, $A$ is the area of the plates and ${\varepsilon _0}$ is the permittivity of free space.
$C' = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{{d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right)}}$ where $K$ is the relative permittivity of the material of the slab and $d'$is the distance between the capacitor plates, $t$ is the thickness of the slab introduced.
Complete step by step answer
A capacitor is a system of conductors and dielectric that can store electric charge. It consists of two conductors containing equal and opposite charges and has a potential difference $V$ between them.
The potential difference between the conductors is proportional to the charge on the capacitor and is given by the relation $Q = CV$where $Q$ is the charge on the positive conductor and $C$ is called the capacitance.
Now, we know that the potential difference between the two plates is given by, $V = E \times d$ where $d$ is the distance between the two plates.
Thus, substituting the value of $V$ in the equation$Q = CV$, we get,
$Q = CEd$
Putting $E = \dfrac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon _0}}}$ and $\sigma = \dfrac{Q}{A}$ where $A$ is the area of the capacitor plate, we get
$Q = C \times \dfrac{Q}{{A{\varepsilon _0}}} \times d$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{d}$ where $C$ be the equivalent capacitance between terminals A and B.
Now, introducing a slab of thickness $t$, the resultant capacitance $C'$ becomes
$C' = \dfrac{{{\varepsilon _0}A}}{{d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right)}}$ where $K$ is the relative permittivity of the material of the slab and $d'$is the new distance between the capacitor plates.
Now, since the potential difference remains same, the capacitance must also not vary
So, $C = C'$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{d} = \dfrac{{A{\varepsilon _0}}}{{d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right)}}$
$
\Rightarrow d = d' - t\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow d = d + 2.4 - 3\left( {1 - \dfrac{1}{K}} \right) \\
\Rightarrow 2.4 - 3 + \dfrac{3}{K} = 0 \\
\Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{K} = 0.6 \\
\Rightarrow K = 5 \\
$
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:To establish the capacitance of an isolated single conductor, we assume the conductor to be a part of a capacitor whose other conductor is at infinity.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




