
A concave lens always forms an image which is
(A) Real, inverted and diminished
(B) Real, erect and diminished
(C) Virtual, erect and magnified
(D) Virtual, erect and diminished
Answer
571.5k+ views
Hint : Conventionally, the radius of the curvature of the concave lens is always negative. So, the focal length which is numerically half of the radius of curvature is also negative. Using the lens formula, we can calculate the image position and get the answer.
Formula used:
Lens formula is given as
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} $
Where, $ f $ is the focal length of the lens, $ u $ is the object distance, $ v $ is the image distance.
Magnification is given as
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u} $ .
Complete step by step answer
The ray diagram for a concave lens is given as
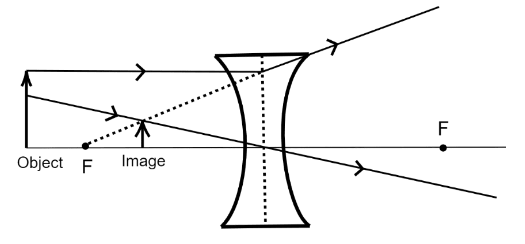
The convention of signs is such that, the coordinates on the left side of the lens are taken negative while the coordinates on the right side are taken as positive.
From the ray diagram, we can conclude that the image is erect.
The object distance is always negative.
For a concave lens, the focal length is also always negative.
We know that
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{f} $ $ - - - - (1) $
In this case of a concave lens, $ u $ and $ f $ have negative non-zero values.
Thus, under any conditions, $ v $ i.e. image distance is always negative. From this, we can conclude that the image formed will always be virtual.
Magnification is given as
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u} $
From the equation $ (1) $ , we can observe that the numeric value $ \dfrac{1}{v} $ will always be greater than $ \dfrac{1}{u} $ .
So, we can say that $ v < u $ in every case.
$ \Rightarrow m < 1 $
This implies that the image is always diminished.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note
Be careful of the apparatus given in the question. It can be a convex lens or convex mirror or a concave mirror. In each of these cases, we will have different answers. For example, the radius of the curvature of the convex lens is positive. Thus all the values will be different accordingly. It is always better to make a ray diagram and then approach the problem.
Formula used:
Lens formula is given as
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} $
Where, $ f $ is the focal length of the lens, $ u $ is the object distance, $ v $ is the image distance.
Magnification is given as
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u} $ .
Complete step by step answer
The ray diagram for a concave lens is given as

The convention of signs is such that, the coordinates on the left side of the lens are taken negative while the coordinates on the right side are taken as positive.
From the ray diagram, we can conclude that the image is erect.
The object distance is always negative.
For a concave lens, the focal length is also always negative.
We know that
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{u} + \dfrac{1}{f} $ $ - - - - (1) $
In this case of a concave lens, $ u $ and $ f $ have negative non-zero values.
Thus, under any conditions, $ v $ i.e. image distance is always negative. From this, we can conclude that the image formed will always be virtual.
Magnification is given as
$ \Rightarrow m = \dfrac{v}{u} $
From the equation $ (1) $ , we can observe that the numeric value $ \dfrac{1}{v} $ will always be greater than $ \dfrac{1}{u} $ .
So, we can say that $ v < u $ in every case.
$ \Rightarrow m < 1 $
This implies that the image is always diminished.
Thus, option (D) is correct.
Note
Be careful of the apparatus given in the question. It can be a convex lens or convex mirror or a concave mirror. In each of these cases, we will have different answers. For example, the radius of the curvature of the convex lens is positive. Thus all the values will be different accordingly. It is always better to make a ray diagram and then approach the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




