
A concave lens of focal length 15 cm forms an image 10 cm from the lens. How far is the object placed from the lens? Draw the ray diagram.
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Define the image formation process in case of a concave lens. Obtain the lens equation which gives the relation between focal length, object distance and image distance of a lens. Put the given values to find the required answer.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where, f is the focal length of the lens, u is the object distance and v is the image distance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The focal length of the concave lens is, $f=-15cm$
Distance of the image from the lens is, $v=-10cm$
Let the distance of the object from the lens is u.
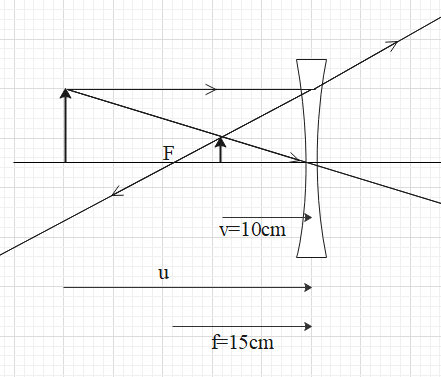
Now, the lens equation is given as,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where, f is the focal length of the lens, u is the object distance and v is the image distance.
Now, putting the given values in the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{-10}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{-15} \\
& \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{15}-\dfrac{1}{10} \\
& \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{2-3}{30} \\
& \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{-1}{30} \\
& u=-30 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get that the object distance from the lens is 30 cm.
Additional information:
Concave lens is a diverging lens. It diverges the incoming light away from the principal axis.
In the above diagram the ray travelling parallel to the principal axis will refract through the lens and will travel in the direction where if we extend it, it will pass through the focal point. There will not be any effect on the ray passing through the centre of the lens. These two rays intersect at the point to form the image.
The image formed in the case of a concave lens is a virtual image in nature. The images are upright and diminished.
Note: In the above question we have used negative signs to represent the focal length and image distance. This is due to sign convention. In the case of a concave lens, both the focal point and the image formed is in the direction from where the incident rays come i.e. in the direction of the object. So, we use negative signs.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where, f is the focal length of the lens, u is the object distance and v is the image distance.
Complete step-by-step answer:
The focal length of the concave lens is, $f=-15cm$
Distance of the image from the lens is, $v=-10cm$
Let the distance of the object from the lens is u.

Now, the lens equation is given as,
$\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{f}$
Where, f is the focal length of the lens, u is the object distance and v is the image distance.
Now, putting the given values in the above equation, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{-10}-\dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{-15} \\
& \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{15}-\dfrac{1}{10} \\
& \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{2-3}{30} \\
& \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{-1}{30} \\
& u=-30 \\
\end{align}$
So, we get that the object distance from the lens is 30 cm.
Additional information:
Concave lens is a diverging lens. It diverges the incoming light away from the principal axis.
In the above diagram the ray travelling parallel to the principal axis will refract through the lens and will travel in the direction where if we extend it, it will pass through the focal point. There will not be any effect on the ray passing through the centre of the lens. These two rays intersect at the point to form the image.
The image formed in the case of a concave lens is a virtual image in nature. The images are upright and diminished.
Note: In the above question we have used negative signs to represent the focal length and image distance. This is due to sign convention. In the case of a concave lens, both the focal point and the image formed is in the direction from where the incident rays come i.e. in the direction of the object. So, we use negative signs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




