
A convexo-concave diverging lens is made of glass of refractive index 1.5 and focal length 24 cm. Radius of curvature for one surface is double that of the other. Then, the radii of curvature for the two surfaces are (in cm):
A.6,12
B.12,14
C.3,6
D.18,36

Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: Recall that for a diverging lens, the focal length is negative. Use the lens maker’s formula to establish a relation between the focal length, the refractive index of the lens and the radii of curvature of both the surfaces. Keep in mind that the radius of curvature of one surface is twice the other. Then, accounting for the curvature sign conventions, arrive at a relationship between the two radii and plug in the numbers to get the actual value of the lens surfaces’ radii of curvature.
Formula Used:
Lens maker’s formula: $\dfrac{1}{f} = (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R_1}-\dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$, where f is the focal length of the lens, $\mu$ is the refractive index of the lens material, $R_1$ and $R_2$ are the radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens.
Complete answer:
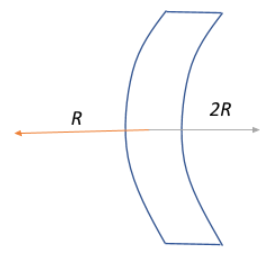
We have a convexo-concave lens as shown in the diagram. This means that one surface is derived from a convex lens and the other surface from a concave lens, and together, they have like a diverging lens, as mentioned in the question.
According to the Cartesian Sign Convention, the focal length of a diverging lens is negative, therefore, focal length of our convexo-concave lens will be $f = -24\;cm$.
The refractive index of the lens is given to be $\mu =1.5$
Let the radius of curvature of the concave surface be $R_2$
Then the radius of curvature of the convex surface will be $R_1 = 2R_2$
These are in accordance with the sign convention since positive radii of curvature is associated with those surfaces that appear to be convex when seen from the left.
We know that the Lens Maker’s Formula relates all the above quantities together as follows:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R_1}-\dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
Substituting the values:
$\Rightarrow -\dfrac{1}{24} = (1.5-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{2R_2}-\dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow -\dfrac{1}{24} = (0.5)\left(-\dfrac{1}{2R_2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow -\dfrac{1}{12} = -\dfrac{1}{2R_2}$
$\Rightarrow R_{2} = 6\;cm$
$\Rightarrow R_{1} = 2R_{2} = 2 \times 6 =12\;cm$
Therefore, the correct choice would be: A. 6,12.
Note:
Keep in mind that all values assume the Cartesian sign convention. For converging lenses, the focal length is positive whereas for diverging lenses focal length is negative.
The sign convention for the optical radius of curvature of lens surfaces:
If the surface seems convex when seen from the left, or when the centre of curvature is to the right of the surface, the radius of curvature is taken as positive, whereas if the surface seems concave when viewed from the left, or when the centre of curvature is to the left of the surface, then the radius of curvature is taken as negative.
Formula Used:
Lens maker’s formula: $\dfrac{1}{f} = (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R_1}-\dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$, where f is the focal length of the lens, $\mu$ is the refractive index of the lens material, $R_1$ and $R_2$ are the radii of curvature of the two surfaces of the lens.
Complete answer:
We have a convexo-concave lens as shown in the diagram. This means that one surface is derived from a convex lens and the other surface from a concave lens, and together, they have like a diverging lens, as mentioned in the question.
According to the Cartesian Sign Convention, the focal length of a diverging lens is negative, therefore, focal length of our convexo-concave lens will be $f = -24\;cm$.
The refractive index of the lens is given to be $\mu =1.5$
Let the radius of curvature of the concave surface be $R_2$
Then the radius of curvature of the convex surface will be $R_1 = 2R_2$
These are in accordance with the sign convention since positive radii of curvature is associated with those surfaces that appear to be convex when seen from the left.
We know that the Lens Maker’s Formula relates all the above quantities together as follows:
$\dfrac{1}{f} = (\mu-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{R_1}-\dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
Substituting the values:
$\Rightarrow -\dfrac{1}{24} = (1.5-1)\left(\dfrac{1}{2R_2}-\dfrac{1}{R_2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow -\dfrac{1}{24} = (0.5)\left(-\dfrac{1}{2R_2}\right)$
$\Rightarrow -\dfrac{1}{12} = -\dfrac{1}{2R_2}$
$\Rightarrow R_{2} = 6\;cm$
$\Rightarrow R_{1} = 2R_{2} = 2 \times 6 =12\;cm$
Therefore, the correct choice would be: A. 6,12.
Note:
Keep in mind that all values assume the Cartesian sign convention. For converging lenses, the focal length is positive whereas for diverging lenses focal length is negative.
The sign convention for the optical radius of curvature of lens surfaces:
If the surface seems convex when seen from the left, or when the centre of curvature is to the right of the surface, the radius of curvature is taken as positive, whereas if the surface seems concave when viewed from the left, or when the centre of curvature is to the left of the surface, then the radius of curvature is taken as negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




