
A cross between pure tall Pea plant with green pods and dwarf Pea plant with yellow pods will produce tall ${ F }_{ 2 }$ plants, out of 16
(a) 15
(b) 13
(c) 12
(d) 7
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: Each pair of alleles showed independent segregation for the genes on different chromosomes. Where the first filial generation (${ F }_{ 1 }$ generation) produces four identical offspring, a phenotypic (appearance) ratio of 9:3:3:1 is shown by the second filial generation, which occurs by crossing the members of the first generation.
Complete step by step answer:
In the dihybrid cross-ratio (9:3:3:1), the 9 reflects the proportion of individuals exhibiting both dominant features, the first 3 reflects the individuals exhibiting the first dominant feature and the second recessive feature, the second 3 represents those displaying the first recessive feature, and the second dominant feature and the 1 represents the homozygous, displaying both recessive features.
To dwarf pea plants with yellow pods (ttgg) a cross is made with a pure tall pea plant with green pods (TTGG). 16 plants are formed in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation, in this, tall green is 9, tall yellow is 3, dwarf green is 3 dwarf yellow is 1. There are twelve tall plants, twelve green plants, four small plants, and four yellow plants.
This is an example of a dihybrid cross since at the same time two characters are being examined in which dwarfness is a recessive trait.
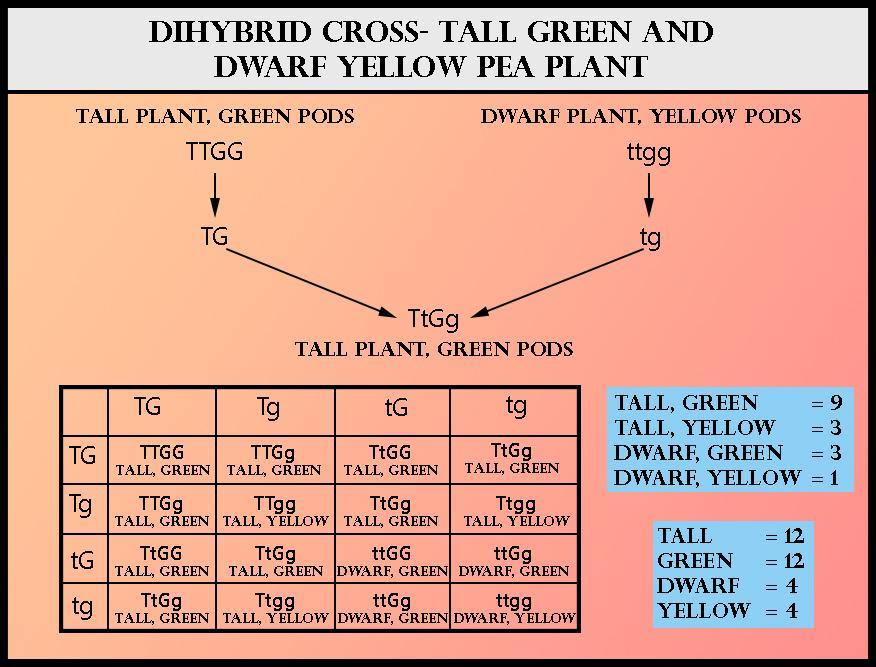
So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) 12’.
Additional information: The Dihybrid cross is a cross between two distinct lines or genes that are separated into two traits observed. According to Mendel's argument, there is a relationship of entirely dominant-recessive traits between the alleles of both these loci.
In the term "Dihybrid Cross," the "di" suggests that two characteristics are involved (e.g. T and G) , the "hybrid" means that each trait has two separate alleles (e.g. T and t, or G and g) , and "cross" means that there are two people (usually a mother and father) who merge or "cross" their genetic material.
Note: In 1865, Mendel introduced to the local Natural History Society the findings of his studies involving nearly 30,000 pea plants. He showed that traits are faithfully transmitted from parent to offspring in dominant and recessive forms, independently of other traits. It is possible to calculate the probability of an offspring inheriting a certain characteristic from its parents using a Punnett square, but in fact, there could be large numbers of different genes responsible for a certain characteristic of the phenotype, so it becomes difficult to prove. Fortunately, the distribution of phenotypes defined by polygenic inheritance typically falls into a normal probability distribution, with an intermediate phenotype of the two parents exhibited by most offspring. Polygenic inheritance, also referred to as quantitative inheritance, refers to a single phenotypic inherited trait that is controlled by two or more distinct genes.
Complete step by step answer:
In the dihybrid cross-ratio (9:3:3:1), the 9 reflects the proportion of individuals exhibiting both dominant features, the first 3 reflects the individuals exhibiting the first dominant feature and the second recessive feature, the second 3 represents those displaying the first recessive feature, and the second dominant feature and the 1 represents the homozygous, displaying both recessive features.
To dwarf pea plants with yellow pods (ttgg) a cross is made with a pure tall pea plant with green pods (TTGG). 16 plants are formed in the ${ F }_{ 2 }$ generation, in this, tall green is 9, tall yellow is 3, dwarf green is 3 dwarf yellow is 1. There are twelve tall plants, twelve green plants, four small plants, and four yellow plants.
This is an example of a dihybrid cross since at the same time two characters are being examined in which dwarfness is a recessive trait.

So, the correct answer is, ‘(c) 12’.
Additional information: The Dihybrid cross is a cross between two distinct lines or genes that are separated into two traits observed. According to Mendel's argument, there is a relationship of entirely dominant-recessive traits between the alleles of both these loci.
In the term "Dihybrid Cross," the "di" suggests that two characteristics are involved (e.g. T and G) , the "hybrid" means that each trait has two separate alleles (e.g. T and t, or G and g) , and "cross" means that there are two people (usually a mother and father) who merge or "cross" their genetic material.
Note: In 1865, Mendel introduced to the local Natural History Society the findings of his studies involving nearly 30,000 pea plants. He showed that traits are faithfully transmitted from parent to offspring in dominant and recessive forms, independently of other traits. It is possible to calculate the probability of an offspring inheriting a certain characteristic from its parents using a Punnett square, but in fact, there could be large numbers of different genes responsible for a certain characteristic of the phenotype, so it becomes difficult to prove. Fortunately, the distribution of phenotypes defined by polygenic inheritance typically falls into a normal probability distribution, with an intermediate phenotype of the two parents exhibited by most offspring. Polygenic inheritance, also referred to as quantitative inheritance, refers to a single phenotypic inherited trait that is controlled by two or more distinct genes.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




