
A current through a horizontal power line flows in east to west direction. What is the direction of the magnetic field at a point directly below and at a point directly above it?
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: To find the magnetic field, we will use the right hand thumb rule. Current flows from east to west, then if we curl our fingers pointing in the direction of current. It will give the direction of the magnetic field. The magnetic field direction at a point above the wire is inward and the magnetic field direction at a point below the wire is outwards.
Complete step-by-step solution:
If we use the right-hand thumb rule, we can find the direction of the magnetic field around the current-carrying conductor. The right-hand thumb rule says that: Imagine that we are taking a current-carrying straight conductor in our right hand such that the thumb directs towards the direction of the current. Then our fingers will coil around the conductor in the magnetic field lines direction.
In the question, the current is from east to west, and hence the direction of the magnetic field would be in the direction of the turn of the fingers. Thus, the magnetic field direction at a point directly below the horizontal power line is outwards and the magnetic field direction at a point directly above the horizontal power line is inwards.
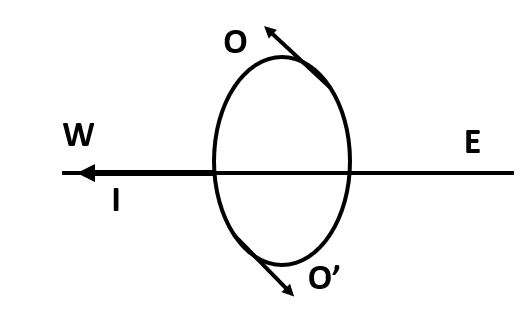
The magnetic field direction at a point beneath the wire is from north to south. The magnetic field direction at a position directly up the wire is from south to north. The current is from east to west. Applying the right-hand thumb rule, we see that the magnetic field direction at a point below the wire is north-south. The magnetic field direction at a point immediately above the wire is from south-north.
Note: The right-hand thumb rule gives the Lorentz force acting on a charged particle in the presence of a magnetic field. The Right-Hand Thumb Rule provides the direction of the cross product. If we bend the fingers of the right hand in the direction of the vectors, then the thumb shows to the cross product. The current in a conductor produces a magnetic field across the wire. The direction of the magnetic field can be found from the Right-Hand Thumb Rule.
Complete step-by-step solution:
If we use the right-hand thumb rule, we can find the direction of the magnetic field around the current-carrying conductor. The right-hand thumb rule says that: Imagine that we are taking a current-carrying straight conductor in our right hand such that the thumb directs towards the direction of the current. Then our fingers will coil around the conductor in the magnetic field lines direction.
In the question, the current is from east to west, and hence the direction of the magnetic field would be in the direction of the turn of the fingers. Thus, the magnetic field direction at a point directly below the horizontal power line is outwards and the magnetic field direction at a point directly above the horizontal power line is inwards.

The magnetic field direction at a point beneath the wire is from north to south. The magnetic field direction at a position directly up the wire is from south to north. The current is from east to west. Applying the right-hand thumb rule, we see that the magnetic field direction at a point below the wire is north-south. The magnetic field direction at a point immediately above the wire is from south-north.
Note: The right-hand thumb rule gives the Lorentz force acting on a charged particle in the presence of a magnetic field. The Right-Hand Thumb Rule provides the direction of the cross product. If we bend the fingers of the right hand in the direction of the vectors, then the thumb shows to the cross product. The current in a conductor produces a magnetic field across the wire. The direction of the magnetic field can be found from the Right-Hand Thumb Rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




