
A diene, buta-1,3-diene was subjected to ozonolysis to prepare aldehydes. Which of the following aldehydes will be obtained during the reaction?
A. \[CHO - CHO + 2HCHO\]
B. \[C{H_3}CHO + 2HCHO\]
C. \[C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO + C{H_3}CHO\]
D. \[2C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO\]
Answer
578.7k+ views
Hint: The two step conversion of an alkene or alkyne into an ozonide followed by its reductive cleavage to yield carbonyl compounds is called ozonolysis. It occurs at a low temperature range of \[196 - 200K\].
Complete step by step answer:
Reaction description:
Step1: When ozone is passed through a solution of buta-1,3-diene in some inert solvent such as $C{H_2}C{l_2},CHC{l_3}{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}CC{l_4}$ at low temperature of range \[196 - 200K\], it oxidises it into ozonides as given below:
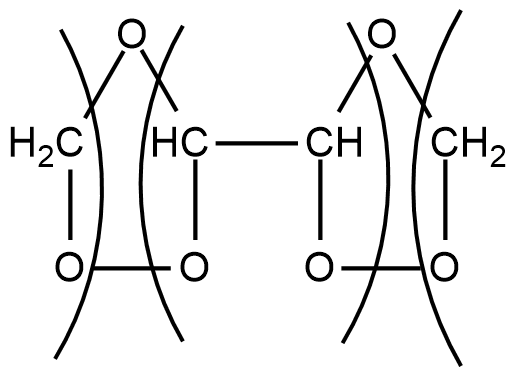
$C{H_2} = CH - CH = C{H_2} + {O_3}\xrightarrow[{196 - 200K}]{{C{H_2}C{l_2}}}$
These ozonides are unstable compounds and also explosive in nature. So they are not isolated.
Step2: In second step, these ozonides are reduced, in situ, with zinc dust and water to give one molecule of $CHO$−$CHO$ and 2 molecules of formaldehyde i.e. $HCHO$.
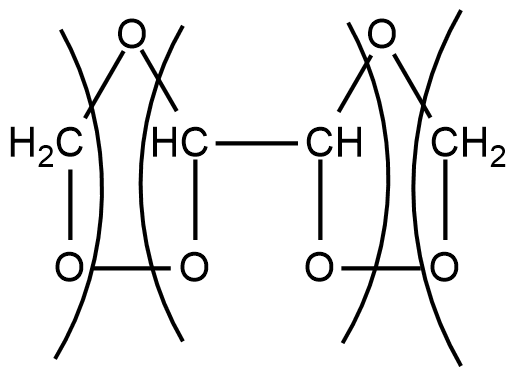
$\xrightarrow[{ - ZnO}]{{Zn/{H_2}O}}CHO - CHO + 2HCHO$
Hence the correct answer is option (A).
Ozonolysis has been exclusively used in the past for the structure elucidation of alkenes. It is the versatile method for locating the position of multiple bonds in an unknown alkene since no two alkenes give the same combination of aldehyde or ketones.
Note:
Ozonides are also reduced by \[{H_2}/Pd\] . Sometimes ozonides give a mixture of ketone and aldehyde also; depending upon the structure of alkene. Instead of \[Zn/{H_2}O\] or catalytic hydrogenation, ozonide can be more conveniently be reduced with dimethyl sulphide,\[{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}S\] and it get oxidised itself to dimethyl sulphoxide.
Complete step by step answer:
Reaction description:
Step1: When ozone is passed through a solution of buta-1,3-diene in some inert solvent such as $C{H_2}C{l_2},CHC{l_3}{\text{ }}or{\text{ }}CC{l_4}$ at low temperature of range \[196 - 200K\], it oxidises it into ozonides as given below:

$C{H_2} = CH - CH = C{H_2} + {O_3}\xrightarrow[{196 - 200K}]{{C{H_2}C{l_2}}}$
These ozonides are unstable compounds and also explosive in nature. So they are not isolated.
Step2: In second step, these ozonides are reduced, in situ, with zinc dust and water to give one molecule of $CHO$−$CHO$ and 2 molecules of formaldehyde i.e. $HCHO$.

$\xrightarrow[{ - ZnO}]{{Zn/{H_2}O}}CHO - CHO + 2HCHO$
Hence the correct answer is option (A).
Ozonolysis has been exclusively used in the past for the structure elucidation of alkenes. It is the versatile method for locating the position of multiple bonds in an unknown alkene since no two alkenes give the same combination of aldehyde or ketones.
Note:
Ozonides are also reduced by \[{H_2}/Pd\] . Sometimes ozonides give a mixture of ketone and aldehyde also; depending upon the structure of alkene. Instead of \[Zn/{H_2}O\] or catalytic hydrogenation, ozonide can be more conveniently be reduced with dimethyl sulphide,\[{\left( {C{H_3}} \right)_2}S\] and it get oxidised itself to dimethyl sulphoxide.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




