
(a) Draw a diagram of the structure of a human ovum surrounded by corona radiata. Label the following parts
(i) Ovum (ii) Plasma membrane (iii) Zona pellucida
(b) State the function of zona pellucida
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint:Ovum is a single cell released from either of reproductive organs, the ovaries, which are capable of developing into a new organism when fertilized with a sperm. Various parts of ovum are –yolk, nucleus, thick and transparent zona pellucida, corona radiata.
Complete answer:
a) Ovum refers to the secondary oocyte stage of oogenesis, where the second maturation division is yet to occur. In this condition the mature ovum is released from the ovary and enters into the uterus for fertilization. In humans, the female ovum is discharged from the graafian follicle with one polar body. Cytoplasm of egg is called ooplasm.
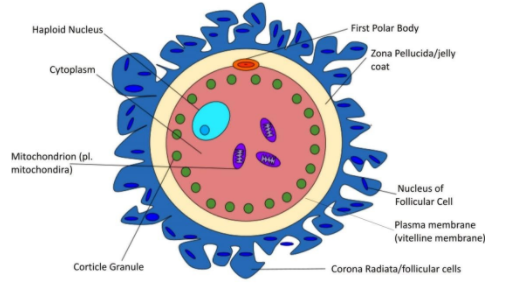
Human ovum is surrounded by a number of egg envelopes which are vitelline membrane (plasma membrane), zona pellucida and corona radiata.
Vitelline membrane is inner, then transparent and is secreted by the ovum itself.
Zona pellucida- It is middle, thick, transparent and non-cellular. It is partly secreted by follicular cells and partly by the oocyte.
Corona radiate- It is an outer thicker coat formed of radially elongated following cells.
Between vitelline membrane and zona pellucida there is a narrow perivitelline space having perivitelline fluid which facilitates rotation of the fertilized egg.
The vitelline membrane is a structure surrounding the outer surface of the plasma membrane of an ovum.
(b) Function of zona pellucida:-
Human oocytes consist of four types of zona pellucida: Glycoprotein ZP1, ZP2, ZP3, and ZP4.
Zona pellucida is responsible to allow species-specific fertilization, to prevent polyspermy and enables the acrosome reaction.
The glycoproteins of zona pellucida bind to capacitated spermatozoa and induce the acrosome reaction. Successful fertilization depends upon the ability of sperm to penetrate the extracellular matrix of the zona pellucida.
The zona pellucida, an extracellular matrix surrounding the female gamete, contains the primary and secondary sperm receptors and plays a vital role in sperm-egg interaction. Although millions of sperm are deposited in the female reproductive tract, fever more than 100 approaches the ovulated egg in the oviduct, and normally only. One successfully penetrates through the zona pellucida to fuse with plasma membrane of ovum. Immediately following fertilization, the plasma membrane and zona pellucida are modified to prevent polyspermy.
Note: An interesting fact about the ovum is that it is 20 times bigger than the sperm cell and is one of the largest cells in the human body. It is the reproductive cell in the female body and is produced in the ovary.
Complete answer:
a) Ovum refers to the secondary oocyte stage of oogenesis, where the second maturation division is yet to occur. In this condition the mature ovum is released from the ovary and enters into the uterus for fertilization. In humans, the female ovum is discharged from the graafian follicle with one polar body. Cytoplasm of egg is called ooplasm.

Human ovum is surrounded by a number of egg envelopes which are vitelline membrane (plasma membrane), zona pellucida and corona radiata.
Vitelline membrane is inner, then transparent and is secreted by the ovum itself.
Zona pellucida- It is middle, thick, transparent and non-cellular. It is partly secreted by follicular cells and partly by the oocyte.
Corona radiate- It is an outer thicker coat formed of radially elongated following cells.
Between vitelline membrane and zona pellucida there is a narrow perivitelline space having perivitelline fluid which facilitates rotation of the fertilized egg.
The vitelline membrane is a structure surrounding the outer surface of the plasma membrane of an ovum.
(b) Function of zona pellucida:-
Human oocytes consist of four types of zona pellucida: Glycoprotein ZP1, ZP2, ZP3, and ZP4.
Zona pellucida is responsible to allow species-specific fertilization, to prevent polyspermy and enables the acrosome reaction.
The glycoproteins of zona pellucida bind to capacitated spermatozoa and induce the acrosome reaction. Successful fertilization depends upon the ability of sperm to penetrate the extracellular matrix of the zona pellucida.
The zona pellucida, an extracellular matrix surrounding the female gamete, contains the primary and secondary sperm receptors and plays a vital role in sperm-egg interaction. Although millions of sperm are deposited in the female reproductive tract, fever more than 100 approaches the ovulated egg in the oviduct, and normally only. One successfully penetrates through the zona pellucida to fuse with plasma membrane of ovum. Immediately following fertilization, the plasma membrane and zona pellucida are modified to prevent polyspermy.
Note: An interesting fact about the ovum is that it is 20 times bigger than the sperm cell and is one of the largest cells in the human body. It is the reproductive cell in the female body and is produced in the ovary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




