
A geostationary satellite is orbiting around an arbitrary planet ‘P’ at a height of \[11R\] above the surface of ‘P’, R being the radius of ‘P’. The time period of another satellite in hours at a height of $2R$ from the surface of ‘P’ is _____. ‘P’ has a time period of rotation of $24$ hours.
(A) $\dfrac{6}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
(B) $3$
(C) $6\sqrt 2 $
(D) $5$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we will use Kepler's third law to find the relation between the time period for a geostationary satellite and the time period for given another satellite, and then, we will solve both equations to find the time period of another given satellite.
Formula used:
If T is the time period and R is the semi-major axis of an object circulating around any other celestial body such as a satellite revolving around planets is given by ${T^2} \propto {R^3}$ or $T \propto {R^{\dfrac {3}{2}}}$
Complete answer:
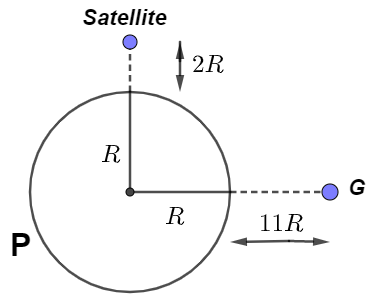
From the drawn diagram, we can see that G is the geostationary satellite orbiting around a planet P at a height of $11R$ which makes the semi-major axis of the satellite G is
$11R + R = 12R$
And let ‘T’ be the time period of a geostationary satellite which is $T = 24hrs$ so using Kepler's law formula ${T^2} \propto {R^3}$ we get,
${(24)^2} \propto {(12R)^3} \to (i)$
Now, for the given another satellite which is at a height of $2R$ which makes semi-major axis $2R + R = 3R$ and let ‘T’ be the time period of this satellite them again using Kepler's third law ${T^2} \propto {R^3}$ we get,
${T^2} \propto {(3R)^3} \to (ii)$
Divide equations (i) and (ii) by equating each other by removing the proportionality constant we get,
$
\dfrac{{{{(24)}^2}}}{{{{(T)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{{{(12R)}^3}}}{{{{(3R)}^3}}} \\
{(\dfrac{{24}}{T})^2} = {(4)^3} \\
T = \sqrt {\dfrac{{24 \times 24}}{{4 \times 4 \times 4}}} \\
T = 3hrs \\
$
So, the Time period of the given satellite is $3hrs$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $3$.
Note: It should be remembered that the other two laws of Kepler are such that planets revolve around the sun in an elliptical orbit having the sun as one of the foci and all planets cover the equal area in equal intervals of time while revolving around the sun.
Formula used:
If T is the time period and R is the semi-major axis of an object circulating around any other celestial body such as a satellite revolving around planets is given by ${T^2} \propto {R^3}$ or $T \propto {R^{\dfrac {3}{2}}}$
Complete answer:

From the drawn diagram, we can see that G is the geostationary satellite orbiting around a planet P at a height of $11R$ which makes the semi-major axis of the satellite G is
$11R + R = 12R$
And let ‘T’ be the time period of a geostationary satellite which is $T = 24hrs$ so using Kepler's law formula ${T^2} \propto {R^3}$ we get,
${(24)^2} \propto {(12R)^3} \to (i)$
Now, for the given another satellite which is at a height of $2R$ which makes semi-major axis $2R + R = 3R$ and let ‘T’ be the time period of this satellite them again using Kepler's third law ${T^2} \propto {R^3}$ we get,
${T^2} \propto {(3R)^3} \to (ii)$
Divide equations (i) and (ii) by equating each other by removing the proportionality constant we get,
$
\dfrac{{{{(24)}^2}}}{{{{(T)}^2}}} = \dfrac{{{{(12R)}^3}}}{{{{(3R)}^3}}} \\
{(\dfrac{{24}}{T})^2} = {(4)^3} \\
T = \sqrt {\dfrac{{24 \times 24}}{{4 \times 4 \times 4}}} \\
T = 3hrs \\
$
So, the Time period of the given satellite is $3hrs$
Hence, the correct option is (B) $3$.
Note: It should be remembered that the other two laws of Kepler are such that planets revolve around the sun in an elliptical orbit having the sun as one of the foci and all planets cover the equal area in equal intervals of time while revolving around the sun.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




