
a. Give chemical tests to distinguish between:
1. Propanal and propanone
2. Benzaldehyde and acetophenone
b. Arrange the following compounds in an increasing order of their property as indicated:
1. Acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert butyl ketone (reactivity towards \[{\text{HCN}}\])
2. Benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength)
3. ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$, ${{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH}}$ (acid strength)
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Propanal and benzaldehyde have aldehydic functional groups whereas propanone and acetophenone have methyl ketone groups. We have to identify the test used to test the presence of methyl ketones. The electron donating groups decrease the strength of the acid while the electron withdrawing groups increase the strength of the acid.
Complete step by step solution:
a. 1. Chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone:
Propanal has an aldehydic functional group and propanone is a methyl ketone.
The structures of propanal and propanone are as follows:
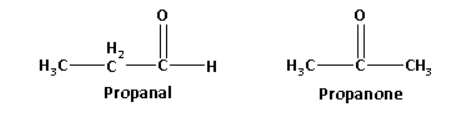
Propanone on reaction with sodium hypoiodite forms a yellow coloured precipitate of iodoform. The reaction of propanone with sodium hypoiodite is as follows:
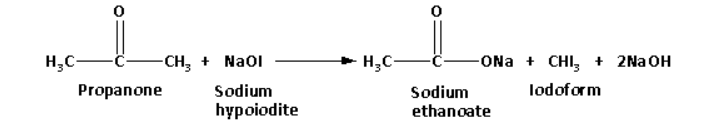
Propanol on reaction with sodium hypoiodite does not form a yellow coloured precipitate.
Thus, the reaction with sodium hypoiodite is the distinguishing test between propanal and propanone. This test is known as the iodoform test.
Thus, the chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone is the iodoform test.
2. Chemical test to distinguish between benzaldehyde and acetophenone:
Benzaldehyde has an aldehydic functional group and acetophenone is a methyl ketone.
The structures of benzaldehyde and acetophenone are as follows:
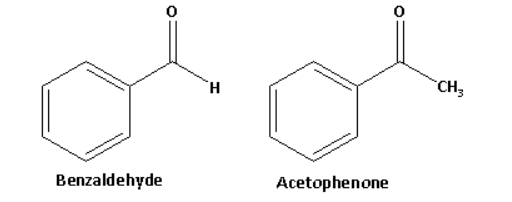
Acetophenone in reaction with sodium hypoiodite forms a yellow coloured precipitate of iodoform. The reaction of acetophenone with sodium hypoiodite is as follows:
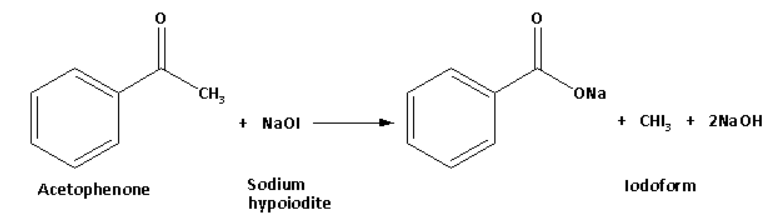
Benzaldehyde on reaction with sodium hypoiodite does not form a yellow coloured precipitate.
Thus, the reaction with sodium hypoiodite is the distinguishing test between benzaldehyde and acetophenone. This test is known as the iodoform test.
Thus, the chemical test to distinguish between benzaldehyde and acetophenone is the iodoform test.
b. 1. Arrange acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert butyl ketone in an increasing order of their reactivity towards \[{\text{HCN}}\]:
The structures of acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert butyl ketone are as follows:
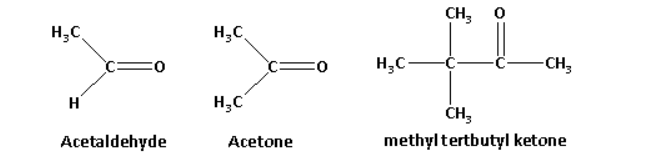
When \[{\text{HCN}}\] reacts with any compound, the nucleophile ${\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }$ is the attacking species.
The methyl group is an electron donating group. As the number of methyl substituents increases, the electron density around the carbonyl carbon increases.
The order of electron density is as follows:
Methyl tert butyl ketone > Acetone > Acetaldehyde
As the electron density around the carbonyl carbon increases, the reactivity of the compound to nucleophilic addition reaction decreases. This is because the carbonyl carbon has high negative charge and the attack of nucleophile which is negatively charged is not possible on the carbonyl carbon.
Thus, the increasing order of reactivity of acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert butyl ketone towards \[{\text{HCN}}\] is as follows:
Methyl tert butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde
2. Arrange benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid in an increasing order of their acid strength:
The structures of benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid are as follows:
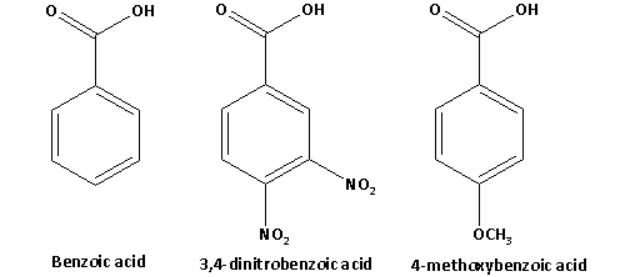
The acid strength is decreased by the electron donating groups. The methoxy group is an electron donating group.
The acid strength is increased by the electron withdrawing groups. The nitro group is an electron withdrawing group.
Thus, the acid strength of 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid is higher than that of benzoic acid and the acid strength of 4-methoxybenzoic acid is less than that of benzoic acid.
Thus, the increasing order of acid strength of benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid is as follows:
4-methoxybenzoic acid < benzoic acid < 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid
3. Arrange ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$, ${{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH}}$ in an increasing order of their acid strengths:
The acid strength is decreased by the electron donating groups. The $ - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$ group is an electron donating group.
The acid strength is increased by the electron withdrawing groups. The $ - {\text{Br}}$ group is an electron withdrawing group.
Thus, ${{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH}}$ has the lowest acid strength.
In ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$, the $ - {\text{Br}}$ group is near the acid functional group and in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$, the $ - {\text{Br}}$ is away from the acid functional group. As the distance increases, the acid strength decreases.
Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$ is a stronger acid than ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$.
Thus, the increasing order of acid strength is as follows:
${{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH}}$ < ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$ < ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$
Note:
The distance between the electron withdrawing group and the carbonyl carbon increases, the electron withdrawing effect decreases. Thus, the strength of the acid decreases.
Complete step by step solution:
a. 1. Chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone:
Propanal has an aldehydic functional group and propanone is a methyl ketone.
The structures of propanal and propanone are as follows:

Propanone on reaction with sodium hypoiodite forms a yellow coloured precipitate of iodoform. The reaction of propanone with sodium hypoiodite is as follows:

Propanol on reaction with sodium hypoiodite does not form a yellow coloured precipitate.
Thus, the reaction with sodium hypoiodite is the distinguishing test between propanal and propanone. This test is known as the iodoform test.
Thus, the chemical test to distinguish between propanal and propanone is the iodoform test.
2. Chemical test to distinguish between benzaldehyde and acetophenone:
Benzaldehyde has an aldehydic functional group and acetophenone is a methyl ketone.
The structures of benzaldehyde and acetophenone are as follows:

Acetophenone in reaction with sodium hypoiodite forms a yellow coloured precipitate of iodoform. The reaction of acetophenone with sodium hypoiodite is as follows:

Benzaldehyde on reaction with sodium hypoiodite does not form a yellow coloured precipitate.
Thus, the reaction with sodium hypoiodite is the distinguishing test between benzaldehyde and acetophenone. This test is known as the iodoform test.
Thus, the chemical test to distinguish between benzaldehyde and acetophenone is the iodoform test.
b. 1. Arrange acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert butyl ketone in an increasing order of their reactivity towards \[{\text{HCN}}\]:
The structures of acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert butyl ketone are as follows:

When \[{\text{HCN}}\] reacts with any compound, the nucleophile ${\text{C}}{{\text{N}}^ - }$ is the attacking species.
The methyl group is an electron donating group. As the number of methyl substituents increases, the electron density around the carbonyl carbon increases.
The order of electron density is as follows:
Methyl tert butyl ketone > Acetone > Acetaldehyde
As the electron density around the carbonyl carbon increases, the reactivity of the compound to nucleophilic addition reaction decreases. This is because the carbonyl carbon has high negative charge and the attack of nucleophile which is negatively charged is not possible on the carbonyl carbon.
Thus, the increasing order of reactivity of acetaldehyde, acetone, methyl tert butyl ketone towards \[{\text{HCN}}\] is as follows:
Methyl tert butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde
2. Arrange benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid in an increasing order of their acid strength:
The structures of benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid are as follows:

The acid strength is decreased by the electron donating groups. The methoxy group is an electron donating group.
The acid strength is increased by the electron withdrawing groups. The nitro group is an electron withdrawing group.
Thus, the acid strength of 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid is higher than that of benzoic acid and the acid strength of 4-methoxybenzoic acid is less than that of benzoic acid.
Thus, the increasing order of acid strength of benzoic acid, 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid is as follows:
4-methoxybenzoic acid < benzoic acid < 3,4-dinitrobenzoic acid
3. Arrange ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$, ${{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH}}$ in an increasing order of their acid strengths:
The acid strength is decreased by the electron donating groups. The $ - {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}$ group is an electron donating group.
The acid strength is increased by the electron withdrawing groups. The $ - {\text{Br}}$ group is an electron withdrawing group.
Thus, ${{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH}}$ has the lowest acid strength.
In ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$, the $ - {\text{Br}}$ group is near the acid functional group and in ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$, the $ - {\text{Br}}$ is away from the acid functional group. As the distance increases, the acid strength decreases.
Thus, ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$ is a stronger acid than ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$.
Thus, the increasing order of acid strength is as follows:
${{\text{(C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CHCOOH}}$ < ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{COOH}}$ < ${\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CH(Br)COOH}}$
Note:
The distance between the electron withdrawing group and the carbonyl carbon increases, the electron withdrawing effect decreases. Thus, the strength of the acid decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




