
A glass slab made of a material of refractive index ${n_1}$ is kept in a medium of refractive index ${n_2}$. A light ray is incident on the slab. Draw the path of the rays emerging from the glass slab, if
A) ${n_1} > {n_2}$
B) ${n_1} = {n_2}$
C) ${n_1} < {n_2}$
Answer
568.2k+ views
Hint: Whenever light falls on any surface, there are three ways in which the ray of light interacts with the surface. The light can be either reflected back into the medium, transmitted through the medium or absorbed by the surface. When the light gets transmitted, it undergoes refraction.
Complete step by step answer:
Refraction is defined as the phenomenon in which a ray of light travelling from one medium to another medium with different optical densities undergo a change in the direction.
The phenomenon is governed by a law known as the Snell’s law of refraction, which states that –
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is always constant and it is termed as refractive index of the pair of media.
If $i$ is the angle of incidence and $r$ is the angle of refraction when the light enters from medium 1 to medium 2, as per Snell’s law of refraction, the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is given by –
${n_{12}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Consider a slab of refractive index ${n_1}$ in another medium of refractive index ${n_2}$ and a ray of light is incident on the slab.
Let us understand the ray formation in each of the following cases:
A) ${n_1} > {n_2}$
Here, the slab has higher optical density than the medium and the refractive index of the slab is higher than that of the refractive index of the medium.
In this case, the light is travelling from a rarer medium to the denser medium.
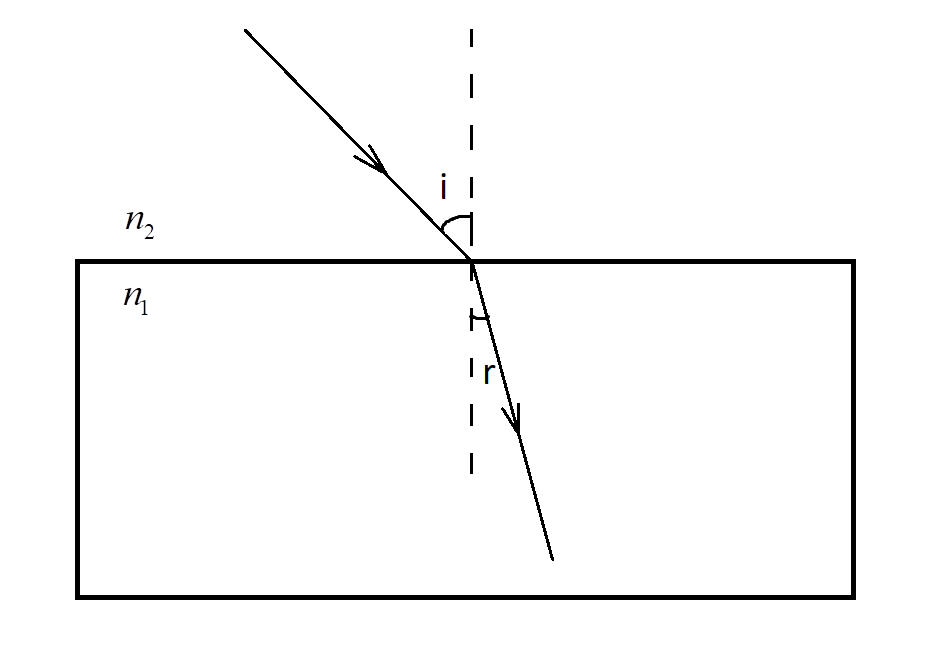
The refracted ray bends towards the normal.
B) ${n_1} = {n_2}$
Here, the slab and the surrounding medium have the same optical density.
In this case, the light is travelling across the same medium.
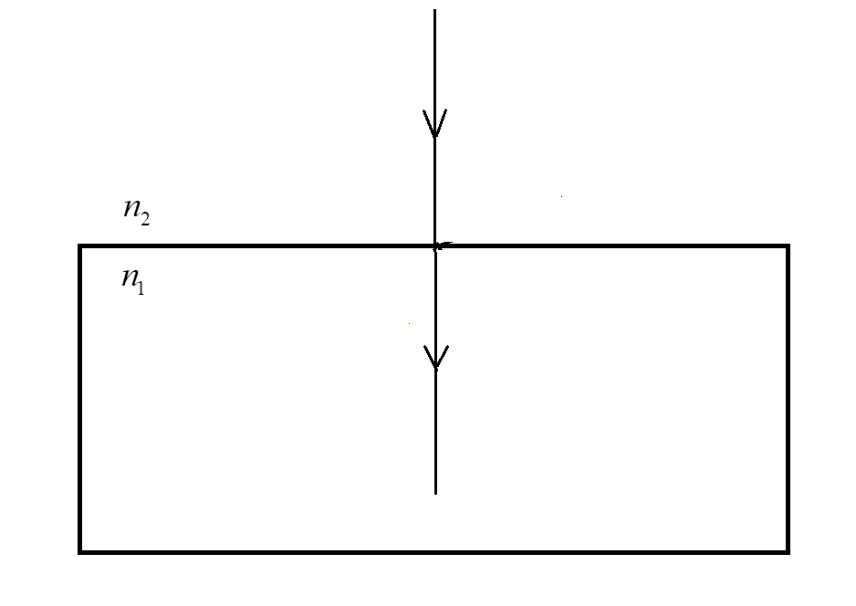
There is no refraction of the light since there is no change across optical density of the pair of the media.
C) ${n_1} < {n_2}$
Here, the slab has lower optical density than the medium and the refractive index of the slab is lesser than that of the refractive index of the medium.
In this case, the light is travelling from a denser medium to the rarer medium.
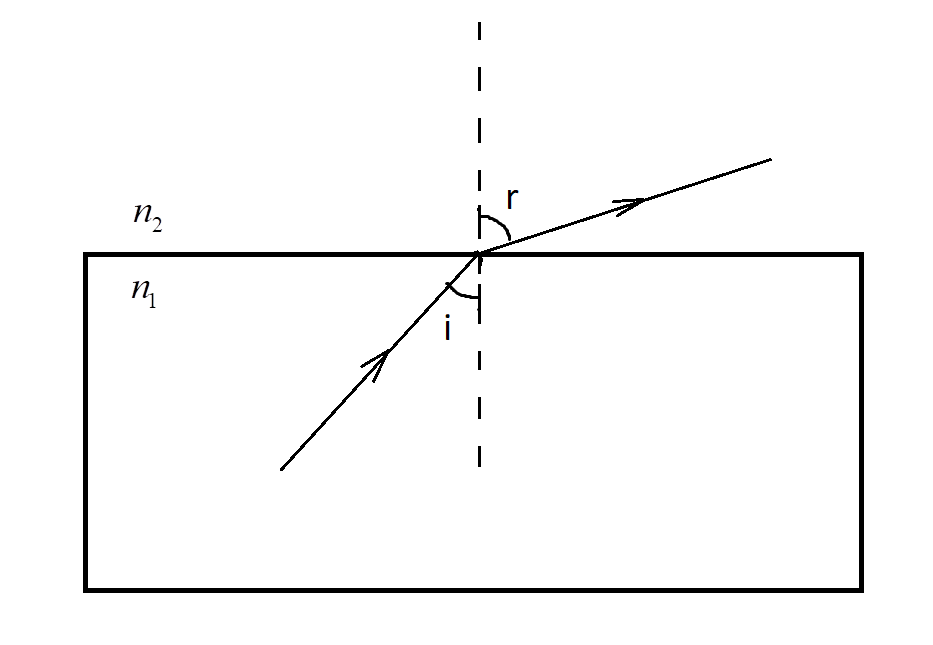
The refracted ray bends away from the normal.
Note: The refractive index of air is 1. Thus, the refractive index of any material such as water or glass or glycerine etc. with respect to air is called the absolute refractive index of the material and it is a property of the material.
Complete step by step answer:
Refraction is defined as the phenomenon in which a ray of light travelling from one medium to another medium with different optical densities undergo a change in the direction.
The phenomenon is governed by a law known as the Snell’s law of refraction, which states that –
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is always constant and it is termed as refractive index of the pair of media.
If $i$ is the angle of incidence and $r$ is the angle of refraction when the light enters from medium 1 to medium 2, as per Snell’s law of refraction, the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is given by –
${n_{12}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}} = \dfrac{{\sin i}}{{\sin r}}$
Consider a slab of refractive index ${n_1}$ in another medium of refractive index ${n_2}$ and a ray of light is incident on the slab.
Let us understand the ray formation in each of the following cases:
A) ${n_1} > {n_2}$
Here, the slab has higher optical density than the medium and the refractive index of the slab is higher than that of the refractive index of the medium.
In this case, the light is travelling from a rarer medium to the denser medium.

The refracted ray bends towards the normal.
B) ${n_1} = {n_2}$
Here, the slab and the surrounding medium have the same optical density.
In this case, the light is travelling across the same medium.

There is no refraction of the light since there is no change across optical density of the pair of the media.
C) ${n_1} < {n_2}$
Here, the slab has lower optical density than the medium and the refractive index of the slab is lesser than that of the refractive index of the medium.
In this case, the light is travelling from a denser medium to the rarer medium.

The refracted ray bends away from the normal.
Note: The refractive index of air is 1. Thus, the refractive index of any material such as water or glass or glycerine etc. with respect to air is called the absolute refractive index of the material and it is a property of the material.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




