
A hemispherical glass body of radius $10\text{ cm}$ and refractive index $1.5$ is silvered on its curved surface. A small air bubble is $6\text{ cm}$ below the flat surface inside it along the axis. The position of the image of the air bubble made by the mirror is seen:
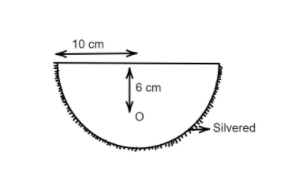
A. $14\text{ cm}$ below flat surface
B. $20\text{ cm}$ below flat surface
C. $16\text{ cm}$ below flat surface
D. $30\text{ cm}$ below flat surface

Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: To solve this question, we will use the mirror formula that gives a relation between the focal length of the mirror, the distance of the object from the pole of the mirror and the distance of the image from the pole of the mirror. Also, we need to use the formula for apparent depth to find out the position of the image of the air bubble.
Complete step by step answer:
The mirror formula is as follows:
\[\dfrac{1}{F}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Here, $F$ is the focal length of the mirror used,
$v$ is the distance of the image from the optical center of the mirror,
$u$ is the distance of the object from the optical center of the mirror.
Now, let us consider the given question, it is given in the question that the radius of the hemispherical glass body is $10\text{ cm}$ hence its focal length will be:
$\begin{align}
& F=-\dfrac{10}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow F=-5\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}$
The distance of the object from the optical center of the glass body will be:
$\begin{align}
& u=-\left( 10-6 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow u=-4\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{-5}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{-4} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{-5}+\dfrac{1}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-4+5}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow v=20\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we will use the formula of apparent depth:
${{H}_{a}}={{H}_{r}}\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{{{\mu }_{2}}}$
Here ${{H}_{a}}$ is the apparent depth, ${{H}_{r}}$ is the real depth, ${{\mu }_{1}}$ is the refractive index of air and ${{\mu }_{2}}$ is the refractive index of the medium.
Substituting the values, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{a}}=30\times \dfrac{1}{1.5} \\
& \Rightarrow {{H}_{a}}=20\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The mirror formula should be used very carefully, keeping in mind the correct sign conventions. Distances are positive if they are measured along the direction of the incident ray. If the incident ray is travelling in the opposite direction, then the distance should be negative.
Complete step by step answer:
The mirror formula is as follows:
\[\dfrac{1}{F}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{u}\]
Here, $F$ is the focal length of the mirror used,
$v$ is the distance of the image from the optical center of the mirror,
$u$ is the distance of the object from the optical center of the mirror.
Now, let us consider the given question, it is given in the question that the radius of the hemispherical glass body is $10\text{ cm}$ hence its focal length will be:
$\begin{align}
& F=-\dfrac{10}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow F=-5\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}$
The distance of the object from the optical center of the glass body will be:
$\begin{align}
& u=-\left( 10-6 \right) \\
& \Rightarrow u=-4\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the values, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{-5}=\dfrac{1}{v}+\dfrac{1}{-4} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{-5}+\dfrac{1}{4} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{-4+5}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v}=\dfrac{1}{20} \\
& \Rightarrow v=20\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we will use the formula of apparent depth:
${{H}_{a}}={{H}_{r}}\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{{{\mu }_{2}}}$
Here ${{H}_{a}}$ is the apparent depth, ${{H}_{r}}$ is the real depth, ${{\mu }_{1}}$ is the refractive index of air and ${{\mu }_{2}}$ is the refractive index of the medium.
Substituting the values, we get:
\[\begin{align}
& {{H}_{a}}=30\times \dfrac{1}{1.5} \\
& \Rightarrow {{H}_{a}}=20\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The mirror formula should be used very carefully, keeping in mind the correct sign conventions. Distances are positive if they are measured along the direction of the incident ray. If the incident ray is travelling in the opposite direction, then the distance should be negative.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




