
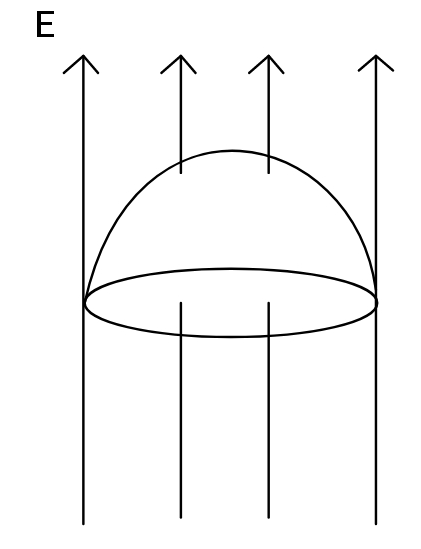
A hemispherical surface of radius R is located in uniform electric field E, as shown. The flux of electric field through the surface is
A. $E \pi R^2$
B. $E 2 \pi R^2$
C. $E 4 \pi R^2$
D. Zero

Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: There are two surfaces involved for the given hemisphere. One surface is the bottom that is a circle of radius R and another is the surface of the hemisphere of the same radius. Use the definition of electric flux to find out the flux through the hemispherical surface.
Formula used:
The flux of electric field through a surface perpendicular to the electric field lines and of area A is:
$\phi = E A$
Complete step by step answer:
To be clear, we are given a hemispherical surface and we need to find the flux through this surface.
The flux of electric field depends on three parameters:
1. Magnitude of electric field, E.
2. Area of the surface, A.
3. Angles that surface normally make an electric field direction.
In our case the third point is a significant one.
By definition, the total number of electric field lines passing normally through a surface (in an electric field) is called electric flux linked with that surface.
In our case, the field lines passing through hemispherical surface are same as the field lines passing through the bottom of the hemisphere i.e., through the circle of radius R. If we see the boundary of this hemisphere, we will note that the boundary is same for the circle and the hemisphere.
The flux passing through the circle is:
$\phi = E (\pi R^2)$
This is also the flux passing through the hemisphere. As what enters through the bottom is only leaving from the top.
Therefore the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
We do not opt for Gauss law to solve this problem as Gauss law applies to closed surfaces only and we are dealing with an open surface. But if we consider the hemisphere to be closed from the bottom we will notice that as there is no charge inside, the flux entering in will be the flux going out so we had to just find flux entering in. If this hemisphere was a conductor then we would have seen no field lines on the other side but this surface is just an imaginary surface in the field, so do not choose zero as the value of flux.
Formula used:
The flux of electric field through a surface perpendicular to the electric field lines and of area A is:
$\phi = E A$
Complete step by step answer:
To be clear, we are given a hemispherical surface and we need to find the flux through this surface.
The flux of electric field depends on three parameters:
1. Magnitude of electric field, E.
2. Area of the surface, A.
3. Angles that surface normally make an electric field direction.
In our case the third point is a significant one.
By definition, the total number of electric field lines passing normally through a surface (in an electric field) is called electric flux linked with that surface.
In our case, the field lines passing through hemispherical surface are same as the field lines passing through the bottom of the hemisphere i.e., through the circle of radius R. If we see the boundary of this hemisphere, we will note that the boundary is same for the circle and the hemisphere.
The flux passing through the circle is:
$\phi = E (\pi R^2)$
This is also the flux passing through the hemisphere. As what enters through the bottom is only leaving from the top.
Therefore the correct answer is option (A).
Note:
We do not opt for Gauss law to solve this problem as Gauss law applies to closed surfaces only and we are dealing with an open surface. But if we consider the hemisphere to be closed from the bottom we will notice that as there is no charge inside, the flux entering in will be the flux going out so we had to just find flux entering in. If this hemisphere was a conductor then we would have seen no field lines on the other side but this surface is just an imaginary surface in the field, so do not choose zero as the value of flux.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




