
A homozygous tall pea plant with purple flowers was crossed with a short plant with white flowers and F2 generation was raised. What will be the proportion of tall plants and short plants in F2 generation? Explain.
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: Gregor Mendel used pea plants for understanding inheritance. He selected pea plants because they were easy to produce, could be easily bred, and had many observable features, such as the colour of petals and the colour of peas.
Complete answer:
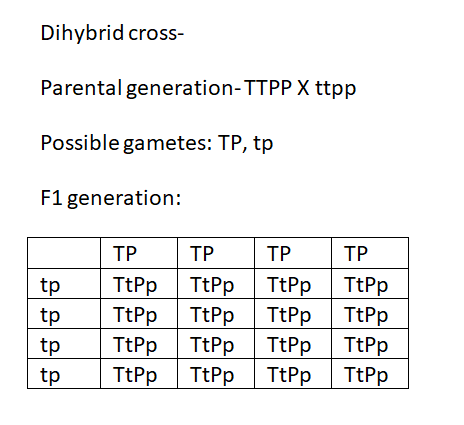
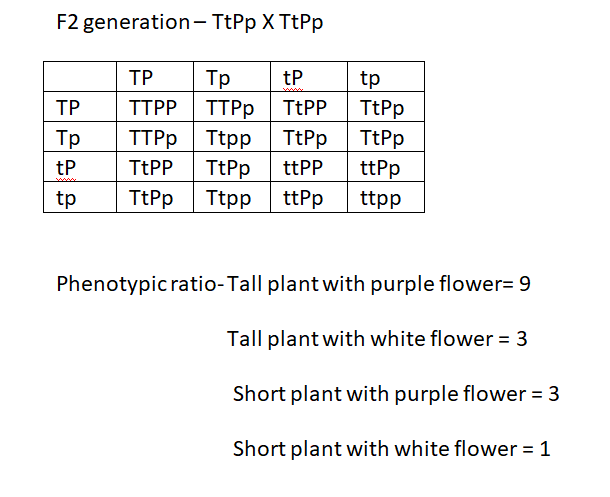
We can follow the dihybrid cross to understand this question.
There would be a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1.
The tall phenotype is dominant and will also be displayed in the heterozygous state.
Pea plants were important for Gregor Mendel in helping him to consider the means by which characteristics are inherited between parent and offspring. He selected pea plants because they were easy to produce, could be easily bred, and had many observable features, such as the colour of petals and the colour of peas.
Note: His methodical hypothesis checking and careful application of statistical models to the study of biological inheritance is more durable than the pea data introduced by Mendel in 1862. Mendel developed mathematical hypotheses about trait inheritance from his first experiments with monohybrid crosses that he could verify with more complicated experiments on dihybrid and even trihybrid crosses. One of the most important contributions Mendel made to biology is this method of establishing statistical assumptions regarding inheritance data.
Complete answer:
We can follow the dihybrid cross to understand this question.
There would be a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1.
The tall phenotype is dominant and will also be displayed in the heterozygous state.


Pea plants were important for Gregor Mendel in helping him to consider the means by which characteristics are inherited between parent and offspring. He selected pea plants because they were easy to produce, could be easily bred, and had many observable features, such as the colour of petals and the colour of peas.
Note: His methodical hypothesis checking and careful application of statistical models to the study of biological inheritance is more durable than the pea data introduced by Mendel in 1862. Mendel developed mathematical hypotheses about trait inheritance from his first experiments with monohybrid crosses that he could verify with more complicated experiments on dihybrid and even trihybrid crosses. One of the most important contributions Mendel made to biology is this method of establishing statistical assumptions regarding inheritance data.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




