
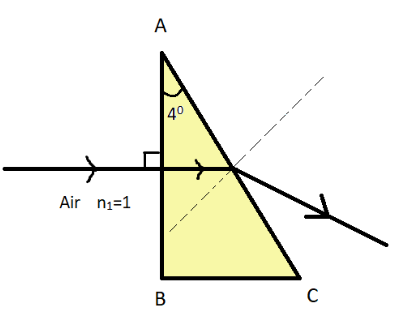
A horizontal ray is incident on a right angled prism with a prism angle of ${4^ \circ }$. If the refractive index of the prism is $1.5$, then the angle of emergence is? Use the given figure.
A. ${4^ \circ }$
B. ${6^ \circ }$
C. ${10^ \circ }$
D. ${0^ \circ }$

Answer
510.3k+ views
Hint: Since the light is incident on a glass prism the light refracts or produces a deviation due to the difference in the medium it is travelling in. The glass medium is optically denser than air medium and hence the deviation is observed. The two equations of angle of deviation are equated and the given values are substituted in-order to find the angle of emergence.
Formula used:
The formula for the angle of deviation for a prism is given by:
$\delta = i + e - A$
The formula which relates the angle of deviation with the refractive index is given by:
$\delta = (\mu - 1)A$
where, $\delta $ is the angle of deviation, $i$ is the angle of incidence, $A$ is the angle of the prism, $e$ is the angle of emergence and $\mu $ is the refractive index.
Complete step by step answer:
We start by extracting all the given data from the question.
The angle of the prism, $A$ is given to be: ${4^ \circ }$
The refractive index, $\mu $ of the glass prism is given to be: $1.5$
When a ray of light falls on the prism a deviation is observed due to a difference in the medium travelled by the incident light and this angle by which it deviates is known as the angle of deviation. Hence it is imperative to calculate this angle of deviation of light.
The angle of deviation is hence said to be the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray. It depends on the angle of the prism, the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence. We now construct the equation for the angle of deviation for the incident light on the surface of the prism. The equation is as follows:
$\delta = i + e - A$ ----($1$)
Next we construct the equation for the angle of deviation in terms of the refractive index. The value of the angle of the prism given in the question is comparatively very small and for a small angled prism, the angle of deviation is given by the below equation:
$\delta = (\mu - 1)A$ ----($2$)
Since the equations ($1$) and ($2$) are identical they are equated.
$ \Rightarrow i + e - A = (\mu - 1)A$
The equation is further expanded:
$ \Rightarrow i + e - A = \mu A - A$
The common terms on both sides of the equation are cancelled out to get:
$ \Rightarrow i + e = \mu A$
The terms of the above equation are rearranged and solved out to find the equation for angle of emergence $e$.
$ \Rightarrow e = \mu A - i$ ----($3$)
The values of $\mu $ and $A$ are already known but the value of angle of incidence needs to be found out. The angle of incidence is said to be the angle between the normal and the incident ray. By keeping this concept as a base the angle of incidence is calculated from the diagram given in the question which will be ${0^ \circ }$ because the incident ray coincides with the normal.
$i = {0^0}$
The next step is to substitute the values that are already given into equation ($3$) to get the value of $e$.
$e = (1.5 \times 4) - 0$
$ \therefore e = {6^ \circ }$
The angle of emergence of the ray of light incident on the glass prism is $e = {6^ \circ }$.
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Additional information: A ray of light suffering refraction through a prism is bent towards the base of the prism. The deviation produced by a prism is maximum when the angle of incidence is ${90^ \circ }$. When a ray of light is refracted through a prism, the sum of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence is equal to the sum of the angle of the prism and the angle of deviation. The factors on which the angle of deviation depends on is the material of the prism, angle of incidence, the wavelength of light used and the angle of the prism.
Note:The common misconception is that the angle of incidence is assumed to be ${90^ \circ }$ when it is actually ${0^ \circ }$ if the diagram is observed closely. The angle is supposed to be calculated from the normal, that is the angle deviated from the normal is said to be the angle of the incident light on the prism.
Formula used:
The formula for the angle of deviation for a prism is given by:
$\delta = i + e - A$
The formula which relates the angle of deviation with the refractive index is given by:
$\delta = (\mu - 1)A$
where, $\delta $ is the angle of deviation, $i$ is the angle of incidence, $A$ is the angle of the prism, $e$ is the angle of emergence and $\mu $ is the refractive index.
Complete step by step answer:
We start by extracting all the given data from the question.
The angle of the prism, $A$ is given to be: ${4^ \circ }$
The refractive index, $\mu $ of the glass prism is given to be: $1.5$
When a ray of light falls on the prism a deviation is observed due to a difference in the medium travelled by the incident light and this angle by which it deviates is known as the angle of deviation. Hence it is imperative to calculate this angle of deviation of light.
The angle of deviation is hence said to be the angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray. It depends on the angle of the prism, the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence. We now construct the equation for the angle of deviation for the incident light on the surface of the prism. The equation is as follows:
$\delta = i + e - A$ ----($1$)
Next we construct the equation for the angle of deviation in terms of the refractive index. The value of the angle of the prism given in the question is comparatively very small and for a small angled prism, the angle of deviation is given by the below equation:
$\delta = (\mu - 1)A$ ----($2$)
Since the equations ($1$) and ($2$) are identical they are equated.
$ \Rightarrow i + e - A = (\mu - 1)A$
The equation is further expanded:
$ \Rightarrow i + e - A = \mu A - A$
The common terms on both sides of the equation are cancelled out to get:
$ \Rightarrow i + e = \mu A$
The terms of the above equation are rearranged and solved out to find the equation for angle of emergence $e$.
$ \Rightarrow e = \mu A - i$ ----($3$)
The values of $\mu $ and $A$ are already known but the value of angle of incidence needs to be found out. The angle of incidence is said to be the angle between the normal and the incident ray. By keeping this concept as a base the angle of incidence is calculated from the diagram given in the question which will be ${0^ \circ }$ because the incident ray coincides with the normal.
$i = {0^0}$
The next step is to substitute the values that are already given into equation ($3$) to get the value of $e$.
$e = (1.5 \times 4) - 0$
$ \therefore e = {6^ \circ }$
The angle of emergence of the ray of light incident on the glass prism is $e = {6^ \circ }$.
Hence the correct answer is option B.
Additional information: A ray of light suffering refraction through a prism is bent towards the base of the prism. The deviation produced by a prism is maximum when the angle of incidence is ${90^ \circ }$. When a ray of light is refracted through a prism, the sum of the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence is equal to the sum of the angle of the prism and the angle of deviation. The factors on which the angle of deviation depends on is the material of the prism, angle of incidence, the wavelength of light used and the angle of the prism.
Note:The common misconception is that the angle of incidence is assumed to be ${90^ \circ }$ when it is actually ${0^ \circ }$ if the diagram is observed closely. The angle is supposed to be calculated from the normal, that is the angle deviated from the normal is said to be the angle of the incident light on the prism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




