
(a) How can you bend light away from the normal?
(b) How must light travel out of a substance if it is not going to be refracted?
Answer
514.8k+ views
Hint: Light, often known as visible light, is electromagnetic radiation that falls within the region of the electromagnetic spectrum that the human eye can see. Between the infrared and ultraviolet, visible light is characterised as having wavelengths in the 400–700 nm range.
Complete step by step answer:
When light or other waves flow through a boundary between two distinct isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air, Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law or the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction.
According to Snell's law, the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or the reciprocal of the indices of refraction:
$\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _2}}}{{\sin {\theta _1}}} = \dfrac{{{v_2}}}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}}$
with each $\theta $equaling the angle measured from the boundary's normal, v equaling the velocity of light in the respective media (SI units are metres per second, or m/s), and n equaling the refractive index (which is unitless) of the respective medium.
We can deviate from the usual by allowing light to pass through a denser medium and into a rarer media.
(a) The refractive index of the two mediums determines the angle of refraction or the degree of bending of light.
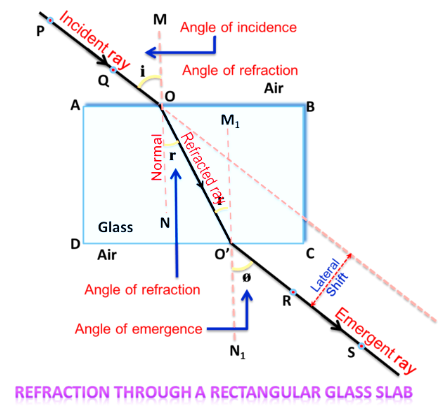
-Light slows down and bends towards the normal when it goes through a low refractive index medium like air (faster medium or optically rarer media) to a high refractive index medium like glass (slower medium or optically denser medium).
-Light travels faster and bends away from the normal as it passes from a material with a high refractive index, such as glass (slower medium or optically denser medium), to a medium with a low refractive index, such as air (faster medium or optically rarer media).
(b) If incident light is not refracted, it must leave a material at a straight angle ($90^{\circ}$).The light beam will not bend if it strikes the glass block at a right angle ($90^{\circ}$, i.e. perpendicular to the glass block) to the surface.
Note: The rule is used in ray tracing to calculate angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to determine a material's refractive index. Metamaterials, which enable light to be bent "backward" at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index, also satisfy the rule.
Complete step by step answer:
When light or other waves flow through a boundary between two distinct isotropic media, such as water, glass, or air, Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law or the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction.
According to Snell's law, the ratio of the sines of the angles of incidence and refraction is equal to the ratio of phase velocities in the two media, or the reciprocal of the indices of refraction:
$\dfrac{{\sin {\theta _2}}}{{\sin {\theta _1}}} = \dfrac{{{v_2}}}{{{v_1}}} = \dfrac{{{n_1}}}{{{n_2}}}$
with each $\theta $equaling the angle measured from the boundary's normal, v equaling the velocity of light in the respective media (SI units are metres per second, or m/s), and n equaling the refractive index (which is unitless) of the respective medium.
We can deviate from the usual by allowing light to pass through a denser medium and into a rarer media.
(a) The refractive index of the two mediums determines the angle of refraction or the degree of bending of light.

-Light slows down and bends towards the normal when it goes through a low refractive index medium like air (faster medium or optically rarer media) to a high refractive index medium like glass (slower medium or optically denser medium).
-Light travels faster and bends away from the normal as it passes from a material with a high refractive index, such as glass (slower medium or optically denser medium), to a medium with a low refractive index, such as air (faster medium or optically rarer media).
(b) If incident light is not refracted, it must leave a material at a straight angle ($90^{\circ}$).The light beam will not bend if it strikes the glass block at a right angle ($90^{\circ}$, i.e. perpendicular to the glass block) to the surface.
Note: The rule is used in ray tracing to calculate angles of incidence or refraction, and in experimental optics to determine a material's refractive index. Metamaterials, which enable light to be bent "backward" at a negative angle of refraction with a negative refractive index, also satisfy the rule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




