
(a) How do primary, secondary and tertiary amines react with nitrous acid?
(b) Elucidate the structure of glucose.
Answer
523.4k+ views
Hint: All the primary, secondary and tertiary amines react with the nitrous and the difference is only in their formation of the end products and if you know the reactions properly, you can easily write their reactions. The glucose is an aldose monosaccharide which consists of the six carbon atoms, an aldehydic group and hydroxyl groups. Now answer the given statements accordingly.
Complete answer:
First of all, let’s discuss the amines. Amines are the organic compounds which consist of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ as the functional group in their compounds.
When the nitrogen atom of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group consists of one alkyl group, then it is called as the primary amine.
When the nitrogen atom of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group consists of two alkyl groups, then it is called as the secondary amine.
When the nitrogen atom of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group consists of three alkyl groups, then it is called as the tertiary amine.
Now considering the statement;
All the primary, secondary and tertiary amines react with the nitrous acid and forms different products as;
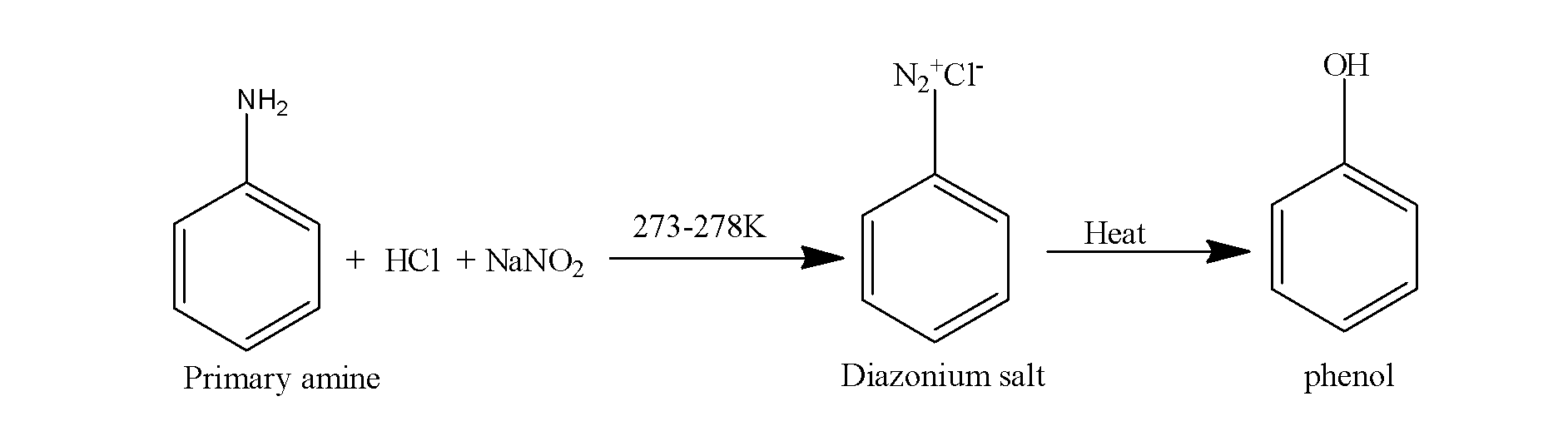
When primary amine is made to react with the nitrous acid, it results in the formation of diazonium salt which when heated, it results in the formation of the phenols.
The reaction is supposed to occur as;
When secondary amine is made to react with the nitrous acid, it results in the formation of nitrosamines which are yellow in color and oily in nature.
The reaction is supposed to occur as;
$\begin{align}
& {{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH+HONO\to {{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}N-N=O+{{H}_{2}}O \\
& \text{secondary Nitrosoamine} \\
& \text{ amine (yellow oily)} \\
\end{align}$
When tertiary amine is made to react with the nitrous acid, it results in the formation of a salt which on warming decomposes to give nitrosamines and alcohol.
The general reaction is supposed to occur as;
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{3}}NH+HONO\to {{R}_{3}}NHN{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{warm}{{R}_{2}}N-N=O+ROH \\
& \text{tertiary salt Nitrosoamine} \\
& \text{ amine } \\
\end{align}$
Now coming to the next part of the statement;
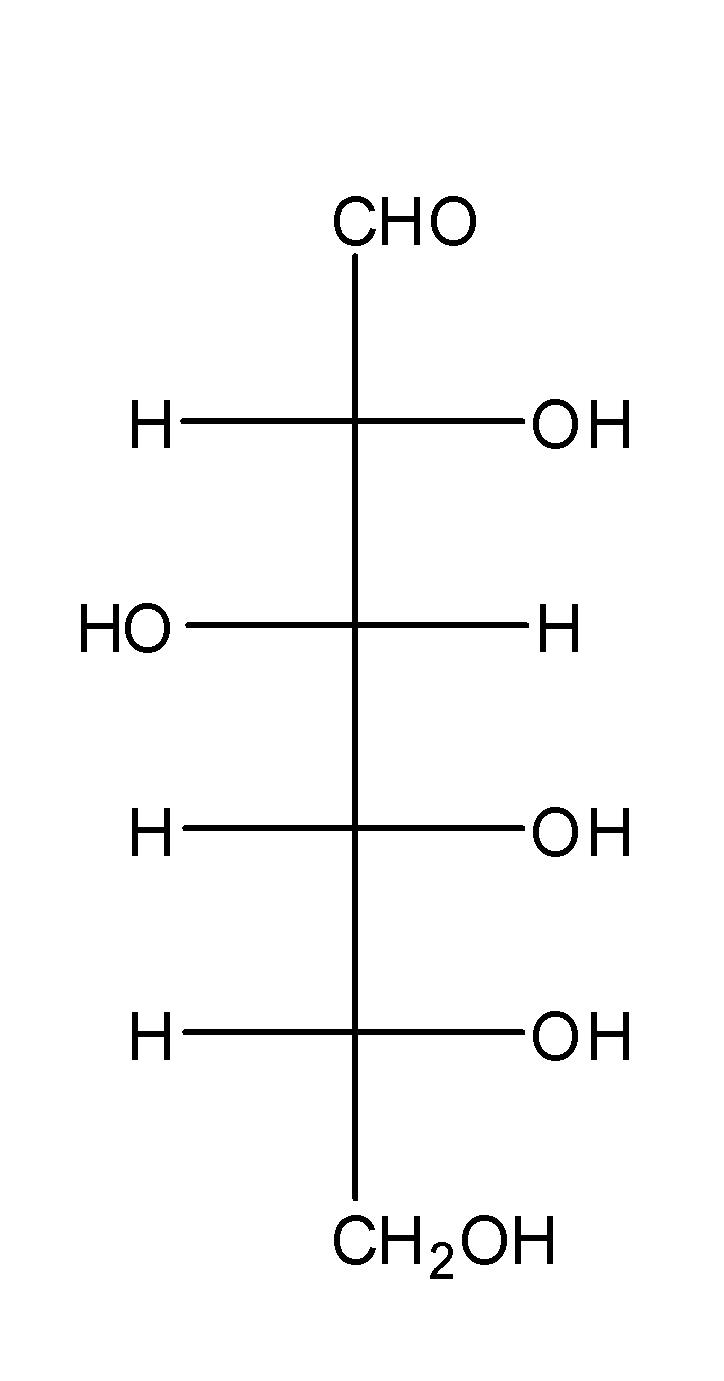
Glucose is a monosaccharide carbohydrate which consists of the six carbon atoms which are linked together to each other in a chain.
It consists of the aldehyde group at the first carbon and five hydroxyl groups are attached to the five carbon atoms.
The structure of glucose is as;
Note:
The reaction of the amines with the nitrous acid is used to distinguish between the primary , secondary and tertiary amines.
When yellow oily nitrosamine produced during the reaction of the secondary amine with nitrous acid; is made to react with the phenol and sulphuric acid, it gives green colour solution and when this green is diluted with water , its color changes to red and then to greenish blue to violet. This overall reaction is known as Libermann’s nitroso reaction.
Complete answer:
First of all, let’s discuss the amines. Amines are the organic compounds which consist of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ as the functional group in their compounds.
When the nitrogen atom of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group consists of one alkyl group, then it is called as the primary amine.
When the nitrogen atom of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group consists of two alkyl groups, then it is called as the secondary amine.
When the nitrogen atom of the $-N{{H}_{2}}$ group consists of three alkyl groups, then it is called as the tertiary amine.
Now considering the statement;
All the primary, secondary and tertiary amines react with the nitrous acid and forms different products as;
When primary amine is made to react with the nitrous acid, it results in the formation of diazonium salt which when heated, it results in the formation of the phenols.
The reaction is supposed to occur as;

When secondary amine is made to react with the nitrous acid, it results in the formation of nitrosamines which are yellow in color and oily in nature.
The reaction is supposed to occur as;
$\begin{align}
& {{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}NH+HONO\to {{({{C}_{2}}{{H}_{5}})}_{2}}N-N=O+{{H}_{2}}O \\
& \text{secondary Nitrosoamine} \\
& \text{ amine (yellow oily)} \\
\end{align}$
When tertiary amine is made to react with the nitrous acid, it results in the formation of a salt which on warming decomposes to give nitrosamines and alcohol.
The general reaction is supposed to occur as;
$\begin{align}
& {{R}_{3}}NH+HONO\to {{R}_{3}}NHN{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow{warm}{{R}_{2}}N-N=O+ROH \\
& \text{tertiary salt Nitrosoamine} \\
& \text{ amine } \\
\end{align}$
Now coming to the next part of the statement;
Glucose is a monosaccharide carbohydrate which consists of the six carbon atoms which are linked together to each other in a chain.
It consists of the aldehyde group at the first carbon and five hydroxyl groups are attached to the five carbon atoms.
The structure of glucose is as;

Note:
The reaction of the amines with the nitrous acid is used to distinguish between the primary , secondary and tertiary amines.
When yellow oily nitrosamine produced during the reaction of the secondary amine with nitrous acid; is made to react with the phenol and sulphuric acid, it gives green colour solution and when this green is diluted with water , its color changes to red and then to greenish blue to violet. This overall reaction is known as Libermann’s nitroso reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




