
(a) How does carboxylate ion get stabilised by resonance? Explain the structure.
(b) Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols. Explain.
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: Resonance is the phenomenon in which the bonding in a complex is determined by several structures known as resonance structures into a resonance hybrid in the valence bond theory. The actual bond lies in between these structures, usually the delocalisation of the electrons is described by this process.
Complete step by step answer:
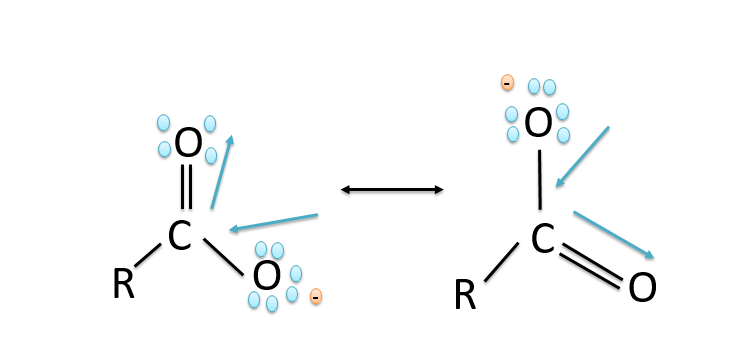
a).The stability of the carboxylate ions is due to the stabilization of the carboxylate ion due to the resonance. The negative charge in the carboxylate ion is delocalised on both the oxygen atoms by the two equivalent structures and thus the charge gets delocalised and the delocalisation of the charges leads to stability. The resonance in the carboxylate ion is shown below:
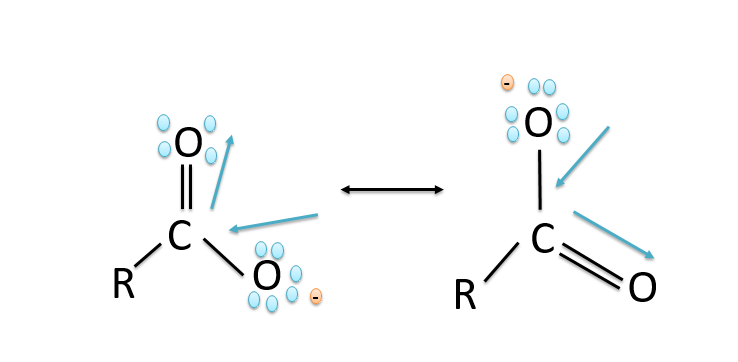
b)Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols because in phenols the negative charge is delocalized less effectively over one oxygen atom and carbon atoms in phenoxide ion less electronegative while in the carboxylic acids the carboxylate ion exhibits higher stability in comparison to phenoxide ion due to which the phenols are less acidic since they rarely give the hydronium ion during the chemical reactions. While the stability of the carboxylate ion accounts for the acidity of carboxylic acids. The resonance structures in phenoxide ions are non-equivalent whereas in carboxylate ions the structures are equivalent in nature. The resonance in the carboxylate ion is shown below:
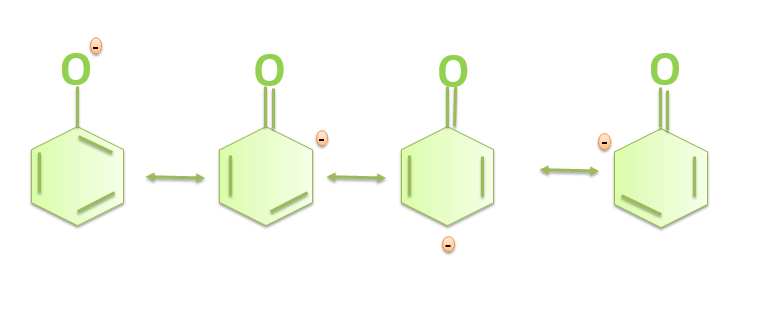
The resonance in the phenoxide ion is shown below:
Note:
The stability of the molecule depends on the delocalisation of the electrons in the molecule, which in turn is dependent on the resonating structures of the molecule. The delocalisation of the molecule allows for the lowering in the overall energy of the molecule, thus more the resonating structures of the molecule more will be the stability of the molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
a).The stability of the carboxylate ions is due to the stabilization of the carboxylate ion due to the resonance. The negative charge in the carboxylate ion is delocalised on both the oxygen atoms by the two equivalent structures and thus the charge gets delocalised and the delocalisation of the charges leads to stability. The resonance in the carboxylate ion is shown below:

b)Carboxylic acids are more acidic than phenols because in phenols the negative charge is delocalized less effectively over one oxygen atom and carbon atoms in phenoxide ion less electronegative while in the carboxylic acids the carboxylate ion exhibits higher stability in comparison to phenoxide ion due to which the phenols are less acidic since they rarely give the hydronium ion during the chemical reactions. While the stability of the carboxylate ion accounts for the acidity of carboxylic acids. The resonance structures in phenoxide ions are non-equivalent whereas in carboxylate ions the structures are equivalent in nature. The resonance in the carboxylate ion is shown below:

The resonance in the phenoxide ion is shown below:

Note:
The stability of the molecule depends on the delocalisation of the electrons in the molecule, which in turn is dependent on the resonating structures of the molecule. The delocalisation of the molecule allows for the lowering in the overall energy of the molecule, thus more the resonating structures of the molecule more will be the stability of the molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




