
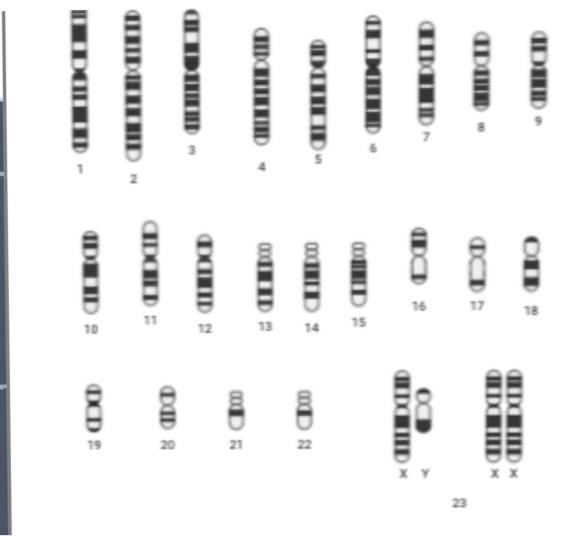
a) Identify the syndrome from the diagram and write it’s genotype.
b) It occurs in both sexes (males and females)? Write the reasons.



Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: There is a term called aneuploidy that is used to describe a condition in which a chromosome is missing or an extra chromosome added into the individual genome. Down's syndrome is an example of aneuploidy.
Complete answer:a) The above disease is Down's syndrome which is a chromosomal anomaly caused due to the presence of three genes on the 21st chromosome or in other words, it is caused because of an extra copy of the 21st chromosome. Nondisjunction (failure in the separation of homologous chromosomes) of chromosomes during meiosis gives rise to this extra copy of the chromosome or at times even improper cell division leads to the formation of this extra copy. The child suffering from Down's syndrome is genetically normal but here the child’s chromosome has the same alleles as that of the mother. So here we can say that disjunction has occurred at the time of oogenesis resulting in duplication of maternal alleles. Since trisomy is (2N+1), the genotype of a person suffering from this will be 45+XX/45+XY.It can also occur due to translocation.
b) Down’s syndrome is an autosomal disorder hence has no sex specification i.e. it can occur in both the sexes. As they are linked with autosomes and none of the sex chromosomes. There's no such compulsion that if a couple has a child with Down's syndrome the second child will mandatorily suffer from Down's syndrome there are about 1% chances of the child to be born with this syndrome.
Note: Down's syndrome causes delays in development both mentally and physically and the person suffering from this disease has dementia. Other than this they might suffer from epilepsy, congenital heart failure, etc. Sex-linked chromosomal disease example is haemophilia.
Complete answer:a) The above disease is Down's syndrome which is a chromosomal anomaly caused due to the presence of three genes on the 21st chromosome or in other words, it is caused because of an extra copy of the 21st chromosome. Nondisjunction (failure in the separation of homologous chromosomes) of chromosomes during meiosis gives rise to this extra copy of the chromosome or at times even improper cell division leads to the formation of this extra copy. The child suffering from Down's syndrome is genetically normal but here the child’s chromosome has the same alleles as that of the mother. So here we can say that disjunction has occurred at the time of oogenesis resulting in duplication of maternal alleles. Since trisomy is (2N+1), the genotype of a person suffering from this will be 45+XX/45+XY.It can also occur due to translocation.
b) Down’s syndrome is an autosomal disorder hence has no sex specification i.e. it can occur in both the sexes. As they are linked with autosomes and none of the sex chromosomes. There's no such compulsion that if a couple has a child with Down's syndrome the second child will mandatorily suffer from Down's syndrome there are about 1% chances of the child to be born with this syndrome.
Note: Down's syndrome causes delays in development both mentally and physically and the person suffering from this disease has dementia. Other than this they might suffer from epilepsy, congenital heart failure, etc. Sex-linked chromosomal disease example is haemophilia.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




