
A lens of focal length $20.0cm$ and aperture radius $2.0cm$ is placed at a distance $30.0cm$ from a point source of light. On the other side a screen is placed at a distance $50.0cm$ from the lens. The radius of the spot of the light formed on the screen is ……..... (neglect spherical aberration through lens)
$\eqalign{
& A.\,\,\dfrac{1}{2}cm \cr
& B.\,\,\dfrac{1}{3}cm \cr
& C.\,\,\dfrac{1}{5}cm \cr
& D.\,1.0cm \cr} $
Answer
585.3k+ views
Hint: First, we have to understand that the image is formed on the screen. As the screen is acting as an obstacle. But the thin lens formula still applies for the original image. The radius of the light spot is actually the height of the image from the principal axis.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete answer:
From the information given in the question, let’s sketch a diagram.
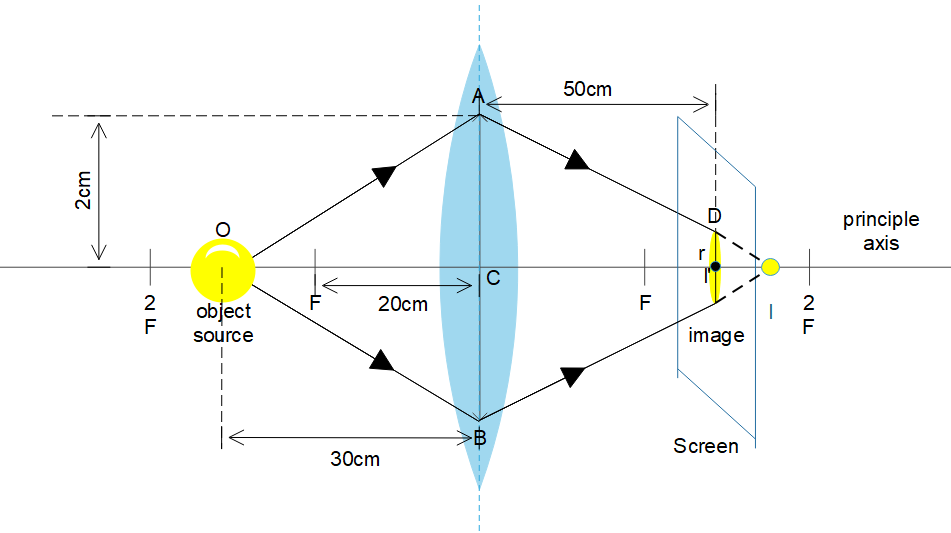
In the diagram,
$O$ is the light source (object)
$I$ is the original image
${I'}$ is the image formed on the screen
$AC$ is the radius of aperture
$D{I'}\left( r \right)$ is the radius of the light spot on the screen
$CI$ is the image distance
$OC$ is the object distance
$OF$ is the focal length.
We have to understand that, here the image is meant to form at I. But the screen acts as interruption and the image is formed on the screen at I’ instead of forming at point I.
According to thin lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where:
$v$ is the Image distance
$u$ is the object distance
$f$ is the focal length
Using this formula and the object distance is u = 30.0 cm and the focal length is f = 20cm, we have
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{30}} = \dfrac{1}{{60}} \cr
& \therefore v = 60cm \cr} $
Consider $\Delta ACI$ and $\Delta D{I'}I$, from the diagram. From properties of similar triangles, we have
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{AC}}{{CI}} = \dfrac{{D{I'}}}{{{I'}I}} \Rightarrow D{I'} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{CI}} \times {I'}I \cr
& \Rightarrow D{I'} = \dfrac{{2cm}}{{60cm}} \times 10cm = \dfrac{1}{3}cm \cr
& \therefore r = \dfrac{1}{3}cm \cr} $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
As the lenses we have considered are converging lenses, the sign convention is such that focal length is always positive. Also remember that, we consider $OF$ as the focal length. Simply put, all distances should be measured from the optical center. Distances measured in the direction of the incident rays are positive.
Formula used:
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Complete answer:
From the information given in the question, let’s sketch a diagram.

In the diagram,
$O$ is the light source (object)
$I$ is the original image
${I'}$ is the image formed on the screen
$AC$ is the radius of aperture
$D{I'}\left( r \right)$ is the radius of the light spot on the screen
$CI$ is the image distance
$OC$ is the object distance
$OF$ is the focal length.
We have to understand that, here the image is meant to form at I. But the screen acts as interruption and the image is formed on the screen at I’ instead of forming at point I.
According to thin lens formula
$\dfrac{1}{f} = \dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where:
$v$ is the Image distance
$u$ is the object distance
$f$ is the focal length
Using this formula and the object distance is u = 30.0 cm and the focal length is f = 20cm, we have
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{{20}} - \dfrac{1}{{30}} = \dfrac{1}{{60}} \cr
& \therefore v = 60cm \cr} $
Consider $\Delta ACI$ and $\Delta D{I'}I$, from the diagram. From properties of similar triangles, we have
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{AC}}{{CI}} = \dfrac{{D{I'}}}{{{I'}I}} \Rightarrow D{I'} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{CI}} \times {I'}I \cr
& \Rightarrow D{I'} = \dfrac{{2cm}}{{60cm}} \times 10cm = \dfrac{1}{3}cm \cr
& \therefore r = \dfrac{1}{3}cm \cr} $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
As the lenses we have considered are converging lenses, the sign convention is such that focal length is always positive. Also remember that, we consider $OF$ as the focal length. Simply put, all distances should be measured from the optical center. Distances measured in the direction of the incident rays are positive.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




