
A lens produces a virtual image between the object and the lens.
A.) Name the lens.
B.) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of this image.
Answer
606.3k+ views
Hint: A diverging lens always forms a virtual image in between the object and the lens. Now think which lens is known as diverging. To draw the ray diagram, consider two rays coming from the object, one parallel to the principal axis and the other passing through the optical centre.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A concave lens spreads out light rays that have been refracted through its, therefore it is called a diverging lens. A concave lens is thinner at its centre than at its edges, and it is this property that makes the light waves diverge after passing through it. So, the concave lens is a diverging lens. After light rays (parallel) have passed through the lens, they appear to come from a point called the principal focus (the point at which the light from a distant source that moves parallel to the axis of the lens is focused).
The image formed by a concave lens:
A. Is virtual i.e. it can’t be obtained on a screen.
B. Appears to be farther than it actually is.
C. Is smaller than the real scale of the object.
D. Is always in between the object and the lens.
E. From the above properties of image formed, we can say that the lens is a concave lens.
Concave lenses are used in:
A. Flashlights, since it diverges the incoming rays to a larger area.
B. In telescopes and binoculars, to form virtual though erect images.
C. In peepholes in the doors.
D. In lasers used for medical treatments.
To make the ray diagram:
At least two rays are necessary to construct an image.
The rays taken are:
A. Ray coming parallel from the object to the lens.
B. Ray coming from the object and crossing the optical centre of the lens.
C. The intersection point of these two rays when joined with the principal axis by a straight line will give the image.
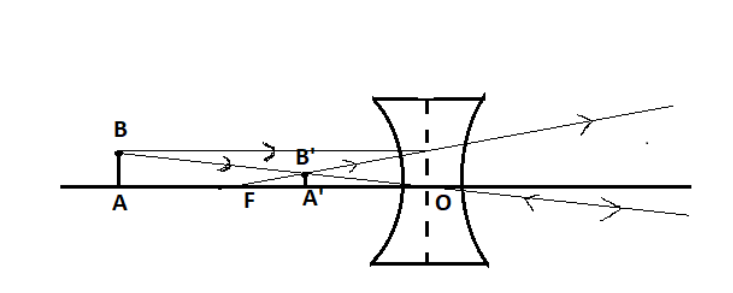
The image formed is virtual, erect and diminished.
Note: The image can be formed by any number of rays (at least 2) and by selecting any pair of rays.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A concave lens spreads out light rays that have been refracted through its, therefore it is called a diverging lens. A concave lens is thinner at its centre than at its edges, and it is this property that makes the light waves diverge after passing through it. So, the concave lens is a diverging lens. After light rays (parallel) have passed through the lens, they appear to come from a point called the principal focus (the point at which the light from a distant source that moves parallel to the axis of the lens is focused).
The image formed by a concave lens:
A. Is virtual i.e. it can’t be obtained on a screen.
B. Appears to be farther than it actually is.
C. Is smaller than the real scale of the object.
D. Is always in between the object and the lens.
E. From the above properties of image formed, we can say that the lens is a concave lens.
Concave lenses are used in:
A. Flashlights, since it diverges the incoming rays to a larger area.
B. In telescopes and binoculars, to form virtual though erect images.
C. In peepholes in the doors.
D. In lasers used for medical treatments.
To make the ray diagram:
At least two rays are necessary to construct an image.
The rays taken are:
A. Ray coming parallel from the object to the lens.
B. Ray coming from the object and crossing the optical centre of the lens.
C. The intersection point of these two rays when joined with the principal axis by a straight line will give the image.

The image formed is virtual, erect and diminished.
Note: The image can be formed by any number of rays (at least 2) and by selecting any pair of rays.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




