
A long straight wire of circular cross section of radius ‘a’ carries a steady current $I$. The current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section .Apply Ampere’ circular law to calculate the magnetic field at a point ‘r’ in the region for (i) $r \prec a$ and (ii) $r \succ a$.Plot a graph showing the nature of variation.
Answer
513k+ views
Hint: Before going through the question let us first discuss Magnetism. Magnetism is a type of physical phenomenon that is mediated by magnetic fields. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles combine to form a magnetic field, which interacts with other currents and magnetic moments. Electromagnetism is a multifaceted phenomenon that includes magnetism.
Complete answer:
Ampere’s Circuital law states that: According to Ampere's circuital theorem, the line integral of the magnetic field surrounding a closed-loop equals the algebraic number of currents passing through the loop.
$\oint {H \cdot dL = {I_{ence}}} $
If a conductor is carrying current I, the current flow creates a magnetic field around the cable.
The left side of the equation states that if a magnetic field is applied at each point along an imaginary path that encircles the wire, the current encircled by this path, as indicated by Ienc, is numerically equal to the current encircled by this route.
Now, coming to the question,
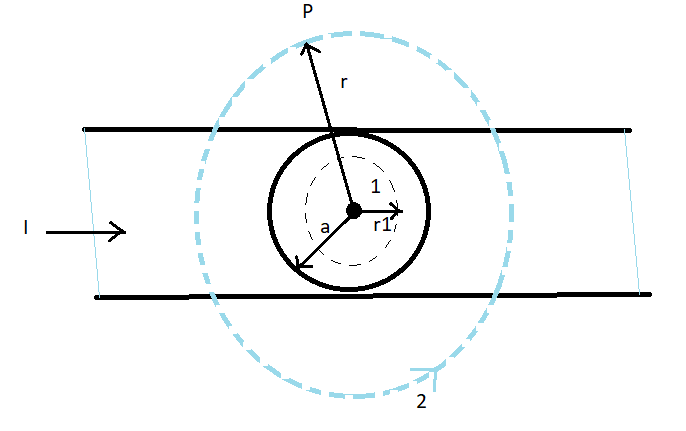
(i) considering the case $r \prec a$. The Ampere loop is a circle that is labelled as 1. For this loop , let’s take the radius of the as ‘r’, $L = 2\pi r$.
The new enclosed current \[{I_e}\] is no longer equal to\[I\], but it is now less than this amount. The latest current enclosed is, since the current distribution is uniform.
${I_e} = I\left( {\dfrac{{\pi {r^2}}}{{\pi {a^2}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{I{r^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$
Using Ampere's law :
$
B\left( {2\pi r} \right) = {\mu _ \circ } \cdot \dfrac{{I{r^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }I}}{{2\pi {a^2}}}} \right)r \\
B \propto r\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(r \prec a) \\
$
(ii) Now, considering the case $r \succ a$
The Amperian loop, denoted by the number 2, is a circle that is concentric to the cross-section. For this loop,
$L = 2\pi r$
${I_e}$ = Enclosed Current by the loop $I$
As a consequence, we have the well-known term for a long straight wire.
$
B\left( {2\pi r} \right) = {\mu _ \circ }I \\
B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }I}}{{2\pi r}} \\
B \propto \dfrac{1}{r}\,\,\left( {r \succ a} \right) \\
$
The magnitude of B is plotted against the distance r from the wire's centre in the figure. The right-hand direction determines the area, which is tangential to the respective circular loop (1 or 2).
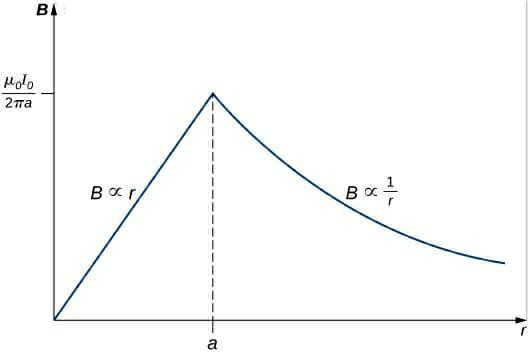
The magnitude of B is plotted against the distance r from the wire's centre in the figure. The right-hand direction defines the field, which is tangential to the respective circular loop (1 or 2).
Note:
Ampere's Law is a mathematical relationship between magnetic fields and electric currents that helps us to bridge the difference between electricity and magnetism. It allows us to measure the magnetic field generated by an electric current flowing through any form of wire.
Complete answer:
Ampere’s Circuital law states that: According to Ampere's circuital theorem, the line integral of the magnetic field surrounding a closed-loop equals the algebraic number of currents passing through the loop.
$\oint {H \cdot dL = {I_{ence}}} $
If a conductor is carrying current I, the current flow creates a magnetic field around the cable.
The left side of the equation states that if a magnetic field is applied at each point along an imaginary path that encircles the wire, the current encircled by this path, as indicated by Ienc, is numerically equal to the current encircled by this route.
Now, coming to the question,

(i) considering the case $r \prec a$. The Ampere loop is a circle that is labelled as 1. For this loop , let’s take the radius of the as ‘r’, $L = 2\pi r$.
The new enclosed current \[{I_e}\] is no longer equal to\[I\], but it is now less than this amount. The latest current enclosed is, since the current distribution is uniform.
${I_e} = I\left( {\dfrac{{\pi {r^2}}}{{\pi {a^2}}}} \right) = \dfrac{{I{r^2}}}{{{a^2}}}$
Using Ampere's law :
$
B\left( {2\pi r} \right) = {\mu _ \circ } \cdot \dfrac{{I{r^2}}}{{{a^2}}} \\
B = \left( {\dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }I}}{{2\pi {a^2}}}} \right)r \\
B \propto r\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(r \prec a) \\
$
(ii) Now, considering the case $r \succ a$
The Amperian loop, denoted by the number 2, is a circle that is concentric to the cross-section. For this loop,
$L = 2\pi r$
${I_e}$ = Enclosed Current by the loop $I$
As a consequence, we have the well-known term for a long straight wire.
$
B\left( {2\pi r} \right) = {\mu _ \circ }I \\
B = \dfrac{{{\mu _ \circ }I}}{{2\pi r}} \\
B \propto \dfrac{1}{r}\,\,\left( {r \succ a} \right) \\
$
The magnitude of B is plotted against the distance r from the wire's centre in the figure. The right-hand direction determines the area, which is tangential to the respective circular loop (1 or 2).

The magnitude of B is plotted against the distance r from the wire's centre in the figure. The right-hand direction defines the field, which is tangential to the respective circular loop (1 or 2).
Note:
Ampere's Law is a mathematical relationship between magnetic fields and electric currents that helps us to bridge the difference between electricity and magnetism. It allows us to measure the magnetic field generated by an electric current flowing through any form of wire.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




