
What is a transformer? Explain the principle, construction, working and theory of a transformer.
Answer
526.3k+ views
Hint – You can start by defining what a transformer is. Then move on to describe the principle behind the transformer. Then describe the basic setup of a transformer. Then finally write how a transformer works.
An electrical device that can change the A.C. current is known as a transformer.
Principle – A transformer works on the principle of mutual induction. Mutual induction is the phenomenon by which when the amount of magnetic flux linked with a coil changes, an E.M.F. is induced in the neighboring coil.
Construction –
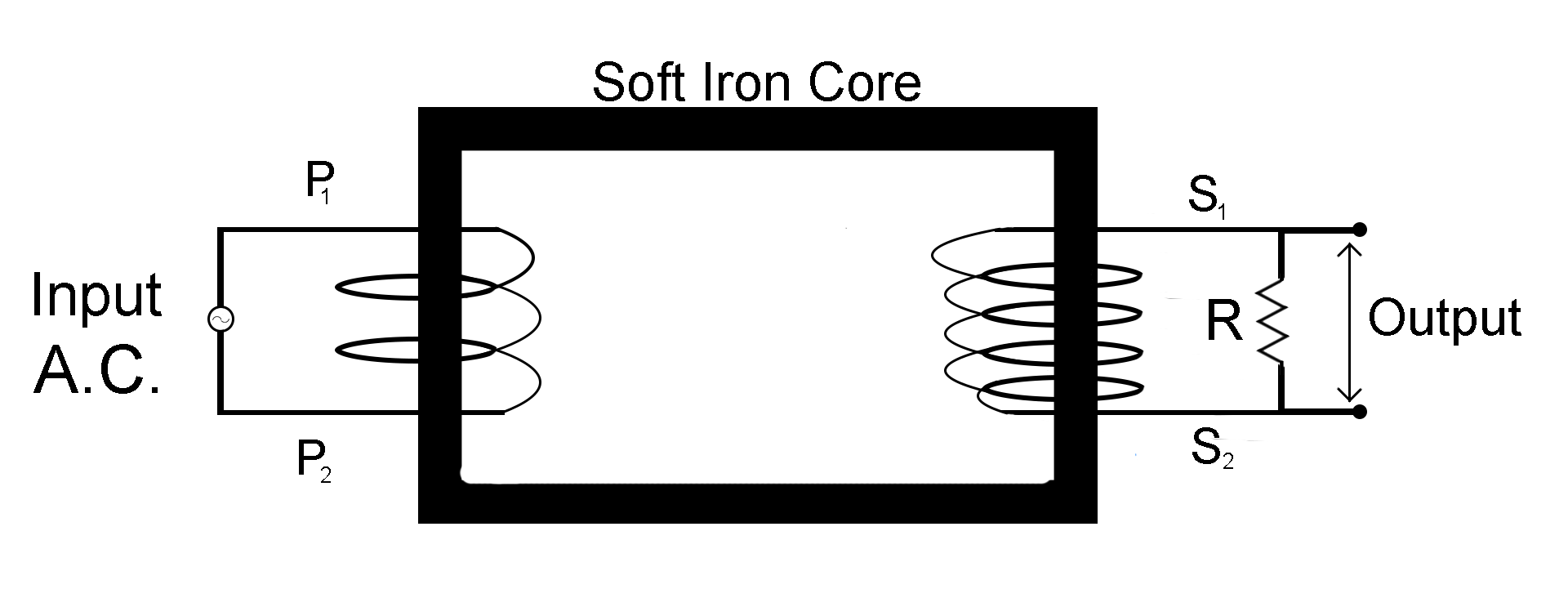
A transformer is made up of a rectangular iron core. Two coils, a primary $({P_{}})$ coil with two sides ${P_1}$ and ${P_2}$, and a secondary $(S)$ coil with two sides ${S_1}$ and ${S_2}$. Both these coils are insulated from the Ferro-magnetic iron core. The source of the alternate current is connected to the primary winding and the output is obtained through the secondary winding which is connected in parallel to a resistance $R$.
Working -
For an ideal transformer, we consider that resistances of the primary and secondary coils are negligible.
Let the $E.M.F.$ of the alternate current supplied by the A.C source be
${E_P} = {E_0}\sin \omega t$
Let’s assume that the primary winding to be a pure inductance, so here ${I_p}$will lag behind the voltage ${E_{P}}$ by $90^\circ $. Thus the power factor for primary coil becomes,$\cos \phi = \cos 90^\circ = 0$.
Let that the number of turns in primary wire be ${N_P}$ and secondary wire be ${N_S}$
According to faraday law, the induced $E.M.F.$ through one turn of both the coils will be the same.
Let the flux through one turn be $\phi $, the flux through the primary coil be ${\phi _p}$ and the flux through the secondary coil be ${\phi _S}$.
So ${\phi _p} = {N_P}\phi $
${\phi _S} = {N_S}\phi $
We also know by Faraday’s law
$E = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$
So for the primary coil this equation becomes
${E_S} = \dfrac{{d{\phi _S}}}{{dt}}$(Equation 1)
And for the secondary coil this equation becomes
${E_P} = \dfrac{{d{\phi _P}}}{{dt}}$(Equation 2)
Dividing equation 1 by equation 2
$\dfrac{{{E_S}}}{{{E_P}}} = \dfrac{{d{\phi _S}}}{{d{\phi _P}}} = \dfrac{{{N_S}\phi }}{{{N_P}\phi }}$
${E_S} = {E_p}\dfrac{{{N_S}}}{{{N_p}}}$(Equation 3)
We know that
$P = VI$
Here
$P = $Power
$V = $Voltage
$I = $Current
For primary coil this equation becomes
${P_P} = {E_P}{I_P}$(Equation 4)
For secondary coil this equation becomes
${P_S} = {E_S}{I_S}$(Equation 5)
For an ideal transformer no energy is lost, so
${P_p} = {P_S}$
${E_P}{I_P} = {E_S}{I_S}$
${I_S} = {I_p}\dfrac{{{E_p}}}{{{E_s}}}$$(\because \dfrac{{{E_p}}}{{{E_S}}} = \dfrac{{{N_p}}}{{{N_S}}})$
${I_S} = {I_p}\dfrac{{{N_p}}}{{{N_S}}}$
Note – A transformer that increases the A.C. voltage is known as a step up transformer (${N_S} > {N_p}$) and the transformer that decreases the A.C. voltage is known as a step down transformer (${N_S} < {N_p}$). Additionally an iron core is used because it is a ferromagnetic material which helps in increasing the strength of the magnetic field.
An electrical device that can change the A.C. current is known as a transformer.
Principle – A transformer works on the principle of mutual induction. Mutual induction is the phenomenon by which when the amount of magnetic flux linked with a coil changes, an E.M.F. is induced in the neighboring coil.
Construction –
A transformer is made up of a rectangular iron core. Two coils, a primary $({P_{}})$ coil with two sides ${P_1}$ and ${P_2}$, and a secondary $(S)$ coil with two sides ${S_1}$ and ${S_2}$. Both these coils are insulated from the Ferro-magnetic iron core. The source of the alternate current is connected to the primary winding and the output is obtained through the secondary winding which is connected in parallel to a resistance $R$.

Working -
For an ideal transformer, we consider that resistances of the primary and secondary coils are negligible.
Let the $E.M.F.$ of the alternate current supplied by the A.C source be
${E_P} = {E_0}\sin \omega t$
Let’s assume that the primary winding to be a pure inductance, so here ${I_p}$will lag behind the voltage ${E_{P}}$ by $90^\circ $. Thus the power factor for primary coil becomes,$\cos \phi = \cos 90^\circ = 0$.
Let that the number of turns in primary wire be ${N_P}$ and secondary wire be ${N_S}$
According to faraday law, the induced $E.M.F.$ through one turn of both the coils will be the same.
Let the flux through one turn be $\phi $, the flux through the primary coil be ${\phi _p}$ and the flux through the secondary coil be ${\phi _S}$.
So ${\phi _p} = {N_P}\phi $
${\phi _S} = {N_S}\phi $
We also know by Faraday’s law
$E = \dfrac{{d\phi }}{{dt}}$
So for the primary coil this equation becomes
${E_S} = \dfrac{{d{\phi _S}}}{{dt}}$(Equation 1)
And for the secondary coil this equation becomes
${E_P} = \dfrac{{d{\phi _P}}}{{dt}}$(Equation 2)
Dividing equation 1 by equation 2
$\dfrac{{{E_S}}}{{{E_P}}} = \dfrac{{d{\phi _S}}}{{d{\phi _P}}} = \dfrac{{{N_S}\phi }}{{{N_P}\phi }}$
${E_S} = {E_p}\dfrac{{{N_S}}}{{{N_p}}}$(Equation 3)
We know that
$P = VI$
Here
$P = $Power
$V = $Voltage
$I = $Current
For primary coil this equation becomes
${P_P} = {E_P}{I_P}$(Equation 4)
For secondary coil this equation becomes
${P_S} = {E_S}{I_S}$(Equation 5)
For an ideal transformer no energy is lost, so
${P_p} = {P_S}$
${E_P}{I_P} = {E_S}{I_S}$
${I_S} = {I_p}\dfrac{{{E_p}}}{{{E_s}}}$$(\because \dfrac{{{E_p}}}{{{E_S}}} = \dfrac{{{N_p}}}{{{N_S}}})$
${I_S} = {I_p}\dfrac{{{N_p}}}{{{N_S}}}$
Note – A transformer that increases the A.C. voltage is known as a step up transformer (${N_S} > {N_p}$) and the transformer that decreases the A.C. voltage is known as a step down transformer (${N_S} < {N_p}$). Additionally an iron core is used because it is a ferromagnetic material which helps in increasing the strength of the magnetic field.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




