
A man can swim in still water at a speed of 3 km/h. He wants to cross a river that flows at 2 km/h and reach the point directly opposite to his starting point. (a) In which direction should he try to swim (that is, find the angle his body makes with the river flows)? (b) how much time will it take to cross the river if the river is 500 m wide?
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint To find the angle between the direction of swimming of the man and that of the bank, first find the angle between the direction of swimming and the vertical. Find the component of the swimming of the man to the vertical to find the time taken to cross the river.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[v = \dfrac{d}{t}\] where \[v\] is the velocity of a body in a particular direction, \[d\] is the displacement traversed by the body in a direction, and \[t\] is the time elapsed for the displacement to be covered.
\[hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}\] where \[hyp\] signifies hypotenuse side of a right angled triangle, \[opp\] is opposite side, and \[adj\] is the adjacent side.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
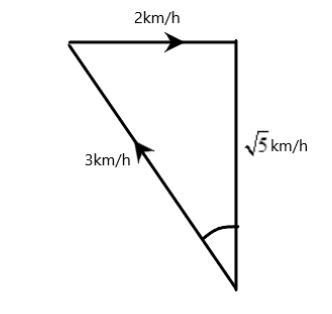
To find the angle between the targeted velocity of the swimming of the man (3km/h) and that of the velocity of the river, we must calculate the angle \[\theta \] first. This can be calculated as in
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) = 41.7^\circ \]
Now, since, the river flow is parallel to the river bank, then the angle the man should try to swim
\[\alpha = 90 + \theta = 131.7^\circ \]
To find the time taken to cross the river, we must find the actual velocity of the man. We can use Pythagoras theorem, which says
\[hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}\] where \[hyp\] signifies hypotenuse side of a right angled triangle, \[opp\] is opposite side, and \[adj\] is the adjacent side.
Hence,
\[{x^2} = {3^2} - {2^2} = 9 - 4 = 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \sqrt 5 km/h\]
Now, from the equation
\[v = \dfrac{d}{t}\] where \[v\] is the velocity of a body in a particular direction, \[d\] is the displacement traversed by the body in a direction, and \[t\] is the time elapsed for the displacement to be covered, we have
\[\sqrt 5 = \dfrac{{0.5}}{t}\] (since 500 m is \[0.5km\])
Hence,
\[t = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{\sqrt 5 }} = 0.22hr\] or \[13.4\] minutes.
Note: Alternatively, one could calculate the real velocity of the man by finding the component of the 3km/h on the vertical axis, as in
\[v = 3\cos 41.7^\circ = 2.23\]
This is equivalent to \[\sqrt 5 \]
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[v = \dfrac{d}{t}\] where \[v\] is the velocity of a body in a particular direction, \[d\] is the displacement traversed by the body in a direction, and \[t\] is the time elapsed for the displacement to be covered.
\[hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}\] where \[hyp\] signifies hypotenuse side of a right angled triangle, \[opp\] is opposite side, and \[adj\] is the adjacent side.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:

To find the angle between the targeted velocity of the swimming of the man (3km/h) and that of the velocity of the river, we must calculate the angle \[\theta \] first. This can be calculated as in
\[\tan \theta = \dfrac{2}{3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{2}{3}} \right) = 41.7^\circ \]
Now, since, the river flow is parallel to the river bank, then the angle the man should try to swim
\[\alpha = 90 + \theta = 131.7^\circ \]
To find the time taken to cross the river, we must find the actual velocity of the man. We can use Pythagoras theorem, which says
\[hy{p^2} = op{p^2} + ad{j^2}\] where \[hyp\] signifies hypotenuse side of a right angled triangle, \[opp\] is opposite side, and \[adj\] is the adjacent side.
Hence,
\[{x^2} = {3^2} - {2^2} = 9 - 4 = 5\]
\[ \Rightarrow x = \sqrt 5 km/h\]
Now, from the equation
\[v = \dfrac{d}{t}\] where \[v\] is the velocity of a body in a particular direction, \[d\] is the displacement traversed by the body in a direction, and \[t\] is the time elapsed for the displacement to be covered, we have
\[\sqrt 5 = \dfrac{{0.5}}{t}\] (since 500 m is \[0.5km\])
Hence,
\[t = \dfrac{{0.5}}{{\sqrt 5 }} = 0.22hr\] or \[13.4\] minutes.
Note: Alternatively, one could calculate the real velocity of the man by finding the component of the 3km/h on the vertical axis, as in
\[v = 3\cos 41.7^\circ = 2.23\]
This is equivalent to \[\sqrt 5 \]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




