
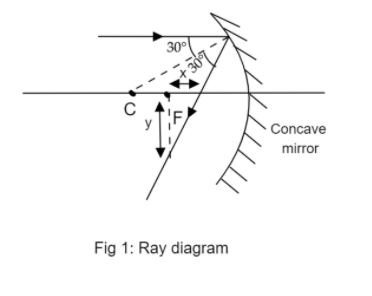
A marginal ray is falling on a concave spherical mirror as shown in the figure below. The ratio of longitudinal (x) and transverse (y) spherical aberration is:
(a) \[\sqrt 3 \]
(b) $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
(c) $\dfrac{2}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
(d) can’t be determined

Answer
587.7k+ views
Hint: This question doesn’t involve much physics, it can be solved by applying concepts of geometry and trigonometry. The reflected ray acts as a transverse for the parallel lines (incident ray and optical axis).
Formula used:
1. Ratio of perpendicular and base for a right angled triangle: $\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b}$ ……(1)
Where,
$\theta $ is the angle from the base
$p$ is the perpendicular
$b$ is the base
Complete step by step answer:
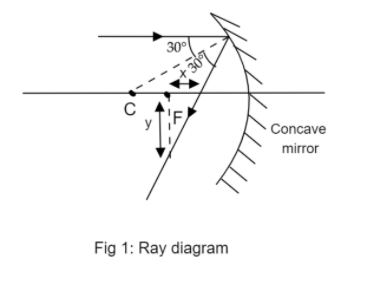
The given ray diagram is:
To find: The ratio of longitudinal (x) and transverse (y) spherical aberration.
Step 1 of 2:
The marginal ray given in the diagram is parallel to the optical axis. The reflected ray cuts a pair of these parallel lines. Therefore, the angle it makes with the marginal ray will be equal to the angle it makes with the optical axis.
The angle made by reflected ray with the marginal ray is the summation:
$\theta = 30^\circ + 30^\circ $
$\theta = 60^\circ $
Step 2 of 2:
Consider the triangle $\Delta FGH$in fig 2 with the right angle at F. Now, $\angle FGH$is the angle $\theta $ we just found. Use eq (1) to find the ratio $\dfrac{y}{x}$:
$\dfrac{y}{x} = \tan \theta $
$\dfrac{y}{x} = \tan 60^\circ $
$\dfrac{y}{x} = \sqrt 3 $
Inverting this to find the required ratio $\dfrac{x}{y}$:
$\dfrac{x}{y} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
The ratio of longitudinal (x) and transverse (y) spherical aberration is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$. Hence option (b) is correct.
Note:
Here, one should take care that just outside the metal surface, for point P metal plate appears infinitely big, therefore, we can use field produced due to infinite metal plate carrying charge approximation.
Formula used:
1. Ratio of perpendicular and base for a right angled triangle: $\tan \theta = \dfrac{p}{b}$ ……(1)
Where,
$\theta $ is the angle from the base
$p$ is the perpendicular
$b$ is the base
Complete step by step answer:
The given ray diagram is:

To find: The ratio of longitudinal (x) and transverse (y) spherical aberration.
Step 1 of 2:
The marginal ray given in the diagram is parallel to the optical axis. The reflected ray cuts a pair of these parallel lines. Therefore, the angle it makes with the marginal ray will be equal to the angle it makes with the optical axis.
The angle made by reflected ray with the marginal ray is the summation:
$\theta = 30^\circ + 30^\circ $
$\theta = 60^\circ $
Step 2 of 2:
Consider the triangle $\Delta FGH$in fig 2 with the right angle at F. Now, $\angle FGH$is the angle $\theta $ we just found. Use eq (1) to find the ratio $\dfrac{y}{x}$:
$\dfrac{y}{x} = \tan \theta $
$\dfrac{y}{x} = \tan 60^\circ $
$\dfrac{y}{x} = \sqrt 3 $
Inverting this to find the required ratio $\dfrac{x}{y}$:
$\dfrac{x}{y} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$
The ratio of longitudinal (x) and transverse (y) spherical aberration is $\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}$. Hence option (b) is correct.
Note:
Here, one should take care that just outside the metal surface, for point P metal plate appears infinitely big, therefore, we can use field produced due to infinite metal plate carrying charge approximation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




