
A mark on the surface of a glass sphere $\mu =1.5$is viewed from a diametrically opposite position. It appears to be at a distance $10cm$ from its actual position. The radius of the sphere is:
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }5cm \\
& \text{B}\text{. }10cm \\
& \text{C}\text{. }15cm \\
& \text{D}\text{. }20cm \\
\end{align}$
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: When a light wave propagates from one medium to another having different values of refractive indices, it experiences some bending in its path, this is called refraction. We will apply the lens maker formula for refraction through the glass sphere and determine the radius of curvature of the sphere.
Complete step by step answer:
Refraction is described as the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another or from a gradual change in the medium. We can say that refraction is the bending of a wave when it passes through one medium to another. The bending of light occurs due to the difference in density between the two mediums.
We are given that when a mark on the surface of a glass sphere$\mu =1.5$is viewed from a diametrically opposite position, it appears to be at a distance $10cm$from its actual position.
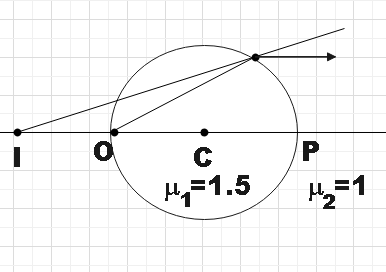
Using the lens maker formula for refraction between two surfaces of different refractive indices,
\[\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}{R}\]
We have,
$\begin{align}
& {{\mu }_{1}}=1.5 \\
& {{\mu }_{2}}=1 \\
& v=10-2R \\
& u=-2R \\
\end{align}$
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{10-2R}-\dfrac{1.5}{\left( -2R \right)}=\dfrac{1-1.5}{-R} \\
& \dfrac{1}{10-2R}+\dfrac{3}{4R}=\dfrac{1}{2R} \\
& \dfrac{1}{10-2R}=-\dfrac{1}{4R} \\
& -4R=10-2R \\
& 2R=-10 \\
& R=-5cm \\
\end{align}$
The radius of curvature is $5cm$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
The causes of Refraction phenomenon are:
The frequency of refracted rays has to remain constant.
Due to the partial reflection and absorption of light at the interface, the intensity of emergent ray after refraction will be less than that of incident ray.
When the wave crosses the boundary between two different media, deviation in the path of the wave occurs which results in the phenomenon of refraction such that the wavelength and speed of wave changes.
Note: There is no change in the position of an opaque dot at the centre of a transparent glass sphere when a person observes it from the outside. All the rays that come out from the object kept at the centre of the transparent sphere will be normal to the surface of the sphere. Hence, the object will be observed at the same position from outside.
Complete step by step answer:
Refraction is described as the change in direction of a wave passing from one medium to another or from a gradual change in the medium. We can say that refraction is the bending of a wave when it passes through one medium to another. The bending of light occurs due to the difference in density between the two mediums.
We are given that when a mark on the surface of a glass sphere$\mu =1.5$is viewed from a diametrically opposite position, it appears to be at a distance $10cm$from its actual position.

Using the lens maker formula for refraction between two surfaces of different refractive indices,
\[\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}}{v}-\dfrac{{{\mu }_{1}}}{u}=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{2}}-{{\mu }_{1}}}{R}\]
We have,
$\begin{align}
& {{\mu }_{1}}=1.5 \\
& {{\mu }_{2}}=1 \\
& v=10-2R \\
& u=-2R \\
\end{align}$
Therefore,
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{1}{10-2R}-\dfrac{1.5}{\left( -2R \right)}=\dfrac{1-1.5}{-R} \\
& \dfrac{1}{10-2R}+\dfrac{3}{4R}=\dfrac{1}{2R} \\
& \dfrac{1}{10-2R}=-\dfrac{1}{4R} \\
& -4R=10-2R \\
& 2R=-10 \\
& R=-5cm \\
\end{align}$
The radius of curvature is $5cm$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Additional information:
The causes of Refraction phenomenon are:
The frequency of refracted rays has to remain constant.
Due to the partial reflection and absorption of light at the interface, the intensity of emergent ray after refraction will be less than that of incident ray.
When the wave crosses the boundary between two different media, deviation in the path of the wave occurs which results in the phenomenon of refraction such that the wavelength and speed of wave changes.
Note: There is no change in the position of an opaque dot at the centre of a transparent glass sphere when a person observes it from the outside. All the rays that come out from the object kept at the centre of the transparent sphere will be normal to the surface of the sphere. Hence, the object will be observed at the same position from outside.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




