
A metal sphere is kept on an insulating stand. A negatively charged rod is brought near it, then the sphere is earthed as shown. On removing the earthing, and taking the negatively charged rod away, what will be the nature of the charge on the sphere? Give the reason for your answer.
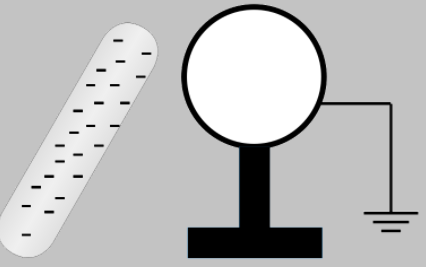

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint: The negatively charged rod induces a positive charge on the nearby region of the sphere. This leads to electron accumulation on the other part of the sphere to maintain electric charge neutrality. Earthing is the process of connecting a low resistance wire, from the object to earth. It provides a conducting path to the electric charges, induced.
Complete answer:
It is given in the question that a metal sphere is kept on an insulating stand. It is initially brought near to a negatively charged conducting rod.
We know that opposite charges repel each other. Since the rod is negatively charged it induces a positive charge accumulation on the nearby surface of the sphere.
But by the law of conservation of charge, the total charge of the sphere must be zero. It means that an equal amount of negative charge is induced on the other side of the sphere. It is shown in the figure below.
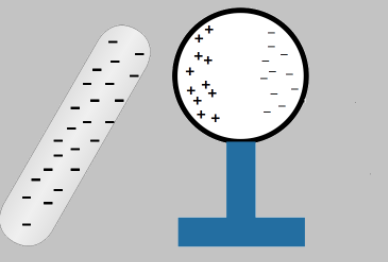
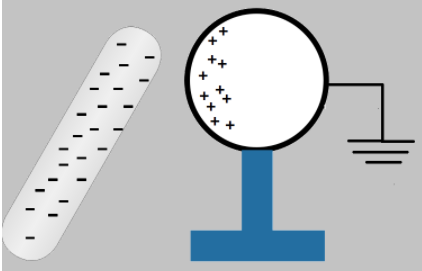
Now, it is said that the sphere is earthed, as shown. This creates a potential difference between the earth and the other side of the sphere. The ground is usually taken to be 0V. Since the negative charges have a lower potential than zero, the negative charge flows from low to high potential, i.e., the earth.
Now if both, the negatively charged rod and the earthing are removed the positive charge remains. It evenly spreads all over the surface of the sphere, as shown.
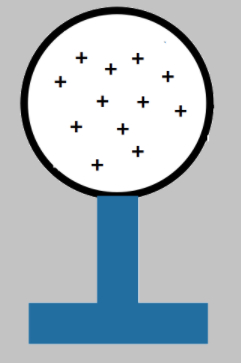
Therefore, the sphere is now positively charged.
Note:
The insulating stand keeps the charge acquired in the sphere, by not conducting a free path from sphere to ground.
The ground is assumed to be a universal sink, functioning at a voltage of 0V. But, the earth has some voltage and charge. Due to its huge size, the absorption or deduction of charge does not affect the charge and voltage of the earth. So, it is considered to be neutral.
The negative charges of the sphere are essentially free electrons and the positive charges are in fact electron-deficient atoms or ions.
Complete answer:
It is given in the question that a metal sphere is kept on an insulating stand. It is initially brought near to a negatively charged conducting rod.
We know that opposite charges repel each other. Since the rod is negatively charged it induces a positive charge accumulation on the nearby surface of the sphere.
But by the law of conservation of charge, the total charge of the sphere must be zero. It means that an equal amount of negative charge is induced on the other side of the sphere. It is shown in the figure below.

Now, it is said that the sphere is earthed, as shown. This creates a potential difference between the earth and the other side of the sphere. The ground is usually taken to be 0V. Since the negative charges have a lower potential than zero, the negative charge flows from low to high potential, i.e., the earth.

Now if both, the negatively charged rod and the earthing are removed the positive charge remains. It evenly spreads all over the surface of the sphere, as shown.

Therefore, the sphere is now positively charged.
Note:
The insulating stand keeps the charge acquired in the sphere, by not conducting a free path from sphere to ground.
The ground is assumed to be a universal sink, functioning at a voltage of 0V. But, the earth has some voltage and charge. Due to its huge size, the absorption or deduction of charge does not affect the charge and voltage of the earth. So, it is considered to be neutral.
The negative charges of the sphere are essentially free electrons and the positive charges are in fact electron-deficient atoms or ions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




