
A monkey is at rest on a weightless rope which goes over a pulley and is tied to a bunch of bananas at the other end. The weight of the bunch of bananas is exactly the same as that of the monkey. The pulley is frictionless and weightless. The monkey starts to climb up the rope to reach the bananas. As he climbs, the distance between him and the bananas will:
$\left( {{A}} \right)$ Decrease
$\left( {{B}} \right)$ Increase
$\left( {{C}} \right)$ First decrease and then increase
$\left( {{D}} \right)$ Remain unchanged
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Here, the monkey accelerates upwards, thus the bunch of bananas also accelerates with the same magnitude which is downwards. The mass of the monkey and bananas are the same. The separation between monkey and bananas remains constant. In case the monkey moves upward then \[{{T > MG}}\].
Complete step by step answer:
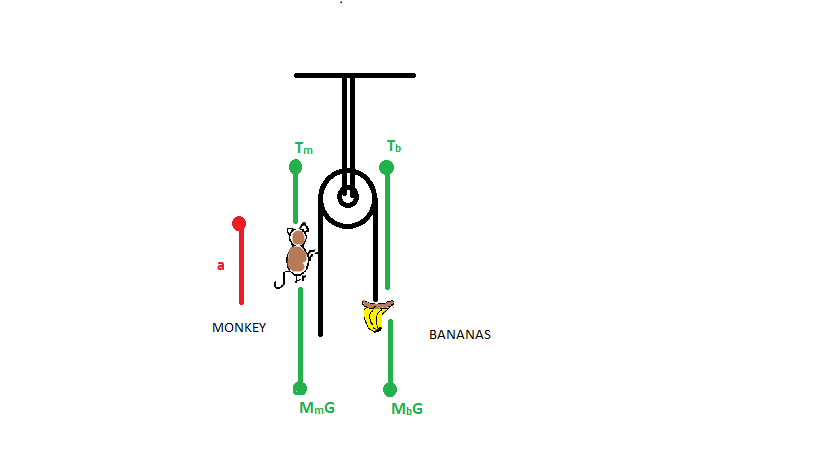
Let us assume that the monkey is moving upward with direction a. The forces acting on the monkey is \[{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{G}}\] and tension \[{{{T}}_{{m}}}\] because of the rope.
Similarly, the forces acting on the bananas are \[{{{M}}_{{b}}}{{G}}\] and tension \[{{{T}}_{{b}}}\] because of the rope.
So, from the above data the net force in the direction of acceleration a (for monkey) is:
\[\Rightarrow {{T = }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{(G + a)}}\]
The net force for bananas is
\[\Rightarrow {{T = M_b G}}\]
Equating both the equations,
\[\Rightarrow {{M_b G = }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{(G + a)}}\]
On multiplying the term we get
\[\Rightarrow {{M_b G = }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{G + }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{a}}\]
According to the question, the mass of the monkey and bananas are the same.
So, \[{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{ = }}{{{M}}_{{b}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{M_m a = 0}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{a = 0}}\].
Therefore, the acceleration \[a\]is zero and the distance between monkey and the banana will remain unchanged.
Hence the correct option is \[D\].
Note: In the above question, bananas are not accelerating in any direction and only the monkey is moving with an acceleration a.
Wrong thinking:
The monkey is moving up by pulling the rope downwards, then the distance between the monkey and bananas will be decreased.
The above one is wrong because the masses of the monkey and bananas are the same as per question.
Complete step by step answer:

Let us assume that the monkey is moving upward with direction a. The forces acting on the monkey is \[{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{G}}\] and tension \[{{{T}}_{{m}}}\] because of the rope.
Similarly, the forces acting on the bananas are \[{{{M}}_{{b}}}{{G}}\] and tension \[{{{T}}_{{b}}}\] because of the rope.
So, from the above data the net force in the direction of acceleration a (for monkey) is:
\[\Rightarrow {{T = }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{(G + a)}}\]
The net force for bananas is
\[\Rightarrow {{T = M_b G}}\]
Equating both the equations,
\[\Rightarrow {{M_b G = }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{(G + a)}}\]
On multiplying the term we get
\[\Rightarrow {{M_b G = }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{G + }}{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{a}}\]
According to the question, the mass of the monkey and bananas are the same.
So, \[{{{M}}_{{m}}}{{ = }}{{{M}}_{{b}}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{M_m a = 0}}\]
\[\Rightarrow {{a = 0}}\].
Therefore, the acceleration \[a\]is zero and the distance between monkey and the banana will remain unchanged.
Hence the correct option is \[D\].
Note: In the above question, bananas are not accelerating in any direction and only the monkey is moving with an acceleration a.
Wrong thinking:
The monkey is moving up by pulling the rope downwards, then the distance between the monkey and bananas will be decreased.
The above one is wrong because the masses of the monkey and bananas are the same as per question.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Laws of Motion Class 11 Physics Chapter 4 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Waves Class 11 Physics Chapter 14 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Mechanical Properties of Fluids Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Units And Measurements Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26




