
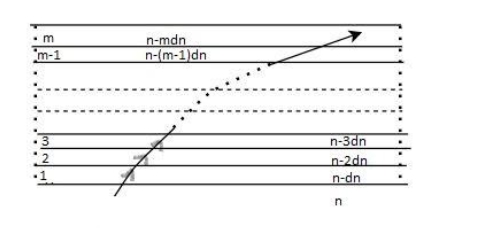
A monochromatic light is travelling in a medium of refractive index $n = 1.6$. It enters a stack of glass layers from the bottom side at an angle $\theta = {30^ \circ }$. The interfaces of the glass layers are parallel to each other. The refractive indices of the different glass layers are monotonically decreasing as ${n_m} = n - m\Delta n$, where ${n_m}$ is the refractive index of the ${m^{th}}$ slab and $\Delta n = 0.1$ (see the figure). The ray is refracted out parallel to the interface between the ${\left( {m - 1} \right)^{th}}$ and ${m^{th}}$ slabs from the right side of the stack. What is the value of the $m$ ?

Answer
577.8k+ views
Hint:Calculate the value of the ${n_m}$ from the relation given in the question. Substitute this value of the refractive index of the slab and also the refractive angles in the snell’s law. The obtained value gives the output of the value of the m constant.
Useful formula:
The snell’s law states that
$n\sin \theta = {n_m}\sin {\theta _r}$
Where $n$ is the refractive index, $\theta $ is the angle between the layers of the glass and the bottom side an ${n_m}$ is the refractive index of the ${m^{th}}$ slab.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the
${n_m} = n - m\Delta n$
$\Delta n = 0.1$
$n = 1.6$
From the above given data, the value of ${n_m}$ is calculated as follows.
${n_m} = n - m\Delta n$
Substituting the values known,
${n_m} = 1.6 - 0.1m$ -------------(1)
By using the snell’s law
$1.6\sin {30^ \circ } = {n_m}\sin 90 \circ $
The ${\theta _r}$ is observed as ${90^ \circ }$ from the diagram given. And substitute the value of (1) in the above equation.
$1.6\sin {30^ \circ } = (1.6 - 0.1m)\sin 90 \circ $
$\dfrac{{1.6}}{2} = 0.1m \times 1$
By performing the simple arithmetic operation,
$0.1m = 0.8$
$m = 8$
Thus the value of the $m$ is $8$.
Note: The snell’s law provides the idea about the relationship between the angle of the incidence and the angle of the refraction. This law is also called the law of refraction. The refractive index depends on the layer of the substance that obstructs the flow of the light.
Useful formula:
The snell’s law states that
$n\sin \theta = {n_m}\sin {\theta _r}$
Where $n$ is the refractive index, $\theta $ is the angle between the layers of the glass and the bottom side an ${n_m}$ is the refractive index of the ${m^{th}}$ slab.
Complete step by step solution:
It is given that the
${n_m} = n - m\Delta n$
$\Delta n = 0.1$
$n = 1.6$
From the above given data, the value of ${n_m}$ is calculated as follows.
${n_m} = n - m\Delta n$
Substituting the values known,
${n_m} = 1.6 - 0.1m$ -------------(1)
By using the snell’s law
$1.6\sin {30^ \circ } = {n_m}\sin 90 \circ $
The ${\theta _r}$ is observed as ${90^ \circ }$ from the diagram given. And substitute the value of (1) in the above equation.
$1.6\sin {30^ \circ } = (1.6 - 0.1m)\sin 90 \circ $
$\dfrac{{1.6}}{2} = 0.1m \times 1$
By performing the simple arithmetic operation,
$0.1m = 0.8$
$m = 8$
Thus the value of the $m$ is $8$.
Note: The snell’s law provides the idea about the relationship between the angle of the incidence and the angle of the refraction. This law is also called the law of refraction. The refractive index depends on the layer of the substance that obstructs the flow of the light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




