
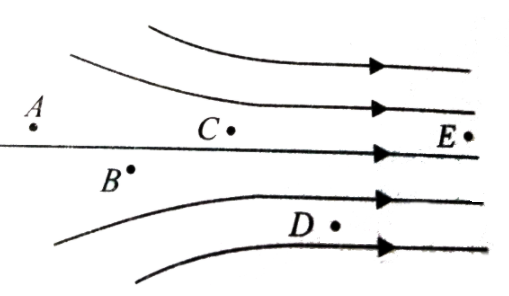
A non-uniform electric field is represented by the diagram.At which of the following points , the electric field is greatest in magnitude.
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
5. E

Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint:
- The magnitude of electric fields depends on how close the electric lines are.
- In fig, we see two types of electric field lines, uniform and non-uniform.
Complete step by step solution:
In the figure, we can see there are two sets of region
a. The first region, where the field lines are non-uniform.
b. The second region, where the field lines are uniform.
Now, if we observe,
- In the first or non-uniform region, points \[A,B,C\] reside, whereas point D resides in the second or uniform region.
- So the closest distance between the electric field lines is observed at point D.
But In the case of point A, the field lines distance is higher compare to the other points \[\left( {point{\text{ }}B,{\text{ }}C,{\text{ }}D} \right).\] So the magnitude of the electric field at point A is minimum.
- If we consider point B, we will discern that the distance between the field lines is lesser than the length at point A whereas higher than at point C and D. So the magnitude at point B will be higher than at point A but lesser than at point C and D.
- Similarly, the distance between the electric field lines at point C is lesser than at point A, B, and higher than at point D.
- Consequently, at point C, we will witness the higher magnitude than the magnitude at point A, B but lesser than at point D.
- But at point D, the distance between the electric field lines is minimum resulting in the maximum magnitude of the Electric field.
So the correct answer is option 4. D
Note:
a. The electric field lines' direction is always from positive to negative charge.
b. The magnitude of the electric field is proportional to the magnitude of the charge.
c. The number of electric field lines is proportional to the magnitude of the charge.
- The magnitude of electric fields depends on how close the electric lines are.
- In fig, we see two types of electric field lines, uniform and non-uniform.
Complete step by step solution:
In the figure, we can see there are two sets of region
a. The first region, where the field lines are non-uniform.
b. The second region, where the field lines are uniform.
Now, if we observe,
- In the first or non-uniform region, points \[A,B,C\] reside, whereas point D resides in the second or uniform region.
- So the closest distance between the electric field lines is observed at point D.
But In the case of point A, the field lines distance is higher compare to the other points \[\left( {point{\text{ }}B,{\text{ }}C,{\text{ }}D} \right).\] So the magnitude of the electric field at point A is minimum.
- If we consider point B, we will discern that the distance between the field lines is lesser than the length at point A whereas higher than at point C and D. So the magnitude at point B will be higher than at point A but lesser than at point C and D.
- Similarly, the distance between the electric field lines at point C is lesser than at point A, B, and higher than at point D.
- Consequently, at point C, we will witness the higher magnitude than the magnitude at point A, B but lesser than at point D.
- But at point D, the distance between the electric field lines is minimum resulting in the maximum magnitude of the Electric field.
So the correct answer is option 4. D
Note:
a. The electric field lines' direction is always from positive to negative charge.
b. The magnitude of the electric field is proportional to the magnitude of the charge.
c. The number of electric field lines is proportional to the magnitude of the charge.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




