
A normal chord of a parabola subtending a right angle at the vertex makes an acute angle \[\theta \] with the X – axis, then the value of \[\theta \] is
(a) \[\arctan 2\]
(b) \[\arctan \sqrt{2}\]
(c) \[\text{arccot} \sqrt{2}\]
(d) None of the above
Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: We solve this problem by assuming the equation of given parabola as standard equation of parabola that is \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\]
We use the condition that the equation of normal at some parametric point \[\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] of the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\]is given as
\[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\]
Then we use the condition two lines of slopes \[{{m}_{1}},{{m}_{2}}\] forms a right angle then
\[{{m}_{1}}\times {{m}_{2}}=-1\]
We also have other condition that if a line makes an angle \[\alpha \] with the X – axis in anti – clockwise direction then the slope of line is given as
\[m=\tan \alpha \]
By using the above two formulas to given conditions we find the required value.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that there is a normal chord that subtends a right angle at the vertex.
Let us assume that the equation of given parabola as standard equation of parabola that is \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\]
Now, let us assume that the normal is drawn at a parametric point \[P\left( a{{t}_{1}}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] such that it touches the parabola again at the point \[Q\left( a{{t}_{2}}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
Now, let us take a rough figure of the given information as follows
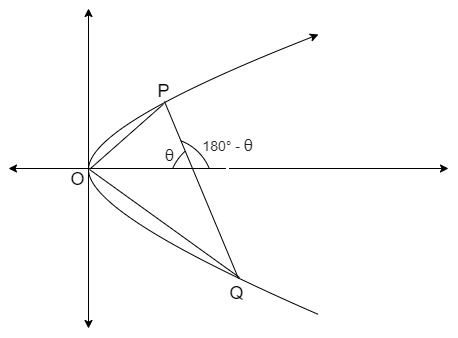
We know that the condition that the equation of normal at some parametric point \[\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] of the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\]is given as
\[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\]
By using the above formula to normal PQ from point P then we get the equation of PQ as
\[y=-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+a{{t}_{1}}^{3}\]
Here, we can see that the slope of the line PQ is given as
\[\Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}={{t}_{1}}\]
We are given that the normal makes an acute angle with X –axis as shown in the figure.
We know that if a line makes an angle \[\alpha \] with the X – axis in anti – clockwise direction then the slope of line is given as
\[m=\tan \alpha \]
By using the above formula to given angle then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}=\tan \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-\theta \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =-{{t}_{1}}............equation(i) \\
\end{align}\]
Here, we can see that Q lies in the equation of PQ.
So, by substituting the point Q in equation of PQ then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2a{{t}_{2}}=-{{t}_{1}}\left( a{{t}_{2}}^{2} \right)+2a{{t}_{1}}+a{{t}_{1}}^{3} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{t}_{2}}-2{{t}_{1}}=-{{t}_{1}}\left( {{t}_{2}}^{2}-{{t}_{1}}^{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By using the formula of algebra that is
\[{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)\]
To above equation then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)=-{{t}_{1}}\left( {{t}_{2}}+{{t}_{1}} \right)\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2=-{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}^{2}.............equation(ii) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us use the condition that PQ makes right angle at vertex
We know that the formula of slope of two points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] is given as
\[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
We also know that the condition two lines of slopes \[{{m}_{1}},{{m}_{2}}\] forms a right angle then
\[{{m}_{1}}\times {{m}_{2}}=-1\]
By using the above two formulas to OP and OQ then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{OP}}\times {{m}_{OQ}}=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{2a{{t}_{1}}-0}{a{{t}_{1}}^{2}-0} \right)\left( \dfrac{2a{{t}_{2}}-0}{a{{t}_{2}}^{2}-0} \right)=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-4 \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the above result in equation (ii) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2=-4-{{t}_{1}}^{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}^{2}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\pm \sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the above result in equation (i) then we get
\[\Rightarrow \tan \theta =-\left( \pm \sqrt{2} \right)\]
We know that \[\theta \] is acute angle so that tangent should be positive.
By using the above condition we get
\[\Rightarrow \theta =\arctan \sqrt{2}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the value of \[\theta \] is \[\arctan \sqrt{2}\]
So, option (a) is correct answer.
Note:
Students may do mistakes in taking the \[\theta \] given with the slope of the line.
We have the condition that if a line makes an angle \[\alpha \] with the X-axis in an anti-clockwise direction then the slope of the line is given as
\[m=\tan \alpha \]
By using the above condition to the above figure then we get the equation as
\[\Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}=\tan \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)\]
But students may miss the direction of the angle to be taken and assume that angle as
\[\Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}=\tan \left( \theta \right)\]
We use the condition that the equation of normal at some parametric point \[\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] of the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\]is given as
\[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\]
Then we use the condition two lines of slopes \[{{m}_{1}},{{m}_{2}}\] forms a right angle then
\[{{m}_{1}}\times {{m}_{2}}=-1\]
We also have other condition that if a line makes an angle \[\alpha \] with the X – axis in anti – clockwise direction then the slope of line is given as
\[m=\tan \alpha \]
By using the above two formulas to given conditions we find the required value.
Complete step by step answer:
We are given that there is a normal chord that subtends a right angle at the vertex.
Let us assume that the equation of given parabola as standard equation of parabola that is \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\]
Now, let us assume that the normal is drawn at a parametric point \[P\left( a{{t}_{1}}^{2},2a{{t}_{1}} \right)\] such that it touches the parabola again at the point \[Q\left( a{{t}_{2}}^{2},2a{{t}_{2}} \right)\]
Now, let us take a rough figure of the given information as follows

We know that the condition that the equation of normal at some parametric point \[\left( a{{t}^{2}},2at \right)\] of the parabola \[{{y}^{2}}=4ax\]is given as
\[y=-tx+2at+a{{t}^{3}}\]
By using the above formula to normal PQ from point P then we get the equation of PQ as
\[y=-{{t}_{1}}x+2a{{t}_{1}}+a{{t}_{1}}^{3}\]
Here, we can see that the slope of the line PQ is given as
\[\Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}={{t}_{1}}\]
We are given that the normal makes an acute angle with X –axis as shown in the figure.
We know that if a line makes an angle \[\alpha \] with the X – axis in anti – clockwise direction then the slope of line is given as
\[m=\tan \alpha \]
By using the above formula to given angle then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}=\tan \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-\theta \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =-{{t}_{1}}............equation(i) \\
\end{align}\]
Here, we can see that Q lies in the equation of PQ.
So, by substituting the point Q in equation of PQ then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2a{{t}_{2}}=-{{t}_{1}}\left( a{{t}_{2}}^{2} \right)+2a{{t}_{1}}+a{{t}_{1}}^{3} \\
& \Rightarrow 2{{t}_{2}}-2{{t}_{1}}=-{{t}_{1}}\left( {{t}_{2}}^{2}-{{t}_{1}}^{2} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By using the formula of algebra that is
\[{{a}^{2}}-{{b}^{2}}=\left( a+b \right)\left( a-b \right)\]
To above equation then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right)=-{{t}_{1}}\left( {{t}_{2}}+{{t}_{1}} \right)\left( {{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 2=-{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}-{{t}_{1}}^{2}.............equation(ii) \\
\end{align}\]
Now, let us use the condition that PQ makes right angle at vertex
We know that the formula of slope of two points \[\left( {{x}_{1}},{{y}_{1}} \right),\left( {{x}_{2}},{{y}_{2}} \right)\] is given as
\[m=\dfrac{{{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}}}{{{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}}}\]
We also know that the condition two lines of slopes \[{{m}_{1}},{{m}_{2}}\] forms a right angle then
\[{{m}_{1}}\times {{m}_{2}}=-1\]
By using the above two formulas to OP and OQ then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{m}_{OP}}\times {{m}_{OQ}}=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{2a{{t}_{1}}-0}{a{{t}_{1}}^{2}-0} \right)\left( \dfrac{2a{{t}_{2}}-0}{a{{t}_{2}}^{2}-0} \right)=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}}=-1 \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}{{t}_{2}}=-4 \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the above result in equation (ii) then we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 2=-4-{{t}_{1}}^{2} \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}^{2}=2 \\
& \Rightarrow {{t}_{1}}=\pm \sqrt{2} \\
\end{align}\]
By substituting the above result in equation (i) then we get
\[\Rightarrow \tan \theta =-\left( \pm \sqrt{2} \right)\]
We know that \[\theta \] is acute angle so that tangent should be positive.
By using the above condition we get
\[\Rightarrow \theta =\arctan \sqrt{2}\]
Therefore, we can conclude that the value of \[\theta \] is \[\arctan \sqrt{2}\]
So, option (a) is correct answer.
Note:
Students may do mistakes in taking the \[\theta \] given with the slope of the line.
We have the condition that if a line makes an angle \[\alpha \] with the X-axis in an anti-clockwise direction then the slope of the line is given as
\[m=\tan \alpha \]
By using the above condition to the above figure then we get the equation as
\[\Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}=\tan \left( {{180}^{\circ }}-\theta \right)\]
But students may miss the direction of the angle to be taken and assume that angle as
\[\Rightarrow {{m}_{PQ}}=\tan \left( \theta \right)\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




