
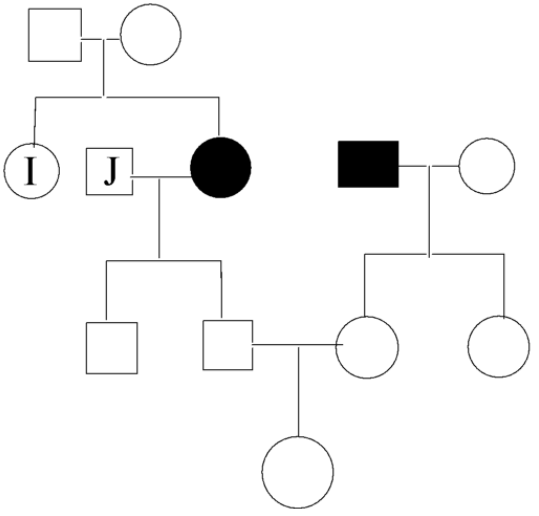
A pedigree chart of a family with an autosomal recessive disease Z is given. Assume that inheritance is Mendelian, which all individuals with homozygous recessive genotype have the disease. Circles within the pedigree represent females and squares represent males. Filled shapes indicate affected individuals, while unfilled shapes indicate unaffected individuals. If J doesn't have the recessive allele, the probability that 'I' will be a ‘carrier of disease Z’ is?
A. 0.67
B. 0.5
C. 0.25
D. 0

Answer
564.6k+ views
Hint: Autosomal recessive is one among several ways in which a trait, disorder, or disease are often passed down through families. An autosomal recessive disorder means two copies of an abnormal gene must be present on the autosomes for the disease or trait to develop.
Complete Answer:
- Inheriting a selected disease condition, or trait depends on the sort of chromosome that is affected. There are two types of chromosomes. They are autosomal chromosomes and sex chromosomes. The trait can be dominant or recessive.
- A mutation during a gene on one among the primary 22 non sex chromosomes (autosomes) can cause an autosomal disorder. And if it is a recessive trait that causes the disease, then it’s called autosomal recessive disorder.
- Genes are available in pairs. In each pair one gene comes from the mother and the other gene comes from the father. Recessive inheritance means both genes during a pair must be abnormal to cause disease. People with just one defective gene within the pair are called carriers. These people are most frequently not affected with the condition i.e., they do not show symptoms. However, they will pass the abnormal gene to their children.
From the given pedigree, the generation II-3 is having the disease. Hence, both the parents must be heterozygous (Rr) ie., they are carriers for this autosomal recessive disease ‘Z’. In the second generation, ‘I’ doesn’t have the disease ie., she is either having homozygous dominant alleles (RR) or heterozygous alleles (Rr).
If we observe the punnett square below, we can say that the probability of ‘I’ being a carrier is $\dfrac{2}{3}$ ie., there’s 0.67 probability that ‘I’ can be a carrier of the disease Z.
Hence, the correct option is A (0.67).
Note: For the genotype RR, ‘I’ would have received the R allele from each parent. For the genotype Rr, she would have received the allele R from either of the parent and the allele r from the other parent. So, there are three possibilities of receiving alleles from the parents. Hence, theirs is 0.67 probability that ‘I’ is a carrier of the disease Z and there’s 0.33 probability of having the normal alleles.
Complete Answer:
- Inheriting a selected disease condition, or trait depends on the sort of chromosome that is affected. There are two types of chromosomes. They are autosomal chromosomes and sex chromosomes. The trait can be dominant or recessive.
- A mutation during a gene on one among the primary 22 non sex chromosomes (autosomes) can cause an autosomal disorder. And if it is a recessive trait that causes the disease, then it’s called autosomal recessive disorder.
- Genes are available in pairs. In each pair one gene comes from the mother and the other gene comes from the father. Recessive inheritance means both genes during a pair must be abnormal to cause disease. People with just one defective gene within the pair are called carriers. These people are most frequently not affected with the condition i.e., they do not show symptoms. However, they will pass the abnormal gene to their children.
From the given pedigree, the generation II-3 is having the disease. Hence, both the parents must be heterozygous (Rr) ie., they are carriers for this autosomal recessive disease ‘Z’. In the second generation, ‘I’ doesn’t have the disease ie., she is either having homozygous dominant alleles (RR) or heterozygous alleles (Rr).
If we observe the punnett square below, we can say that the probability of ‘I’ being a carrier is $\dfrac{2}{3}$ ie., there’s 0.67 probability that ‘I’ can be a carrier of the disease Z.
| R | r | |
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | Rr | rr |
Hence, the correct option is A (0.67).
Note: For the genotype RR, ‘I’ would have received the R allele from each parent. For the genotype Rr, she would have received the allele R from either of the parent and the allele r from the other parent. So, there are three possibilities of receiving alleles from the parents. Hence, theirs is 0.67 probability that ‘I’ is a carrier of the disease Z and there’s 0.33 probability of having the normal alleles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




