
A plane flying horizontally at \[100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] releases an object which reaches the ground in \[10\,{\text{s}}\]. At what angle with the horizontal it hits the ground?
A. \[55^\circ \]
B. \[45^\circ \]
C. \[60^\circ \]
D. \[75^\circ \]
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Use the formula:
\[v = u + at\] and find the horizontal and vertical component of velocity.
Use the formula:
\[\tan \theta = \,\,\dfrac{{{v_Y}}}{{{v_X}}}\] to find the angle.
Complete step by step solution:
In this given problem, the plane is flying horizontally, whose velocity is \[100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\]. During the flight, it suddenly drops an object from it. The object does not fall horizontally, rather it will move at an inclination with the horizontal.
Let the angle at which the object falls to the ground be \[\theta \].
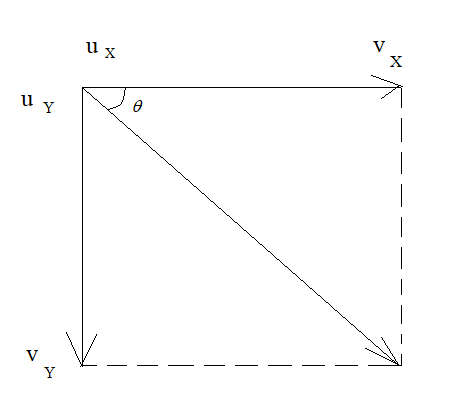
In the figure, the initial and the final velocity of the horizontal motion are indicated along with the initial and final velocity of the vertical motion.
\[{u_X}\] indicates the initial velocity along the horizontal motion.
\[{v_X}\] indicates the final velocity along the horizontal motion.
\[{u_Y}\] indicates the initial velocity along the vertical motion.
\[{v_Y}\] indicates the final velocity along the vertical motion.
Applying the formula, along the vertical component:
\[{u_X} = 100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\], \[{v_X} = ?\], \[{a_X} = 0\] and \[t = 10\,{\text{s}}\]
\[
{v_X} = {u_X} + {a_X}t \\
= 100 + 0 \times 10 \\
= 100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} \\
\]
Applying the formula, along the horizontal component:
\[{u_Y} = 0\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\], \[{v_X} = ?\], \[{a_X} = 10\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\] and \[t = 10\,{\text{s}}\]
\[
{v_Y} = {u_Y} + {a_Y}t \\
= 0 + 10 \times 10 \\
= 100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} \\
\]
The horizontal component of velocity is \[100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] and the vertical component of velocity is \[100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\].
To find angle at which the object hits the ground:
Find tangent:
\[
\tan \theta = \,\,\dfrac{{{v_Y}}}{{{v_X}}} \\
\tan \theta = \,\,\dfrac{{100}}{{100}} \\
\tan \theta = \,\,1 \\
\theta = \,\,{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 1 \right) \\
\]
\[\theta = 45^\circ \]
The angle at which the object hits the ground is \[45^\circ \].
Note: In this problem, you are asked to find the angle at which the object hits the ground. For this, you have to take the vertical and the horizontal component separately. While calculating the horizontal component of velocity, take acceleration due to gravity as zero, as the gravitational pull does not act along the horizontal direction.
\[v = u + at\] and find the horizontal and vertical component of velocity.
Use the formula:
\[\tan \theta = \,\,\dfrac{{{v_Y}}}{{{v_X}}}\] to find the angle.
Complete step by step solution:
In this given problem, the plane is flying horizontally, whose velocity is \[100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\]. During the flight, it suddenly drops an object from it. The object does not fall horizontally, rather it will move at an inclination with the horizontal.
Let the angle at which the object falls to the ground be \[\theta \].

In the figure, the initial and the final velocity of the horizontal motion are indicated along with the initial and final velocity of the vertical motion.
\[{u_X}\] indicates the initial velocity along the horizontal motion.
\[{v_X}\] indicates the final velocity along the horizontal motion.
\[{u_Y}\] indicates the initial velocity along the vertical motion.
\[{v_Y}\] indicates the final velocity along the vertical motion.
Applying the formula, along the vertical component:
\[{u_X} = 100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\], \[{v_X} = ?\], \[{a_X} = 0\] and \[t = 10\,{\text{s}}\]
\[
{v_X} = {u_X} + {a_X}t \\
= 100 + 0 \times 10 \\
= 100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} \\
\]
Applying the formula, along the horizontal component:
\[{u_Y} = 0\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\], \[{v_X} = ?\], \[{a_X} = 10\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 2}}\] and \[t = 10\,{\text{s}}\]
\[
{v_Y} = {u_Y} + {a_Y}t \\
= 0 + 10 \times 10 \\
= 100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}} \\
\]
The horizontal component of velocity is \[100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\] and the vertical component of velocity is \[100\,{\text{m}}{{\text{s}}^{ - 1}}\].
To find angle at which the object hits the ground:
Find tangent:
\[
\tan \theta = \,\,\dfrac{{{v_Y}}}{{{v_X}}} \\
\tan \theta = \,\,\dfrac{{100}}{{100}} \\
\tan \theta = \,\,1 \\
\theta = \,\,{\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( 1 \right) \\
\]
\[\theta = 45^\circ \]
The angle at which the object hits the ground is \[45^\circ \].
Note: In this problem, you are asked to find the angle at which the object hits the ground. For this, you have to take the vertical and the horizontal component separately. While calculating the horizontal component of velocity, take acceleration due to gravity as zero, as the gravitational pull does not act along the horizontal direction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




