
A plot given shows P – T curves (where P is the pressure and T is the temperature) for two solvents X and Y, and isomolar solutions of NaCl in these solvents. NaCl completely dissociates in both the solvents. In addition to an equal number of moles of non-volatile solute S in equal amount (in Kg) of these solvents, the elevation of the boiling point of solvent X is three times that of solvent. Solute S is known to undergo dimerization in these solvents. If the degree of dimerization is 0.7 in solvent Y, the degree of dimerization in solvent X is:

Answer
533.7k+ views
Hint: The elevation in the boiling point is equal to the product of ionization of solute, molality, and molal elevation constant. The formula is $\Delta {{T}_{b}}=i\text{ x m x }{{\text{K}}_{b}}$. The value of i can be calculated by the reaction $2(S)\to {{S}_{2}}$.
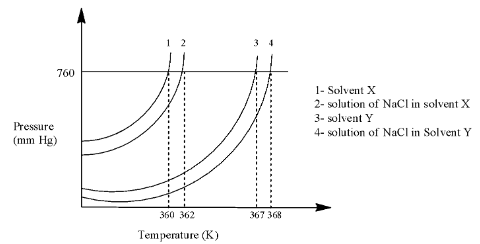
Complete answer: In the graph, there are four lines in which the first 2 lines are used for solvent X and the last two lines are used for solvent Y.
Line 2 is at 362 K and line 1 is at 360 K, so we can calculate the elevation in the boiling point as:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=362-360=2$
Line 4 is at 368 K and line 3 is at 367 K, so we can calculate the elevation in the boiling point as:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}=368-367=1$
According to the formula, we can write for X and Y as:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=i\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}$
$\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}=i\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(Y)}}$
When we divide the above equations, we get:
$\dfrac{{{K}_{b(X)}}}{{{K}_{b(Y)}}}=2$
Since the dimerization takes place, we can write the equation as:
$2(S)\to {{S}_{2}}$
After the equilibrium is attained, the concentration of S will be $1-\alpha $ and the value of ${{S}_{2}}$ will be $\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$
So, the value of i, will be:
$i=(1-\dfrac{\alpha }{2})$
Now, putting these values in the elevation in boiling point equation, we get:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{1}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}$
$\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}=(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{2}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(Y)}}$
In the question, it is given that:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=3\text{ x }\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}$
Combining, all these we can write:
$(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{1}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}=3\text{ x }(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{2}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}$
$2\text{ x }(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{1}}}{2})=3\text{ x }(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{2}}}{2})$
${{a}_{2}}$ = 0.7 and ${{a}_{1}}$ = 0.05.
The degree of dimerization of solvent X is 0.05.
Note: Don’t get confused between the formulas $\Delta {{T}_{b}}=i\text{ x m x }{{\text{K}}_{b}}$ and $\Delta {{T}_{b}}=\text{ m x }{{\text{K}}_{b}}$, the former is used when there is any electrolyte or ionic compound is present in the solution and the latter is used when covalent compound is present.
Complete answer: In the graph, there are four lines in which the first 2 lines are used for solvent X and the last two lines are used for solvent Y.
Line 2 is at 362 K and line 1 is at 360 K, so we can calculate the elevation in the boiling point as:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=362-360=2$
Line 4 is at 368 K and line 3 is at 367 K, so we can calculate the elevation in the boiling point as:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}=368-367=1$
According to the formula, we can write for X and Y as:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=i\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}$
$\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}=i\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(Y)}}$
When we divide the above equations, we get:
$\dfrac{{{K}_{b(X)}}}{{{K}_{b(Y)}}}=2$
Since the dimerization takes place, we can write the equation as:
$2(S)\to {{S}_{2}}$
After the equilibrium is attained, the concentration of S will be $1-\alpha $ and the value of ${{S}_{2}}$ will be $\dfrac{\alpha }{2}$
So, the value of i, will be:
$i=(1-\dfrac{\alpha }{2})$
Now, putting these values in the elevation in boiling point equation, we get:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{1}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}$
$\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}=(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{2}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{m}}_{NaCl}}\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(Y)}}$
In the question, it is given that:
$\Delta {{T}_{b(X)}}=3\text{ x }\Delta {{T}_{b(Y)}}$
Combining, all these we can write:
$(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{1}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}=3\text{ x }(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{2}}}{2})\text{ x }{{\text{K}}_{b(X)}}$
$2\text{ x }(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{1}}}{2})=3\text{ x }(1-\dfrac{{{\alpha }_{2}}}{2})$
${{a}_{2}}$ = 0.7 and ${{a}_{1}}$ = 0.05.
The degree of dimerization of solvent X is 0.05.
Note: Don’t get confused between the formulas $\Delta {{T}_{b}}=i\text{ x m x }{{\text{K}}_{b}}$ and $\Delta {{T}_{b}}=\text{ m x }{{\text{K}}_{b}}$, the former is used when there is any electrolyte or ionic compound is present in the solution and the latter is used when covalent compound is present.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




