
What is a positive deviation from Raoult’s law and its example?
Answer
510k+ views
Hint :The French chemist Francois Marte Raoult gives the quantitative relationship between partial pressure and mole fraction of two component solution .according to the Raoult’s law “the partial vapour pressure of each component of volatile liquid is equal to product of the vapour pressure of pure component of solution and its mole fraction”.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When we take a solution of two components, say $A$ and $B$. If the force of attraction between $A - B$ is weaker than $A - A$ and $B - B$ in the solution, then the escaping tendency of molecules of components from solution increases and becomes more than the escaping tendency of pure liquid.
As a result, each component of solution has a partial vapour pressure greater than expected.
When the total vapour pressure of solution becomes more than expected, vapour pressure of pure liquid on the basis of Raoult’s law is termed as positive deviation.
${p_A} > {p_A}^ \circ {x_A}$ And \[{p_B} > {p_B}^ \circ {x_B}\]
Where ${P_A}$ and ${P_B}$ is vapour pressure of component
${P_A}^ \circ $and ${P_B}^ \circ $ is Vapour pressure of pure component
${x_A}$and ${x_B}$ is Mole fraction of components
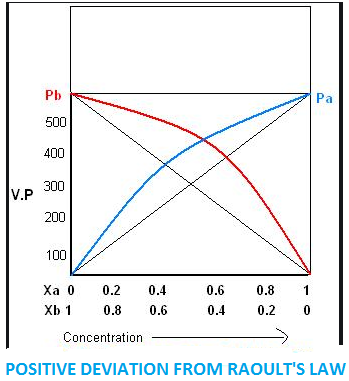
Conditions of solution with positive deviation –
$\Delta {{\rm H}_{mixing}}$ for these solutions is not zero because energy is required in order to break the bond between $A - A$ and $B - B$. Hence, the dissolution process of such a solution is endothermic.
$\Delta {V_{mixing}}$ for these solutions is not zero because the magnitude of intermolecular forces between the components in solution is decreased which means that particles are loosely held in solution . Therefore, there will be an increase in the volume of solution on mixing. Thus, $\Delta {V_{mixing}}$ is positive.
EXAMPLES-
-ethyl alcohol and cyclohexane
-acetone and carbon disulphide
-benzene and acetone
-chloroform and carbon tetrachloride
-acetone and ethyl alcohol
-ethyl alcohol and water
Note :
Non-ideal solutions have a tendency to show positive deviation as well as negative deviation. Solution showing negative deviation includes- acetone –chloroform, chloroform –diethyl ether, chloroform- nitric acid, acetone- aniline etc. in negative deviation $\Delta {{\rm H}_{mixing}}$ and $\Delta {V_{mixing}}$ shows negative values.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
When we take a solution of two components, say $A$ and $B$. If the force of attraction between $A - B$ is weaker than $A - A$ and $B - B$ in the solution, then the escaping tendency of molecules of components from solution increases and becomes more than the escaping tendency of pure liquid.
As a result, each component of solution has a partial vapour pressure greater than expected.
When the total vapour pressure of solution becomes more than expected, vapour pressure of pure liquid on the basis of Raoult’s law is termed as positive deviation.
${p_A} > {p_A}^ \circ {x_A}$ And \[{p_B} > {p_B}^ \circ {x_B}\]
Where ${P_A}$ and ${P_B}$ is vapour pressure of component
${P_A}^ \circ $and ${P_B}^ \circ $ is Vapour pressure of pure component
${x_A}$and ${x_B}$ is Mole fraction of components

Conditions of solution with positive deviation –
$\Delta {{\rm H}_{mixing}}$ for these solutions is not zero because energy is required in order to break the bond between $A - A$ and $B - B$. Hence, the dissolution process of such a solution is endothermic.
$\Delta {V_{mixing}}$ for these solutions is not zero because the magnitude of intermolecular forces between the components in solution is decreased which means that particles are loosely held in solution . Therefore, there will be an increase in the volume of solution on mixing. Thus, $\Delta {V_{mixing}}$ is positive.
EXAMPLES-
-ethyl alcohol and cyclohexane
-acetone and carbon disulphide
-benzene and acetone
-chloroform and carbon tetrachloride
-acetone and ethyl alcohol
-ethyl alcohol and water
Note :
Non-ideal solutions have a tendency to show positive deviation as well as negative deviation. Solution showing negative deviation includes- acetone –chloroform, chloroform –diethyl ether, chloroform- nitric acid, acetone- aniline etc. in negative deviation $\Delta {{\rm H}_{mixing}}$ and $\Delta {V_{mixing}}$ shows negative values.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




