
A primary alkyl halide would prefer to undergo _____________
(a) \[{{S}_{N}}1\] reaction
(b) \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction
(c) \[\alpha -elimination\]
(d) racemisation
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Primary alkyl halide would undergo the reaction which has the stability order \[{{1}^{\circ }}>{{2}^{\circ }}>{{3}^{\circ }}carbocation\]. It would undergo a bimolecular substitution reaction. Primary alkyl halide has very little steric hindrance.
Complete answer:
In \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reactions, the attack of the nucleophile occurs from the backside on the \[\alpha -carbon\] (i.e., carbon carrying the halogen). Therefore, the presence of bulky substituents on or near the atom tends to hinder (block) the approach of the nucleophile to the due to steric hindrance and thus makes the reaction to occur. The greater the steric hindrance, the slower is the reaction. Of all the alkyl halides, methyl halides are the most reactive toward \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction because they have three small hydrogen atoms on the \[\alpha -carbon\]. On the other hand, tertiary alkyl halide with three bulky alkyl groups is the least reactive followed by secondary alkyl halide two bulky alkyl groups and primary alkyl halide with one bulky alkyl group. Thus, the overall order of reactivity in \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction is:
Methyl halide > primary alkyl halide > secondary alkyl halide > tertiary alkyl halide.
Hence the \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction of primary alkyl halide as follows:
First, the nucleophile will attack from the backside, the halogen bond starts breaking and the new carbon-OH bond starts forming. These two processes take place simultaneously in a single step and no intermediate is formed.
The reaction is given below:
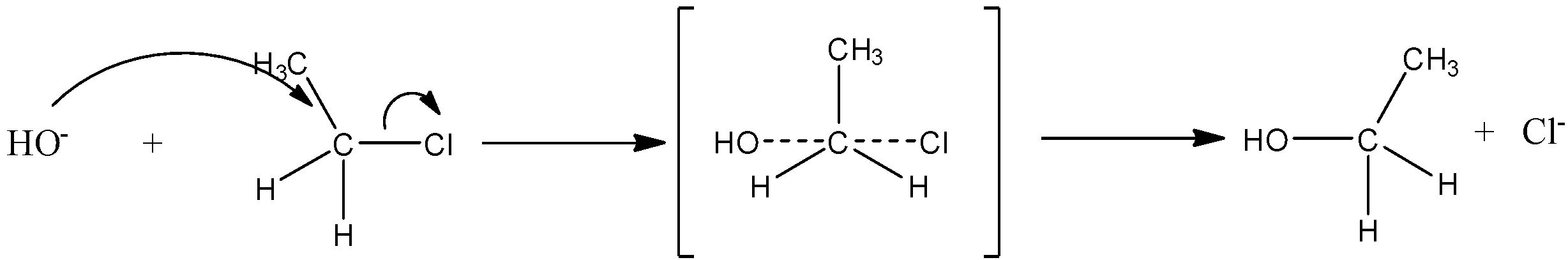
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction is a bimolecular reaction and it follows second order kinetics i.e., the rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of both the reactants. The \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction occurs through a transition state in which both the reactants are partially bonded to each other.
Complete answer:
In \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reactions, the attack of the nucleophile occurs from the backside on the \[\alpha -carbon\] (i.e., carbon carrying the halogen). Therefore, the presence of bulky substituents on or near the atom tends to hinder (block) the approach of the nucleophile to the due to steric hindrance and thus makes the reaction to occur. The greater the steric hindrance, the slower is the reaction. Of all the alkyl halides, methyl halides are the most reactive toward \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction because they have three small hydrogen atoms on the \[\alpha -carbon\]. On the other hand, tertiary alkyl halide with three bulky alkyl groups is the least reactive followed by secondary alkyl halide two bulky alkyl groups and primary alkyl halide with one bulky alkyl group. Thus, the overall order of reactivity in \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction is:
Methyl halide > primary alkyl halide > secondary alkyl halide > tertiary alkyl halide.
Hence the \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction of primary alkyl halide as follows:
First, the nucleophile will attack from the backside, the halogen bond starts breaking and the new carbon-OH bond starts forming. These two processes take place simultaneously in a single step and no intermediate is formed.
The reaction is given below:

So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction is a bimolecular reaction and it follows second order kinetics i.e., the rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of both the reactants. The \[{{S}_{N}}2\] reaction occurs through a transition state in which both the reactants are partially bonded to each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




