
A pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plant to pure short plant in \[{F_2}\] generation will be?
Answer
518.4k+ views
Hint: As we can see in the question, it is a monohybrid cross (when inheritance of only one character is observed). To find the ratio of \[{F_2}\] generation, first we need to cross TT $ \times $ tt and then self-cross of the hybrid of \[{F_1}\] generation to get the progenies of \[{F_2}\] generation. A pure tall plant means its allele should be genotypically homozygous, i.e., TT.
Complete answer:
Mendel has chosen as pairs \[14\] true pea varieties. One of them is the height of the plant recognized with the allele ‘T’ that represents the dominant condition ‘tall’ and the allele ‘t’ which is ‘dwarf’ and recessive.
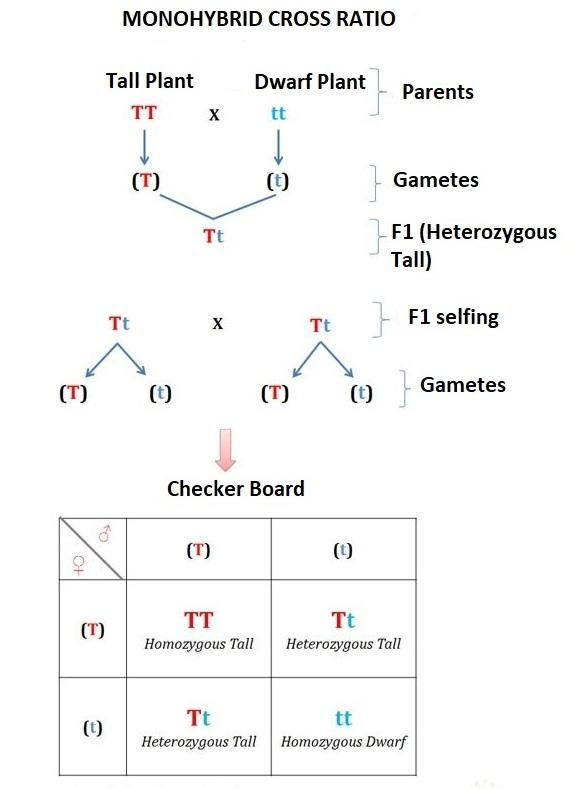
Monohybrid phenotypic ratio- \[Tall:{\text{ }}Dwarf\]= \[\;3:{\text{ }}1\]
Monohybrid genotypic ratio –\[\;TT:{\text{ }}Tt:{\text{ }}tt\]= \[1:{\text{ }}2:{\text{ }}1\]
Hence, A pure large plant with a pure, short plant is crossed (tt). In generation \[F2\]the ratio of pure large plants to pure short plants is \[TT:{\text{ }}tt{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1:1\].
Note:
The ratio of tall: dwarf plants would be\[3:{\text{ }}1\]. But here, in the question it has been asked to find the ratio of pure tall and pure dwarf plants. Out of these \[3\]tall plants, only one is pure homozygous (TT) tall and the other two are heterozygous (Tt) tall. So, the actual genotypic ratio is\[TT:{\text{ }}Tt:{\text{ }}tt{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}1:2:1\].
Additional Information:
Mendel laws:
Law of Dominance: It says that a dominant allele shows its effect in \[{F_1}\]generation in heterozygous condition and recessive allele fails to express itself in presence of dominant allele. It has exceptions of non-mendelian inheritances like codominance, incomplete dominance, etc.
Law of Segregation/ Law of Purity of gametes: According to this law, the alleles present in \[{F_1}\]generation segregate at the time of gamete formation, therefore gametes are pure for a particular trait. This law has no exception.
Law of Independent Assortment: This law cannot be seen in a monohybrid cross. The law states that when two pairs of hybrid features are combined, one pair is separated from another. Exception, connection.
DIHYBRID CROSS
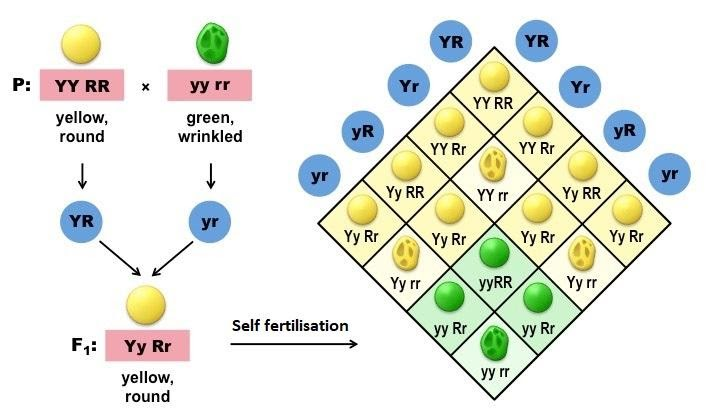
Phenotypic ratio: Round Yellow: Round green: wrinkled Yellow: wrinkled green
(R Y) : (R_yy) : (rrY) : (rryy)-
Nine : Three : Three : One
Genotypic ratio: RRYY: RRYy: RrYY: RrYy: RRyy: Rryy: rrYY: rrYy: rryy-
One : Two : Two : Four : One : Two : One : Two : One
Complete answer:
Mendel has chosen as pairs \[14\] true pea varieties. One of them is the height of the plant recognized with the allele ‘T’ that represents the dominant condition ‘tall’ and the allele ‘t’ which is ‘dwarf’ and recessive.

Monohybrid phenotypic ratio- \[Tall:{\text{ }}Dwarf\]= \[\;3:{\text{ }}1\]
Monohybrid genotypic ratio –\[\;TT:{\text{ }}Tt:{\text{ }}tt\]= \[1:{\text{ }}2:{\text{ }}1\]
Hence, A pure large plant with a pure, short plant is crossed (tt). In generation \[F2\]the ratio of pure large plants to pure short plants is \[TT:{\text{ }}tt{\text{ }} = {\text{ }}1:1\].
Note:
The ratio of tall: dwarf plants would be\[3:{\text{ }}1\]. But here, in the question it has been asked to find the ratio of pure tall and pure dwarf plants. Out of these \[3\]tall plants, only one is pure homozygous (TT) tall and the other two are heterozygous (Tt) tall. So, the actual genotypic ratio is\[TT:{\text{ }}Tt:{\text{ }}tt{\text{ }}-{\text{ }}1:2:1\].
Additional Information:
Mendel laws:
Law of Dominance: It says that a dominant allele shows its effect in \[{F_1}\]generation in heterozygous condition and recessive allele fails to express itself in presence of dominant allele. It has exceptions of non-mendelian inheritances like codominance, incomplete dominance, etc.
Law of Segregation/ Law of Purity of gametes: According to this law, the alleles present in \[{F_1}\]generation segregate at the time of gamete formation, therefore gametes are pure for a particular trait. This law has no exception.
Law of Independent Assortment: This law cannot be seen in a monohybrid cross. The law states that when two pairs of hybrid features are combined, one pair is separated from another. Exception, connection.
DIHYBRID CROSS

Phenotypic ratio: Round Yellow: Round green: wrinkled Yellow: wrinkled green
(R Y) : (R_yy) : (rrY) : (rryy)-
Nine : Three : Three : One
Genotypic ratio: RRYY: RRYy: RrYY: RrYy: RRyy: Rryy: rrYY: rrYy: rryy-
One : Two : Two : Four : One : Two : One : Two : One
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




