
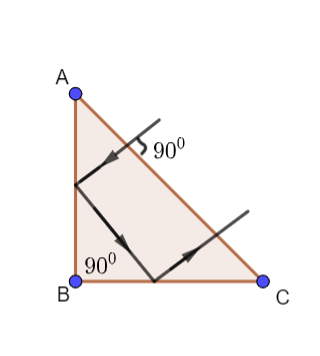
A ray falls on a prism ABC (AB=AC) and travels as shown in the figure. The minimum refractive index of the prism material should be
A. $\dfrac{4}{3}$
B. $\sqrt 2 $
C. $1.5$
D. $\sqrt 3 $

Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint: This question involves the use of modified form of Snell’s law given as ${\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2} = ........... = {\mu _n}\sin {\theta _n}$ where ${\mu _i}$ is the refractive index of the ${i^{th}}$ material and $\sin {\theta _i}$ is the sine of angle of incidence on the ${i^{th}}$ material. We will first identify the two surfaces where refraction is taking place. Then we will apply the modified form of Snell’s law and make proper substitutions. We will take ${\mu _{air}} = 1$ .
Complete step by step solution:
The refractive index of a material is the ability of the material to bend a ray of light entering through an interface towards or away from the normal.
This is mathematically given as the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction.
A more commonly used form is the below mentioned mathematical expression.
${\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2} = ........... = {\mu _n}\sin {\theta _n}$
Here ${\mu _i}$ is the refractive index of the ${i^{th}}$ material and $\sin {\theta _i}$ is the sine of angle of incidence on the ${i^{th}}$ material.
This is a modified form of the Snell’s law
Now let us understand the sequence of paths followed by the light ray.
First the light ray is incident on the surface AC from outside the prism at an angle ${90^0}$ . Since, it enters along the normal it does not undergo any refraction. This light ray is now incident on the surface AB and gets reflected. It is now incident on the surface BC from which it gets reflected.
The diagram would be
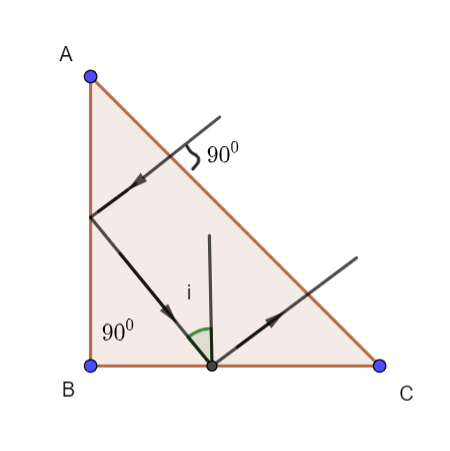
The light ray would follow the laws of reflection which state that the angle of incidence would be equal to the angle of reflection. Here, the sum of both these angles is ${90^0}$ . So, we can say that
$2\angle i = {90^0}$
$\angle i = {45^0}$
Now, this light ray is incident on the surface AC from inside the prism with the angle of incidence equal to ${45^0}$ .
Applying the modified form of the Snell’s law, we have
${\mu _{air}}\sin {90^0} = {\mu _{prism}}\sin {45^0}$
We know that ${\mu _{air}} = 1$ .
Making proper substitutions, we have
$1 = {\mu _{prism}} \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow {\mu _{prism}} = \sqrt 2 $
Note: We apply Snell’s law only where refraction is taking place. The reflecting surfaces have a different relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. The minimum refractive index condition is satisfied on its own here since we have already chosen the maximum value of angle of incidence which is ${90^0}$ .
Complete step by step solution:
The refractive index of a material is the ability of the material to bend a ray of light entering through an interface towards or away from the normal.
This is mathematically given as the ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction.
A more commonly used form is the below mentioned mathematical expression.
${\mu _1}\sin {\theta _1} = {\mu _2}\sin {\theta _2} = ........... = {\mu _n}\sin {\theta _n}$
Here ${\mu _i}$ is the refractive index of the ${i^{th}}$ material and $\sin {\theta _i}$ is the sine of angle of incidence on the ${i^{th}}$ material.
This is a modified form of the Snell’s law
Now let us understand the sequence of paths followed by the light ray.
First the light ray is incident on the surface AC from outside the prism at an angle ${90^0}$ . Since, it enters along the normal it does not undergo any refraction. This light ray is now incident on the surface AB and gets reflected. It is now incident on the surface BC from which it gets reflected.
The diagram would be

The light ray would follow the laws of reflection which state that the angle of incidence would be equal to the angle of reflection. Here, the sum of both these angles is ${90^0}$ . So, we can say that
$2\angle i = {90^0}$
$\angle i = {45^0}$
Now, this light ray is incident on the surface AC from inside the prism with the angle of incidence equal to ${45^0}$ .
Applying the modified form of the Snell’s law, we have
${\mu _{air}}\sin {90^0} = {\mu _{prism}}\sin {45^0}$
We know that ${\mu _{air}} = 1$ .
Making proper substitutions, we have
$1 = {\mu _{prism}} \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }}$
$ \Rightarrow {\mu _{prism}} = \sqrt 2 $
Note: We apply Snell’s law only where refraction is taking place. The reflecting surfaces have a different relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection. The minimum refractive index condition is satisfied on its own here since we have already chosen the maximum value of angle of incidence which is ${90^0}$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




