
A ray incident parallel to principal axis on a concave mirror at an angle $\theta $ after two reflections, reflected ray becomes parallel to incident ray. If $\theta =\dfrac{\pi }{N}$ (in radian) then find the value of N.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:As the ray becomes parallel after two reflections, so the sum of all the angles it made on the same side of the parallel lines is 180°.The centre of the reflecting surface of a sphere of which a spherical mirror is made up of is called the centre of curvature of the spherical mirror. The centre of curvature of a concave mirror lies in front of it.
Complete step by step answer:
Let a ray parallel to the principal axis PQ meet the mirror at A as shown in the figure. After reflection from the surface it meets at B. After reflection from B it emerges parallel to the principal axis. It is given that $\theta $ is the angle made by the incident ray with the centre of curvature.
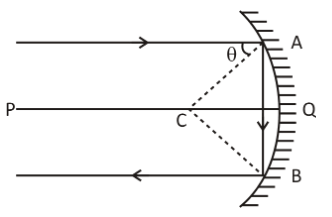
As the ray incident parallel to the principal axis on a concave mirror at an angle after two reflections, reflected ray becomes parallel to incident ray. So taking the centre of curvature as reference(refer the following figure), the sum of the interior opposite angles on the same side of parallel lines is 180°.
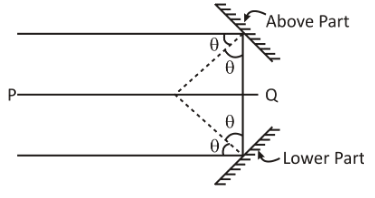
Therefore, we have
$4\theta = 180 \\
\Rightarrow 4\theta = \pi $ (In radians)
$ \therefore \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
Comparing it with the equation $\theta =\dfrac{\pi }{N}$, we get N = 4
Hence, the value of N is 4.
Note:In a concave mirror, a ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus. In case of a convex mirror it appears to diverge from the principal focus. A ray passing through the principal focus of a concave mirror after reflection, will emerge parallel to the principal axis. So after first reflection the given ray will pass through the principal focus and after second reflection, it will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
Complete step by step answer:
Let a ray parallel to the principal axis PQ meet the mirror at A as shown in the figure. After reflection from the surface it meets at B. After reflection from B it emerges parallel to the principal axis. It is given that $\theta $ is the angle made by the incident ray with the centre of curvature.

As the ray incident parallel to the principal axis on a concave mirror at an angle after two reflections, reflected ray becomes parallel to incident ray. So taking the centre of curvature as reference(refer the following figure), the sum of the interior opposite angles on the same side of parallel lines is 180°.

Therefore, we have
$4\theta = 180 \\
\Rightarrow 4\theta = \pi $ (In radians)
$ \therefore \theta =\dfrac{\pi }{4}$
Comparing it with the equation $\theta =\dfrac{\pi }{N}$, we get N = 4
Hence, the value of N is 4.
Note:In a concave mirror, a ray parallel to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus. In case of a convex mirror it appears to diverge from the principal focus. A ray passing through the principal focus of a concave mirror after reflection, will emerge parallel to the principal axis. So after first reflection the given ray will pass through the principal focus and after second reflection, it will emerge parallel to the principal axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




