
A ray of light makes a grazing incidence on the first face of a prism and the emergent ray is normal to the ${{2}^{nd}}$ face of the prism. If $D$ is the angle of deviation, then the refracting angle of the prism is equal to
$A)\text{ }{{90}^{0}}-2D$
$B)\text{ }{{90}^{0}}-D$
$C)\text{ }{{90}^{0}}-\dfrac{D}{2}$
$D)\text{ 18}{{0}^{0}}-2D$
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: This problem can be solved by using the direct formula for the angle of deviation for a light through a prism in terms of the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the refracting angle of the prism. Grazing incidence would mean that the angle of incidence is ${{90}^{0}}$.
Formula used:
$D=i+e-A$
Complete step by step answer:
We will solve this problem by using the direct formula for the angle of deviation for a light ray passing through a prism in terms of the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the refracting angle of the prism.
The angle of deviation $D$ for a light ray going through a prism of refracting angle $A$ is given by
$D=i+e-A$ --(1)
Where $i$ is the angle of incidence and $e$ is the angle of emergence.
Now, let us analyze the question.
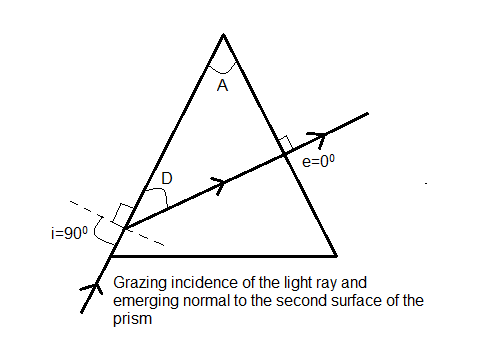
Since, the light ray makes a grazing incidence, it can be said that it travels parallel to the first surface of the prism and hence it will be perpendicular to the normal to the surface and makes a ${{90}^{0}}$ angle with it. This angle is nothing but the angle of incidence, by definition.
Therefore, the angle of incidence will be $i={{90}^{0}}$.
Now, the emergent ray is normal to the second surface of the prism. Therefore, it makes a zero angle with the normal to the second surface. This angle is nothing but the angle of emergence.
Therefore, the angle of emergence is $e={{0}^{0}}$.
The angle of deviation of the light ray is given to be $D$.
Let the angle of the prism or the refracting angle of the prism be $A$.
Therefore, using (1), we get
$D={{90}^{0}}+{{0}^{0}}-A$
$\Rightarrow D={{90}^{0}}-A$
$\Rightarrow A={{90}^{0}}-D$
Hence, we have got the refracting angle of the prism as ${{90}^{0}}-D$.
Therefore, the correct option is $(B)\text{ }{{90}^{0}}-D$.
Note:
Students must not get confused and think that the angle of deviation in this case is the angle of minimum deviation and hence, apply the corresponding formulas pertaining to the angle of minimum deviation. That is a special case and happens when the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence are equal (which is certainly not the case in this question). When this happens, the light ray passes parallel to the base of the prism, inside the prism. If the formulae for the angle of minimum deviation were applied in this question, the student would have arrived at a completely wrong answer.
Formula used:
$D=i+e-A$
Complete step by step answer:
We will solve this problem by using the direct formula for the angle of deviation for a light ray passing through a prism in terms of the angle of incidence, the angle of emergence and the refracting angle of the prism.
The angle of deviation $D$ for a light ray going through a prism of refracting angle $A$ is given by
$D=i+e-A$ --(1)
Where $i$ is the angle of incidence and $e$ is the angle of emergence.
Now, let us analyze the question.

Since, the light ray makes a grazing incidence, it can be said that it travels parallel to the first surface of the prism and hence it will be perpendicular to the normal to the surface and makes a ${{90}^{0}}$ angle with it. This angle is nothing but the angle of incidence, by definition.
Therefore, the angle of incidence will be $i={{90}^{0}}$.
Now, the emergent ray is normal to the second surface of the prism. Therefore, it makes a zero angle with the normal to the second surface. This angle is nothing but the angle of emergence.
Therefore, the angle of emergence is $e={{0}^{0}}$.
The angle of deviation of the light ray is given to be $D$.
Let the angle of the prism or the refracting angle of the prism be $A$.
Therefore, using (1), we get
$D={{90}^{0}}+{{0}^{0}}-A$
$\Rightarrow D={{90}^{0}}-A$
$\Rightarrow A={{90}^{0}}-D$
Hence, we have got the refracting angle of the prism as ${{90}^{0}}-D$.
Therefore, the correct option is $(B)\text{ }{{90}^{0}}-D$.
Note:
Students must not get confused and think that the angle of deviation in this case is the angle of minimum deviation and hence, apply the corresponding formulas pertaining to the angle of minimum deviation. That is a special case and happens when the angle of incidence and the angle of emergence are equal (which is certainly not the case in this question). When this happens, the light ray passes parallel to the base of the prism, inside the prism. If the formulae for the angle of minimum deviation were applied in this question, the student would have arrived at a completely wrong answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




